Abstract
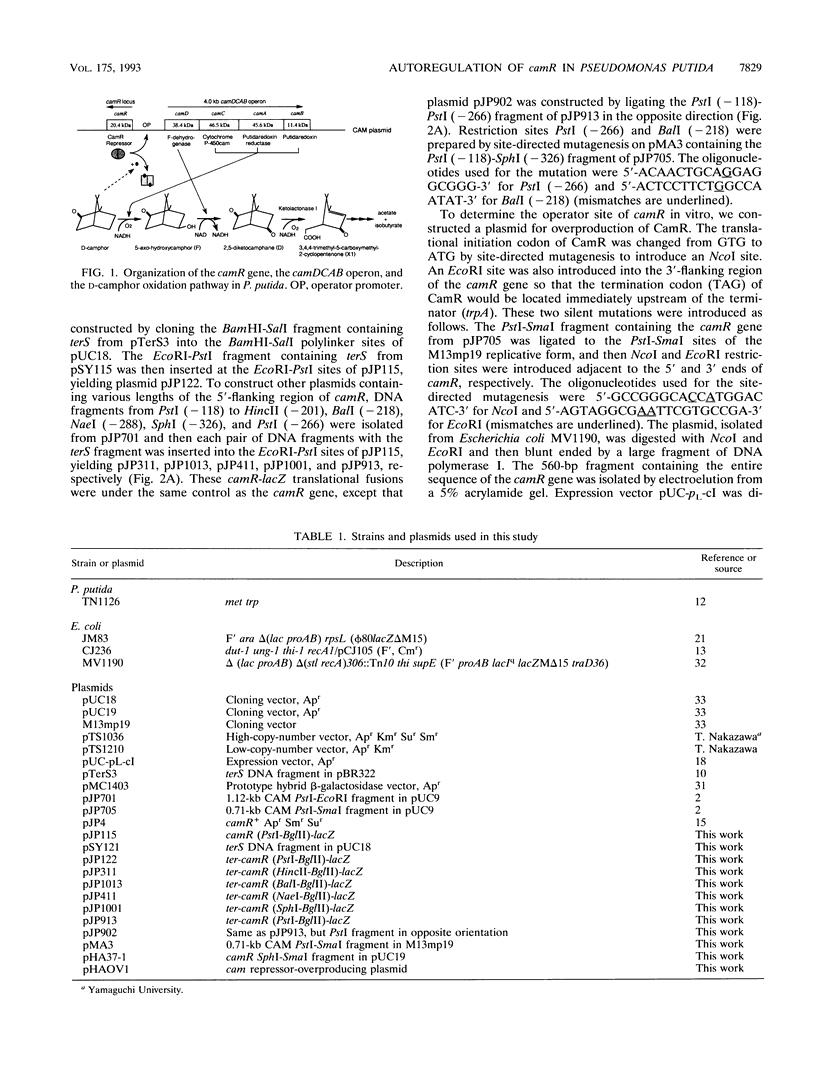
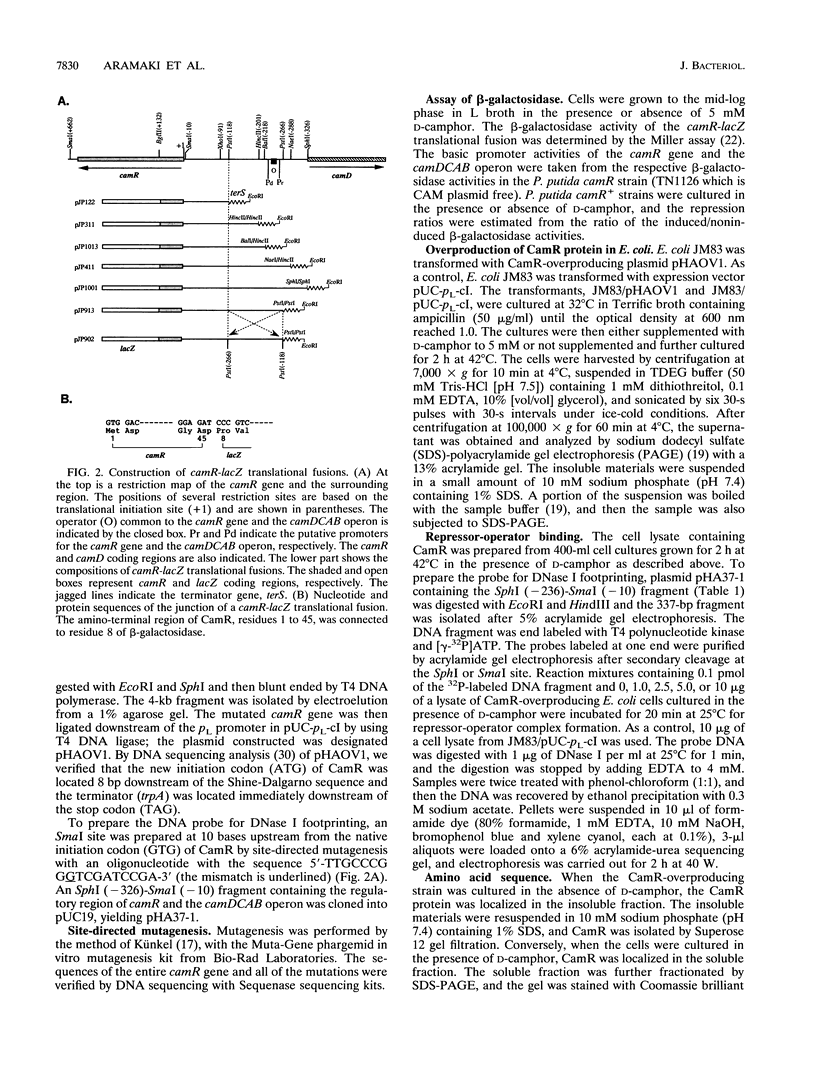
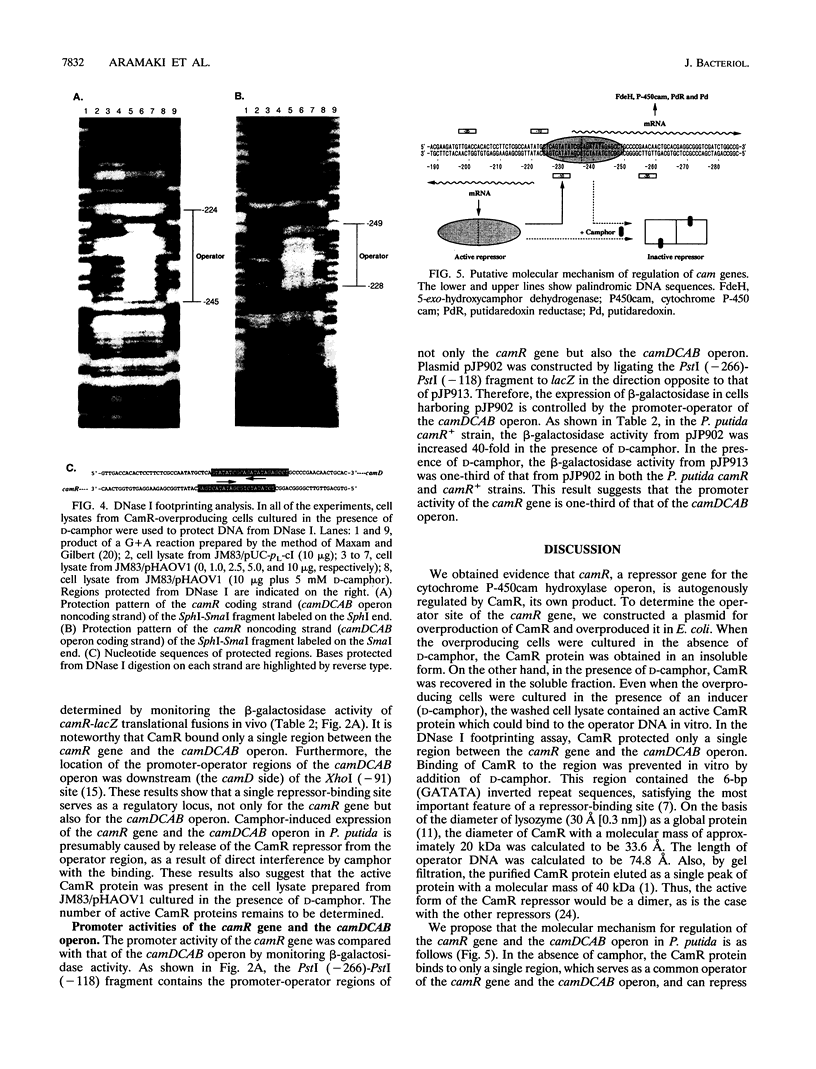
The regulatory gene camR on the CAM plasmid of Pseudomonas putida (ATCC 17453) negatively controls expression of the cytochrome P-450cam hydroxylase operon (camDCAB) for the camphor degradation pathway and is oriented in a direction opposite to that of the camDCAB operon. In this study, we examined expression of the camR gene by monitoring the beta-galactosidase activity of camR-lacZ translational fusions in P. putida camR and camR+ strains. We found that the camR gene was autogenously regulated by its own product, CamR. To search for an operator site of the camR gene, a cam repressor (CamR)-overproducing plasmid, pHAOV1, was constructed by placing the camR gene under the control of a pL promoter. The translational initiation codon of CamR was changed by site-directed mutagenesis from GTG to ATG to improve translation efficiency. Judging from sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis analysis, the CamR protein was expressed up to about 10% of the soluble protein of CamR-overproducing Escherichia coli JM83/pHAOV1 cells. Results of DNase I footprinting assays using the cell lysate indicated that the CamR repressor covered a single region between the camR gene and the camDCAB operon. Our findings also suggest that the camR gene autogenously regulates its own expression by binding of the gene product, CamR, to the operator, which also serves as an operator of the camDCAB operon.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakrabarty A. M. Plasmids in Pseudomonas. Annu Rev Genet. 1976;10:7–30. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.10.120176.000255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark B. F., Marcker K. A. The role of N-formyl-methionyl-sRNA in protein biosynthesis. J Mol Biol. 1966 Jun;17(2):394–406. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80150-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita M., Aramaki H., Horiuchi T., Amemura A. Transcription of the cam operon and camR genes in Pseudomonas putida PpG1. J Bacteriol. 1993 Nov;175(21):6953–6958. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.21.6953-6958.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goeddel D. V., Yansura D. G., Winston C., Caruthers M. H. Studies on gene control regions. VII. Effect of 5-bromuracil-substituted lac operators on the lac operator-lac repressor interaction. J Mol Biol. 1978 Aug 25;123(4):661–687. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90211-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartline R. A., Gunsalus I. C. Induction specificity and catabolite repression of the early enzymes in camphor degradation by Pseudomonas putida. J Bacteriol. 1971 May;106(2):468–478. doi: 10.1128/jb.106.2.468-478.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedegaard J., Gunsalus I. C. Mixed function oxidation. IV. An induced methylene hydroxylase in camphor oxidation. J Biol Chem. 1965 Oct;240(10):4038–4043. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirano M., Shigesada K., Imai M. Construction and characterization of plasmid and lambda phage vector systems for study of transcriptional control in Escherichia coli. Gene. 1987;57(1):89–99. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90180-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inouye S., Nakazawa A., Nakazawa T. Determination of the transcription initiation site and identification of the protein product of the regulatory gene xylR for xyl operons on the TOL plasmid. J Bacteriol. 1985 Sep;163(3):863–869. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.3.863-869.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joyce C. M., Grindley N. D. Method for determining whether a gene of Escherichia coli is essential: application to the polA gene. J Bacteriol. 1984 May;158(2):636–643. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.2.636-643.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katagiri M., Ganguli B. N., Gunsalus I. C. A soluble cytochrome P-450 functional in methylene hydroxylation. J Biol Chem. 1968 Jun 25;243(12):3543–3546. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koga H., Aramaki H., Yamaguchi E., Takeuchi K., Horiuchi T., Gunsalus I. C. camR, a negative regulator locus of the cytochrome P-450cam hydroxylase operon. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jun;166(3):1089–1095. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.3.1089-1095.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koga H., Yamaguchi E., Matsunaga K., Aramaki H., Horiuchi T. Cloning and nucleotide sequences of NADH-putidaredoxin reductase gene (camA) and putidaredoxin gene (camB) involved in cytochrome P-450cam hydroxylase of Pseudomonas putida. J Biochem. 1989 Nov;106(5):831–836. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a122939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):488–492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuroki M., Murakami M., Wakisaka M., Ikeda S., Oikawa S., Oshima T., Nakazato H., Kosaki G., Matsuoka Y. Immunoreactivity of recombinant carcinoembryonic antigen proteins expressed in Escherichia coli. Immunol Invest. 1992 Jun;21(3):241–257. doi: 10.3109/08820139209072262. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Napoli C., Gold L., Singer B. S. Translational reinitiation in the rIIB cistron of bacteriophage T4. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jul 5;149(3):433–449. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90480-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pabo C. O., Sauer R. T. Protein-DNA recognition. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:293–321. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.001453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palchaudhuri S. Molecular characterization of hydrocarbon degradative plasmids in Pseudomonas putida. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Jul 25;77(2):518–525. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(77)80010-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy P., Peterkofsky A., McKenney K. Translational efficiency of the Escherichia coli adenylate cyclase gene: mutating the UUG initiation codon to GUG or AUG results in increased gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(17):5656–5660. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.17.5656. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rheinwald J. G., Chakrabarty A. M., Gunsalus I. C. A transmissible plasmid controlling camphor oxidation in Pseudomonas putida. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Mar;70(3):885–889. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.3.885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg M., Court D. Regulatory sequences involved in the promotion and termination of RNA transcription. Annu Rev Genet. 1979;13:319–353. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.13.120179.001535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapira S. K., Chou J., Richaud F. V., Casadaban M. J. New versatile plasmid vectors for expression of hybrid proteins coded by a cloned gene fused to lacZ gene sequences encoding an enzymatically active carboxy-terminal portion of beta-galactosidase. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(1):71–82. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90169-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. Production of single-stranded plasmid DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1987;153:3–11. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)53044-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]