Abstract
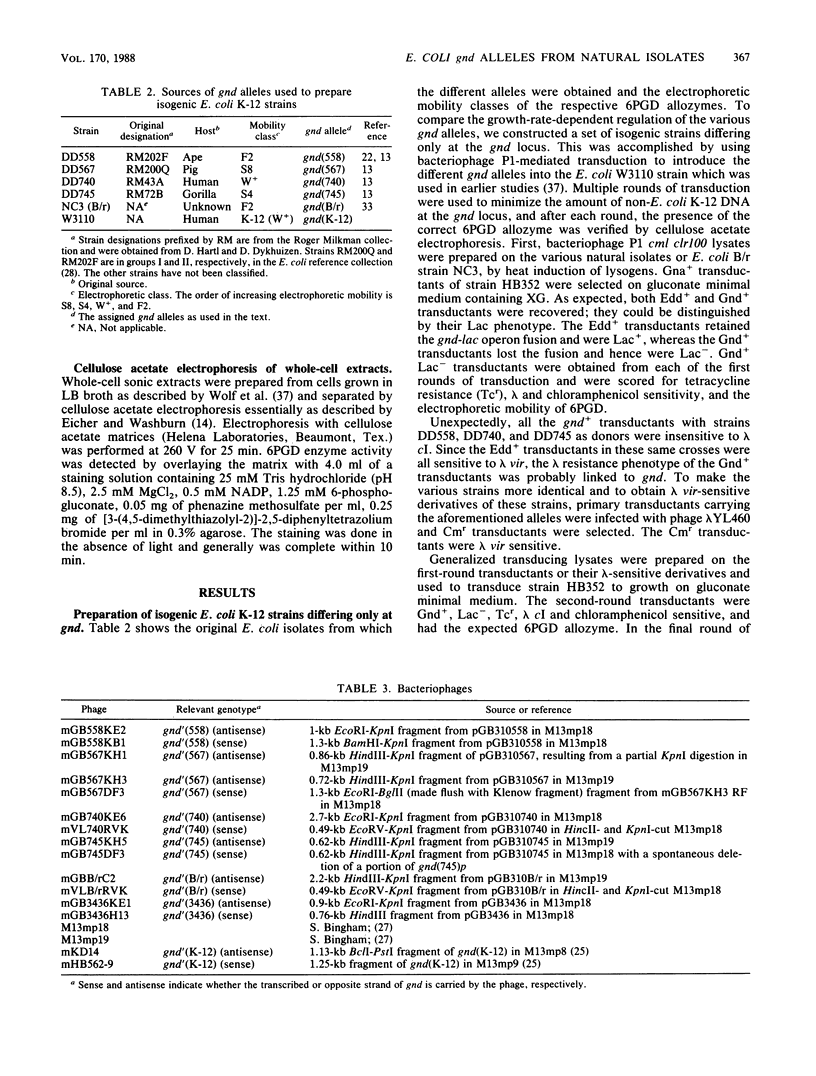
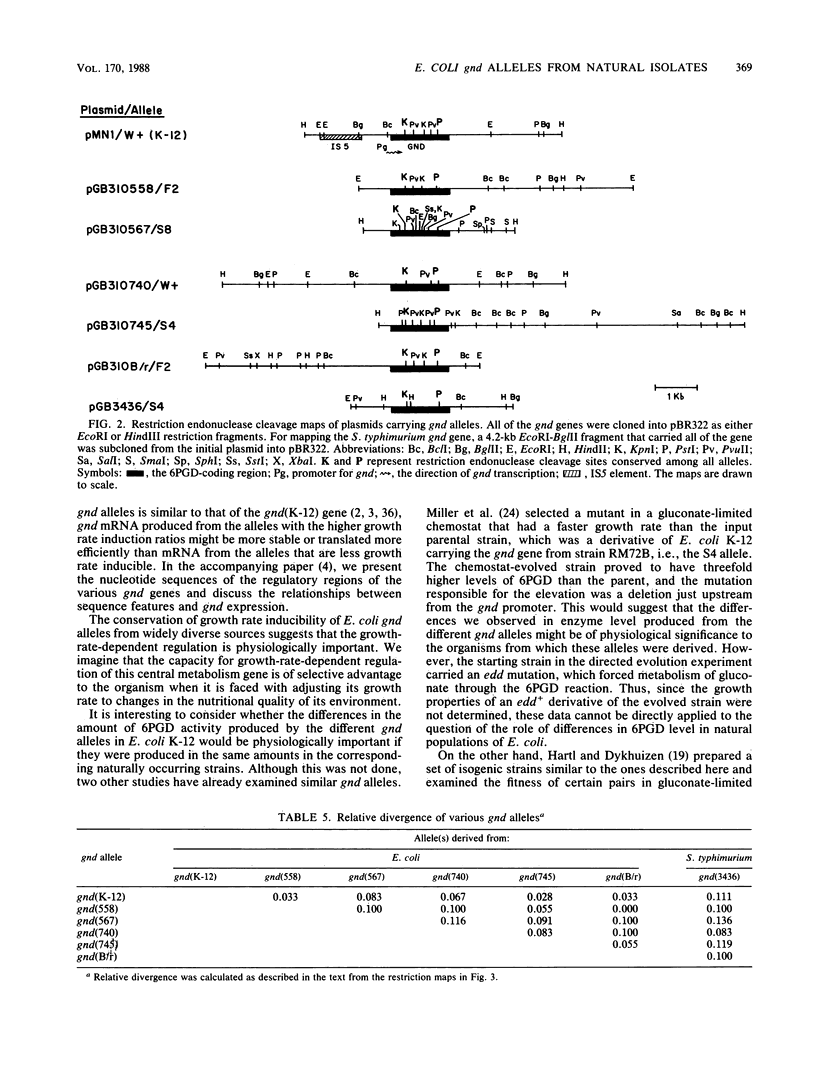
6-Phosphogluconate dehydrogenase (6PGD), encoded by gnd, is highly polymorphic among isolates of Escherichia coli form natural populations. As a means of characterizing the growth-rate-dependent regulation of the level of 6PGD, five gnd alleles, including the E. coli B/r allele, were crossed into E. coli K-12 with bacteriophage P1. In each of the isogenic strains, the level of 6PGD was two- to threefold higher in cells grown on glucose than in cells grown on acetate. The level of enzyme activity in the acetate-grown cells varied about sixfold within the set of isogenic strains. The physiological importance of these differences in enzyme level is discussed. The gnd gene was cloned from five E. coli strains and Salmonella typhimurium LT-2 and mapped with twelve restriction endonucleases. gnd was located and oriented on the chromosomal DNAs. The restriction maps of the genes were aligned at conserved restriction sites, and the relative divergence of the genes was estimated from restriction site polymorphisms. The E. coli gnd genes differed from the S. typhimurium gene by about 11%. Most of the E. coli genes differed from one another by less than 5%, but one allele differed from the others by about 10%. Only the gnd gene from E. coli K-12 had an IS5 element located nearby.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bachmann B. J. Linkage map of Escherichia coli K-12, edition 7. Microbiol Rev. 1983 Jun;47(2):180–230. doi: 10.1128/mr.47.2.180-230.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker H. V., 2nd, Wolf R. E., Jr Essential site for growth rate-dependent regulation within the Escherichia coli gnd structural gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(24):7669–7673. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.24.7669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker H. V., 2nd, Wolf R. E., Jr Growth rate-dependent regulation of 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase level in Escherichia coli K-12: beta-galactosidase expression in gnd-lac operon fusion strains. J Bacteriol. 1983 Feb;153(2):771–781. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.2.771-781.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barcak G. J., Wolf R. E., Jr Comparative nucleotide sequence analysis of growth-rate-regulated gnd alleles from natural isolates of Escherichia coli and from Salmonella typhimurium LT-2. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jan;170(1):372–379. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.1.372-379.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhaduri S., Kasai T., Schlessinger D., Raskas H. J. pMB9 plasmids bearing the Salmonella typhimurium his operon and gnd gene. Gene. 1980 Feb;8(3):239–253. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90002-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer H. W., Roulland-Dussoix D. A complementation analysis of the restriction and modification of DNA in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1969 May 14;41(3):459–472. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90288-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Del Giudice L. Method for isolating restriction- and modificationless mutants of Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jan;137(1):673–676. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.1.673-676.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dykhuizen D., Hartl D. L. Selective neutrality of 6PGD allozymes in E. coli and the effects of genetic background. Genetics. 1980 Dec;96(4):801–817. doi: 10.1093/genetics/96.4.801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eicher E. M., Washburn L. L. Assignment of genes to regions of mouse chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Feb;75(2):946–950. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.2.946. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engler J. A., van Bree M. P. The nucleotide sequence and protein-coding capability of the transposable element IS5. Gene. 1981 Aug;14(3):155–163. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90111-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrish E. E., Baker H. V., 2nd, Wolf R. E., Jr Different control circuits for growth rate-dependent regulation of 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase and protein components of the translational machinery in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1982 Nov;152(2):584–594. doi: 10.1128/jb.152.2.584-594.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harshman L., Riley M. Conservation and variation of nucleotide sequences in Escherichia coli strains isolated from nature. J Bacteriol. 1980 Nov;144(2):560–568. doi: 10.1128/jb.144.2.560-568.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartl D. L., Dykhuizen D. E. Potential for selection among nearly neutral allozymes of 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6344–6348. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6344. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milkman R. Electrophoretic variation in Escherichia coli from natural sources. Science. 1973 Dec 7;182(4116):1024–1026. doi: 10.1126/science.182.4116.1024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. D., Dykhuizen D. E., Green L., Hartl D. L. Specific deletion occurring in the directed evolution of 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase in Escherichia coli. Genetics. 1984 Dec;108(4):765–772. doi: 10.1093/genetics/108.4.765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nasoff M. S., Baker H. V., 2nd, Wolf R. E., Jr DNA sequence of the Escherichia coli gene, gnd, for 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase. Gene. 1984 Mar;27(3):253–264. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90070-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nasoff M. S., Wolf R. E., Jr Molecular cloning, correlation of genetic and restriction maps, and determination of the direction of transcription of gnd of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1980 Aug;143(2):731–741. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.2.731-741.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrander J., Kempe T., Messing J. Construction of improved M13 vectors using oligodeoxynucleotide-directed mutagenesis. Gene. 1983 Dec;26(1):101–106. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90040-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ochman H., Selander R. K. Standard reference strains of Escherichia coli from natural populations. J Bacteriol. 1984 Feb;157(2):690–693. doi: 10.1128/jb.157.2.690-693.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds A. E., Mahadevan S., LeGrice S. F., Wright A. Enhancement of bacterial gene expression by insertion elements or by mutation in a CAP-cAMP binding site. J Mol Biol. 1986 Sep 5;191(1):85–95. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90424-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnetz K., Toloczyki C., Rak B. Beta-glucoside (bgl) operon of Escherichia coli K-12: nucleotide sequence, genetic organization, and possible evolutionary relationship to regulatory components of two Bacillus subtilis genes. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jun;169(6):2579–2590. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.6.2579-2590.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoner B., Kahn M. The nucleotide sequence of IS5 from Escherichia coli. Gene. 1981 Aug;14(3):165–174. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90112-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selander R. K., Levin B. R. Genetic diversity and structure in Escherichia coli populations. Science. 1980 Oct 31;210(4469):545–547. doi: 10.1126/science.6999623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wanner B. L., Kodaira R., Neidhardt F. C. Physiological regulation of a decontrolled lac operon. J Bacteriol. 1977 Apr;130(1):212–222. doi: 10.1128/jb.130.1.212-222.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler M. E., Roth D. J., Hartman P. E. Promoter- and attenuator-related metabolic regulation of the Salmonella typhimurium histidine operon. J Bacteriol. 1978 Feb;133(2):830–843. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.2.830-843.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf R. E., Jr Integration of specialized transducing bacteriophage lambda cI857 St68 h80 dgnd his by an unusual pathway promotes formation of deletions and generates a new translocatable element. J Bacteriol. 1980 May;142(2):588–602. doi: 10.1128/jb.142.2.588-602.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf R. E., Jr, Prather D. M., Shea F. M. Growth-rate-dependent alteration of 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase and glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase levels in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1979 Sep;139(3):1093–1096. doi: 10.1128/jb.139.3.1093-1096.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf R. E., Jr, Shea F. M. Combined use of strain construction and affinity chromatography in the rapid, high-yield purification of 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase from Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1979 Apr;138(1):171–175. doi: 10.1128/jb.138.1.171-175.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



