Abstract
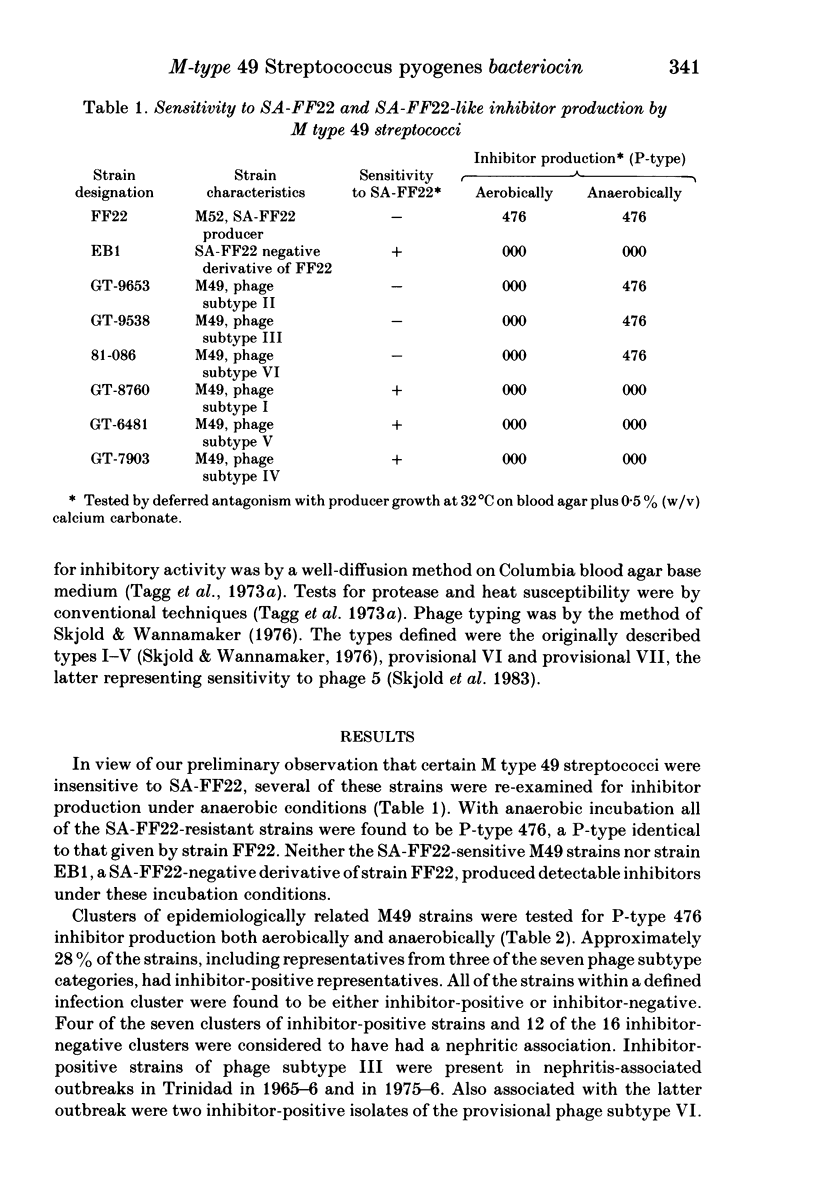
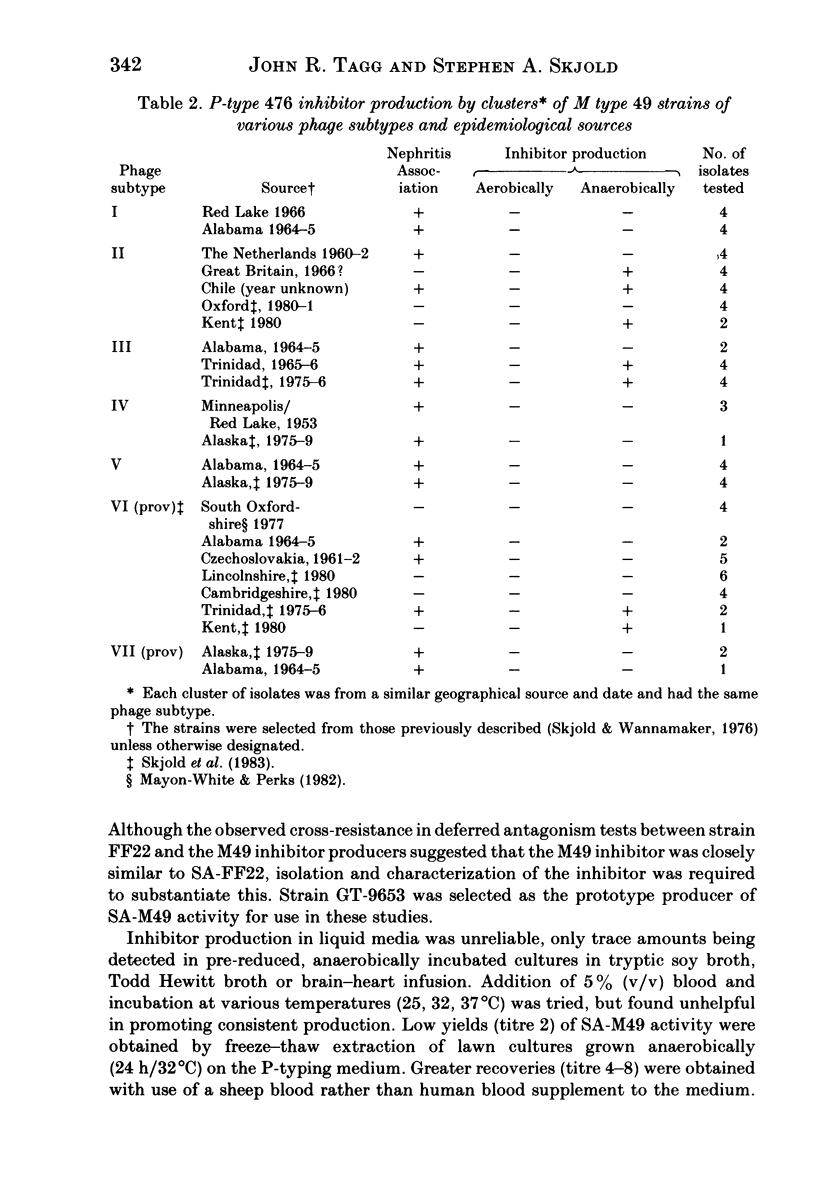
Bacteriocin production (P)-typing of 75 M-type 49 group-A streptococci obtained from a variety of epidemiological incidents in different countries gave no evidence of production under the usual aerobic test conditions. However, with anaerobic incubation, 28% of the strains gave a pattern of inhibitory activity against the indicator strains which was indistinguishable from that previously attributed to the bacteriocin, streptococcin A-FF22 (SA-FF22). Isolation and partial purification of the M type 49 bacteriocin (SA-M49) by freeze-thaw elution from anaerobically grown lawn cultures, followed by ammonium sulphate precipitation and Sephadex chromatography, showed the activity to be associated with a heat-stable proteinaceous molecule of molecular weight approximately 8000 - properties similar to those of SA-FF22. SA-FF22 and SA-M49 were found to have identical inhibitory spectra including immunity of the producer strains to the inhibitory activity of both the homologous and heterologous bacteriocin preparations. SA-M49 production occurred in some strains of phage subtypes II, III and provisional VI and, since it was a consistent property for all isolates from single outbreaks of infection, it provides a means of discriminating between strains of each of these three phage subtypes. There was no evidence of any increased incidence of SA-M49 production in M-type 49 strains associated with nephritic sequelae.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Johnson D. W., Tagg J. R., Wannamaker L. W. Production of a bacteriocine-like substance by group-A streptococci of M-type 4 and T-pattern 4. J Med Microbiol. 1979 Nov;12(4):413–427. doi: 10.1099/00222615-12-4-413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxted W. R., Fraser C. A., Parker M. T. Streptococcus pyogenes, type 49. A nephritogenic Streptococcus with a wide geographical distribution. Lancet. 1967 Mar 25;1(7491):641–644. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(67)92540-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayon-White R. T., Perks E. M. Why type streptococci? The epidemiology of group A streptococci in Oxfordshire 1976-1980. J Hyg (Lond) 1982 Jun;88(3):439–452. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400070303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson W. J., Tagg J. R. M-type 57 group A streptococcus bacteriocin. Can J Microbiol. 1983 Oct;29(10):1445–1451. doi: 10.1139/m83-221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skjold S. A., Wannamaker L. W., Johnson D. R., Margolis H. S. Type 49 Streptococcus pyogenes: phage subtypes as epidemiological markers in isolates from skin sepsis and acute glomerulonephritis. J Hyg (Lond) 1983 Aug;91(1):71–76. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400060046. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skjold S. A., Wannamaker L. W. Method for phage typing group A type 49 streptococci. J Clin Microbiol. 1976 Sep;4(3):232–238. doi: 10.1128/jcm.4.3.232-238.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tagg J. R., Bannister L. V. "Fingerprinting" beta-haemolytic streptococci by their production of and sensitivity to bacteriocine-like inhibitors. J Med Microbiol. 1979 Nov;12(4):397–411. doi: 10.1099/00222615-12-4-397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tagg J. R., Dajani A. S., Wannamaker L. W. Bacteriocins of gram-positive bacteria. Bacteriol Rev. 1976 Sep;40(3):722–756. doi: 10.1128/br.40.3.722-756.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tagg J. R., Dajani A. S., Wannamaker L. W., Gray E. D. Group A streptococcal bacteriocin. Production, purification, and mode of action. J Exp Med. 1973 Nov 1;138(5):1168–1183. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.5.1168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tagg J. R., Read R. S., McGiven A. R. Bacteriocin of a group A streptococcus: partial purification and properties. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 Sep;4(3):214–221. doi: 10.1128/aac.4.3.214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tagg J. R., Wannamaker L. W. Streptococcin A-FF22: nisin-like antibiotic substance produced by a group A streptococcus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Jul;14(1):31–39. doi: 10.1128/aac.14.1.31. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


