Abstract
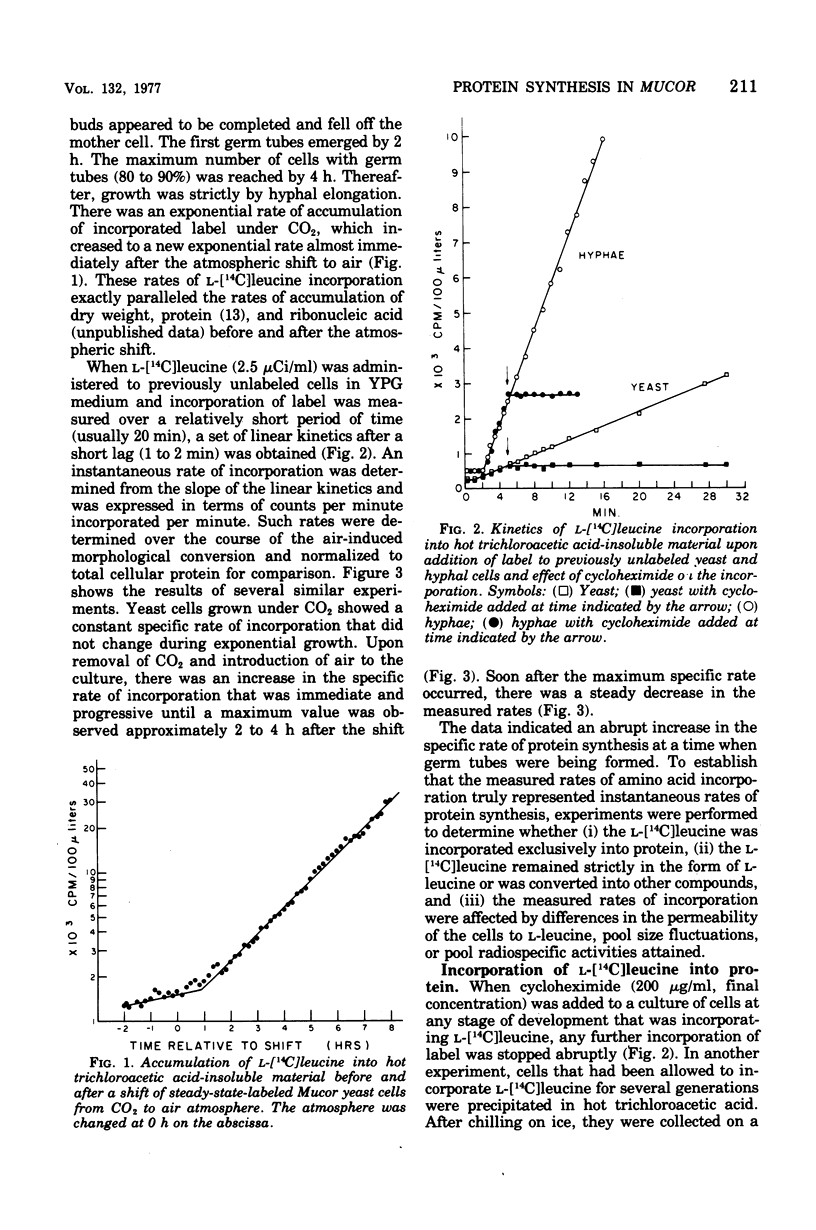
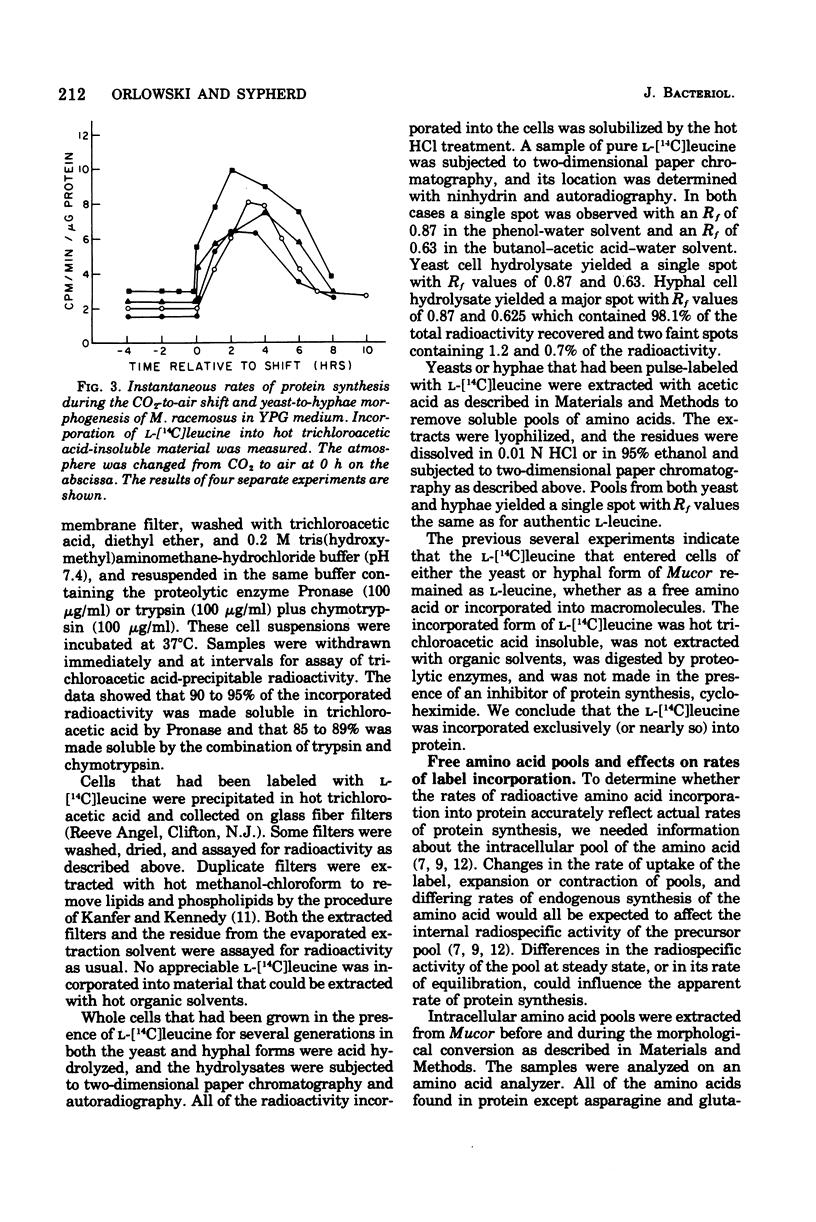
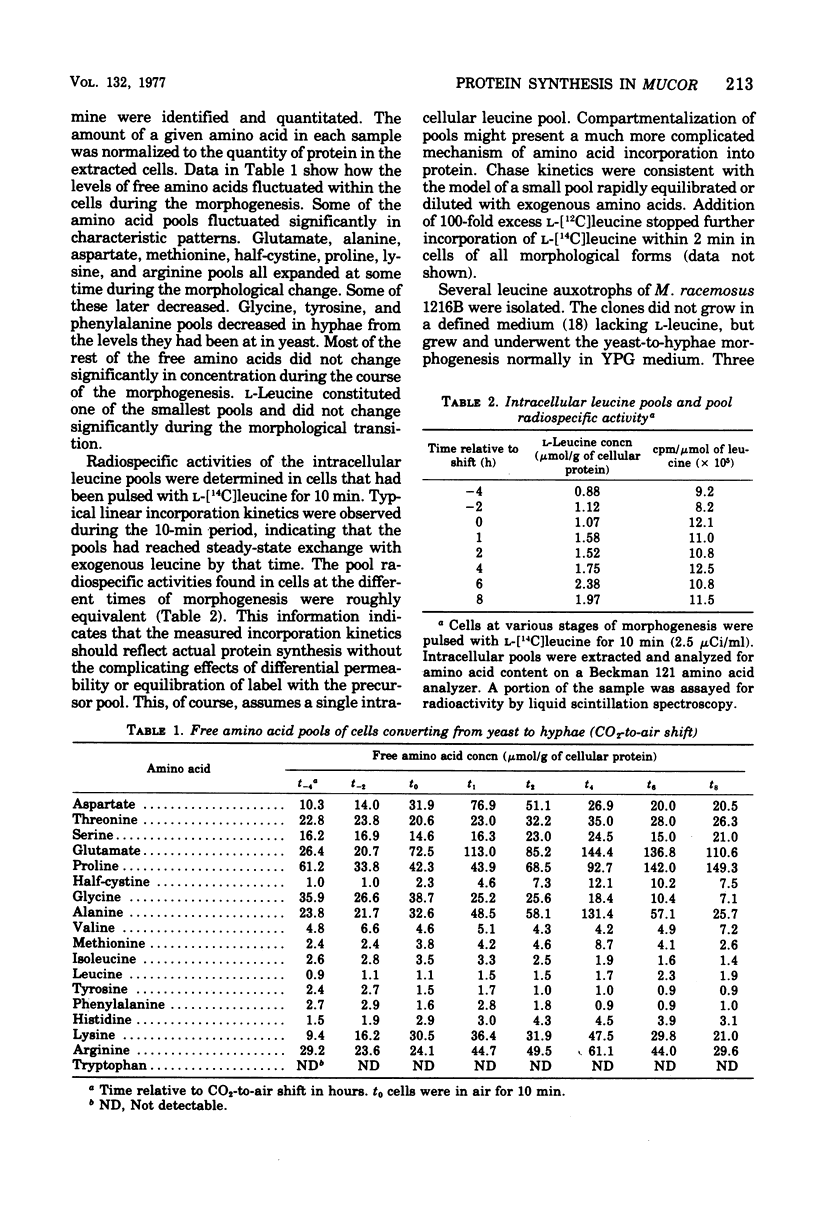
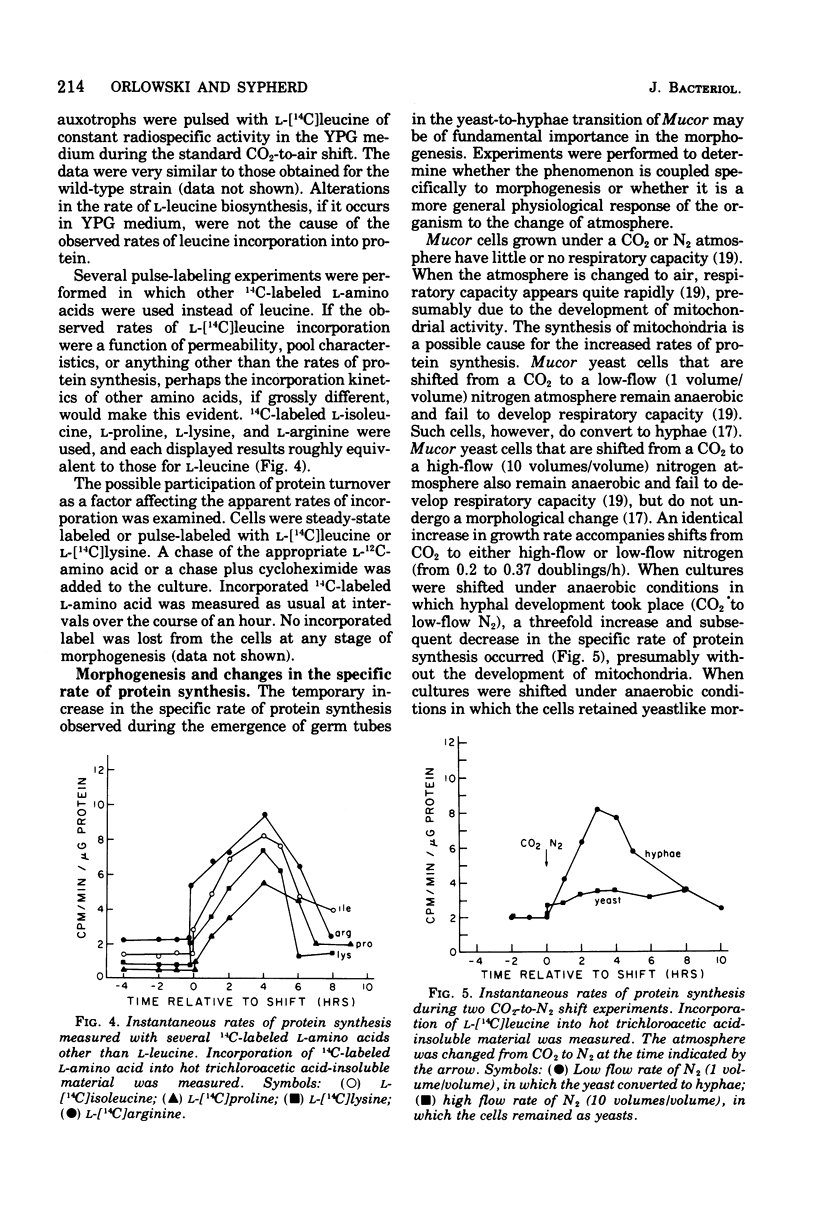
Cells of Mucor racemosus were labeled with l-[14C]leucine during the yeast-to-hyphae morphogenesis that follows a change of atmosphere from CO2 to air. Pulse-labeling kinetics and the steady-state accumulation of incorporated l-[14C]leucine were determined throughout the period of cellular differentiation. We determined that the l-[14C]leucine was taken up by all forms of the organism, was not altered from the form of l-leucine, and was incorporated exclusively into protein. The intracellular pool of free l-leucine was small in comparison with those of the other l-amino acids, remained relatively constant in size during morphogenesis, and was rapidly equilibrated with exogenous leucine. Approximately the same internal radiospecific activities were attained throughout development shortly after addition of l-[14C]leucine to a culture. Experiments performed with leucine auxotrophs suggested that endogenous synthesis of leucine in prototrophs does not affect the measured rates of incorporation. Experiments performed with 14C-labeled l-isoleucine, l-proline, l-lysine, and l-arginine produced results qualitatively the same as with l-leucine. The accumulation of incorporated l-[14C]leucine in a culture of M. racemosus undergoing the air-induced yeast-to-hyphae transition reflected the change in growth rate that accompanied the morphogenesis. However, the specific rate of protein synthesis measured throughout the developmental process displayed a characteristic acceleration during the emergence of germ tubes which was followed by a decline when all further growth took the form of hyphal elongation. Data are presented suggesting that this response is a correlate of morphogenesis rather than a consequence of the atmospheric change per se.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BARTNICKI-GARCIA S., NICKERSON W. J. Isolation, composition, and structure of cell walls of filamentous and yeast-like forms of Mucor rouxii. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Mar 26;58:102–119. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90822-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernlohr R. W. 18 Oxygen probes of protein turnover, amino acid transport, and protein synthesis in Bacillus licheniformis. J Biol Chem. 1972 Aug 10;247(15):4893–4899. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernlohr R. W. Changes in amino acid permeation during sporulation. J Bacteriol. 1967 Mar;93(3):1031–1044. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.3.1031-1044.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COWIE D. B., McCLURE F. T. Metabolic pools and the synthesis of macromolecules. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1959 Jan;31(1):236–245. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(59)90460-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crabeel M., Grenson M. Regulation of histidine uptake by specific feedback inhibition of two histidine permeases in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Eur J Biochem. 1970 May 1;14(1):197–204. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb00278.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fry B. J., Gross P. R. Patterns and rates of protein synthesis in sea urchin embryos. II. The calculation of absolute rates. Dev Biol. 1970 Feb;21(1):125–146. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(70)90065-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall M. J., Kolankaya N. The physiology of mould-yeast dimorphism in the genus Mycotypha (Mucorales). J Gen Microbiol. 1974 May;82(1):25–34. doi: 10.1099/00221287-82-1-25. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hod Y., Hershko A. Relationship of the pool of intracellular valine to protein synthesis and degradation in cultured cells. J Biol Chem. 1976 Jul 25;251(14):4458–4457. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopper A. K., Magee P. T., Welch S. K., Friedman M., Hall B. D. Macromolecule synthesis and breakdown in relation to sporulation and meiosis in yeast. J Bacteriol. 1974 Aug;119(2):619–628. doi: 10.1128/jb.119.2.619-628.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KANFER J., KENNEDY E. P. METABOLISM AND FUNCTION OF BACTERIAL LIPIDS. I. METABOLISM OF PHOSPHOLIPIDS IN ESCHERICHIA COLI B. J Biol Chem. 1963 Sep;238:2919–2922. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen A. D., Sypherd P. S. Cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate and morphogenesis in Mucor racemosus. J Bacteriol. 1974 Feb;117(2):432–438. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.2.432-438.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MATCHETT W. H., DEMOSS J. A. PHYSIOLOGICAL CHANNELING OF TRYPTOPHAN IN NEUROSPORA CRASSA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Apr 4;86:91–99. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(64)90162-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mooney D. T., Sypherd P. S. Volatile factor involved in the dimorphism of Mucor racemosus. J Bacteriol. 1976 Jun;126(3):1266–1270. doi: 10.1128/jb.126.3.1266-1270.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orlowski M., Sypherd P. S. Cyclic guanosine 3',5'-monophosphate in the dimorphic fungus Mucor racemosus. J Bacteriol. 1976 Mar;125(3):1226–1228. doi: 10.1128/jb.125.3.1226-1228.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paznokas J. L., Sypherd P. S. Respiratory capacity, cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate, and morphogenesis of Mucor racemosus. J Bacteriol. 1975 Oct;124(1):134–139. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.1.134-139.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulz B. E., Kraepelin G., Hinkelmann W. Factors affecting dimorphism in Mycotypha (Mucorales): a correlation with the fermentation-respiration equilibrium. J Gen Microbiol. 1974 May;82(1):1–13. doi: 10.1099/00221287-82-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terenzi H. F., Storck R. Stimulation of fermentation and yeast-like morphogenesis in Mucor rouxii by phenethyl alcohol. J Bacteriol. 1969 Mar;97(3):1248–1261. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.3.1248-1261.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timberlake W. E. Alterations in RNA and protein synthesis associated with steroid hormone-induced sexual morphogenesis in the water mold Achlya. Dev Biol. 1976 Jul 15;51(2):202–214. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(76)90138-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss R. L. Compartmentation and control of arginine metabolism in Neurospora. J Bacteriol. 1976 Jun;126(3):1173–1179. doi: 10.1128/jb.126.3.1173-1179.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss R. L., Davis R. H. Control of arginine utilization in Neurospora. J Bacteriol. 1977 Feb;129(2):866–873. doi: 10.1128/jb.129.2.866-873.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiemken A., Dürr M. Characterization of amino acid pools in the vacuolar compartment of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Arch Microbiol. 1974;101(1):45–57. doi: 10.1007/BF00455924. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZALOKAR M. Kinetics of amino acid uptake and protein synthesis in Neurospora. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1961 Jan 29;46:423–432. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(61)90573-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zorzopulos J., Jobbagy A. J., Terenzi H. F. Effects of ethylenediaminetetraacetate and chloramphenicol on mitochondrial activity and morphogenesis in Mucor rouxii. J Bacteriol. 1973 Sep;115(3):1198–1204. doi: 10.1128/jb.115.3.1198-1204.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


