Abstract
BACKGROUND: This investigation deals with the molecular mechanism of anti-human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) action of pentoxifylline (PTX) [1-(5'-oxohexyl)-3, 7-dimethylxanthine] a drug widely used for the treatment of conditions involving defective regional microcirculation. MATERIALS AND METHODS: The inhibition by PTX of protein kinase C (PKC) or cAMP-dependent protein kinase (PKA)-mediated activation by phorbol ester (PMA) and tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha) of HIV-1-LTR-regulated reporter gene expression was studied in human CD4+ T lymphocytes (Jurkat) and human embryo kidney cells (293-27-2). A protein kinase C is involved in activation of NF-kappa B in whole cells, identified by using inhibitors specific for PKC- or PKA-catalyzed NF-kappa B activation in whole cell and cell-free systems. RESULTS: PTX inhibited PKC- or PKA-catalyzed activation of NF-kappa B in cytoplasmic extracts from unstimulated Jurkat or 293-27-2 cells, but not interaction of preactivated NF-kappa B with its motifs. Calphostin C, a specific inhibitor of PKC, inhibited NF-kappa B activation and HIV-1 LTR-driven reporter gene expression in both PMA- and TNF-alpha-treated cells. In contrast, although H88 specifically inhibited PKA activity in the cell-free extract, it did not affect NF-kappa B action in PMA- or TNF-alpha-treated cells. CONCLUSIONS: The mechanism of inhibitory action of PTX on virus replication and NF-kappa B-induced transactivation of HIV-1 gene expression has been elucidated as due to blocking PKC-dependent PMA- or TNF-alpha-induced activation of NF-kappa B in Jurkat and 293-27-2 cells. Other protein kinase inhibitors may be useful in down regulating transcription of HIV-1 provirus and thereby virus replication in HIV-infected patients.
Full text
PDF



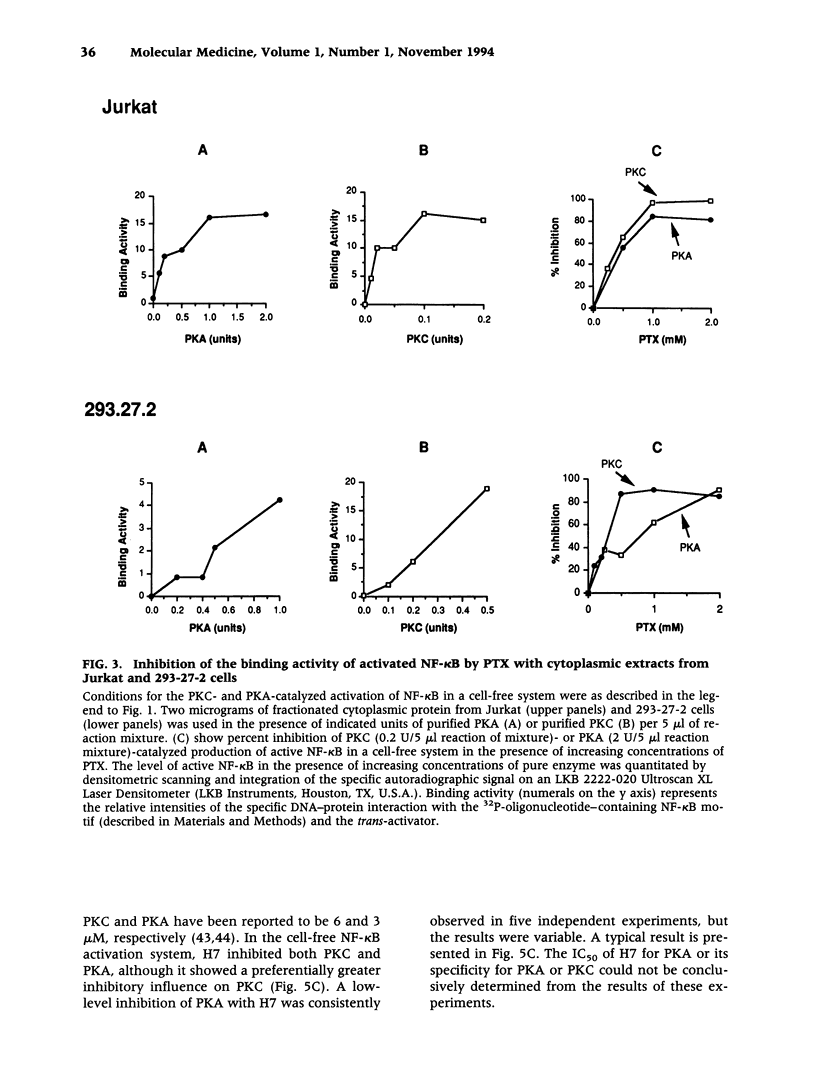
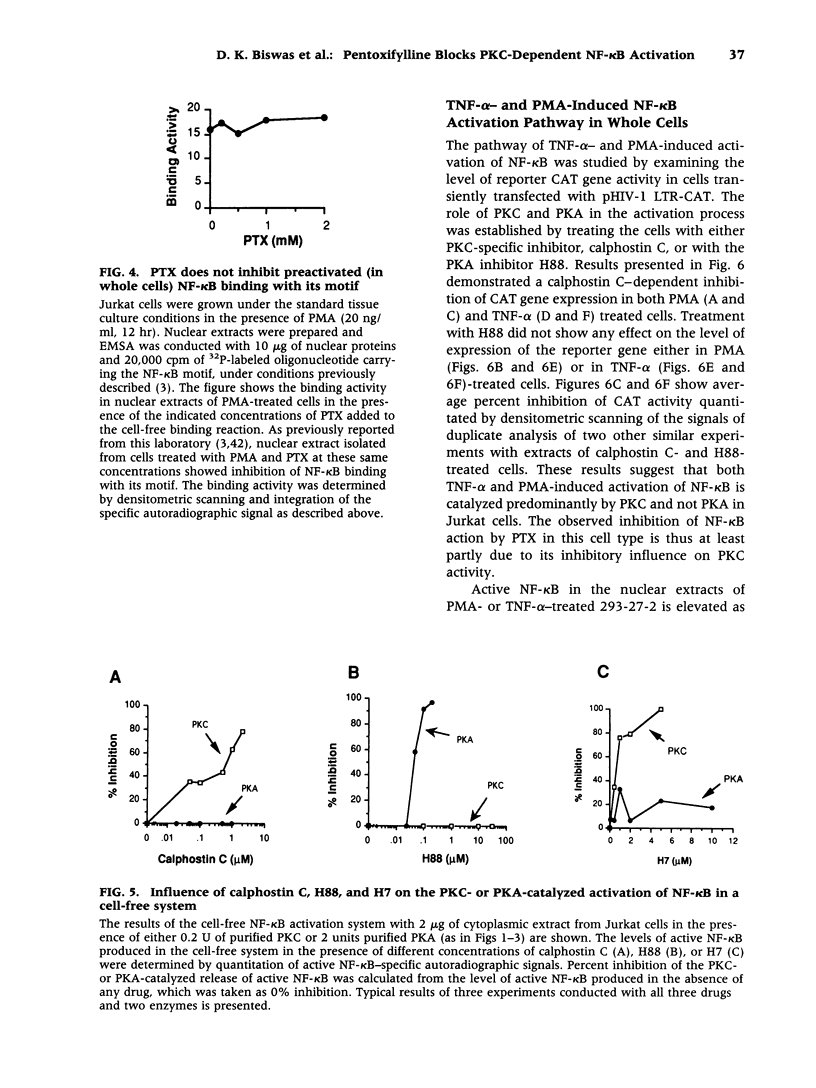
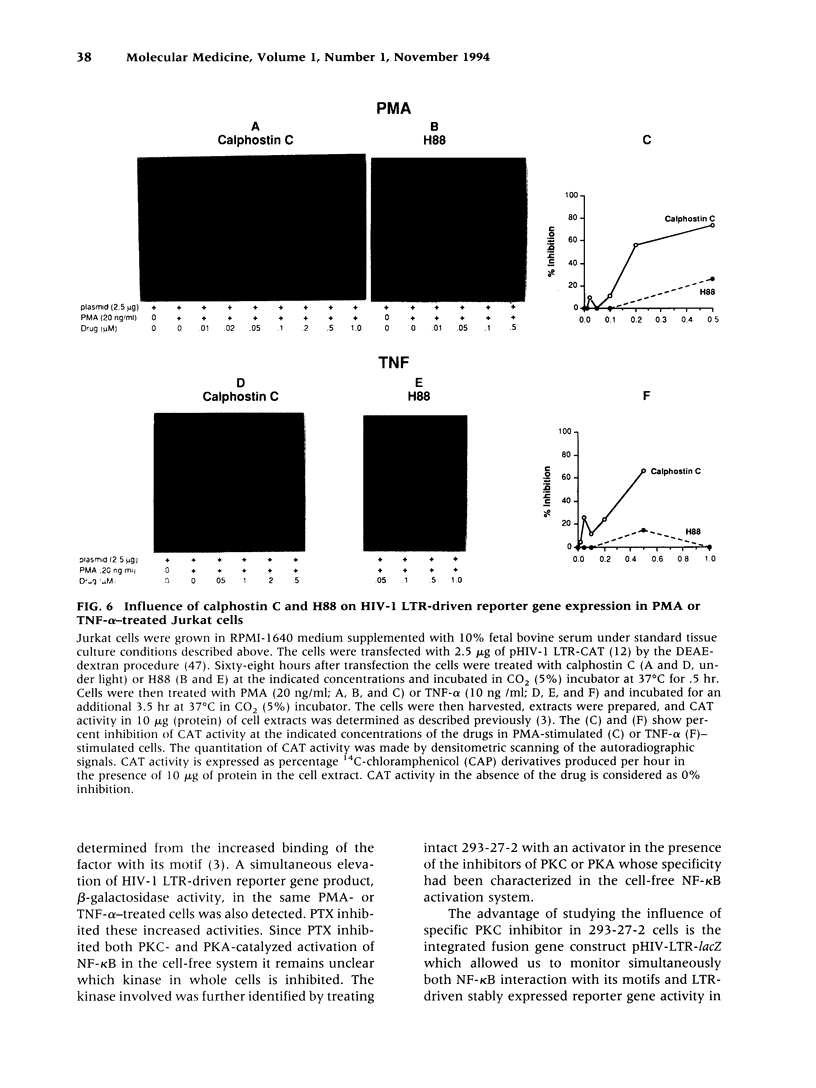
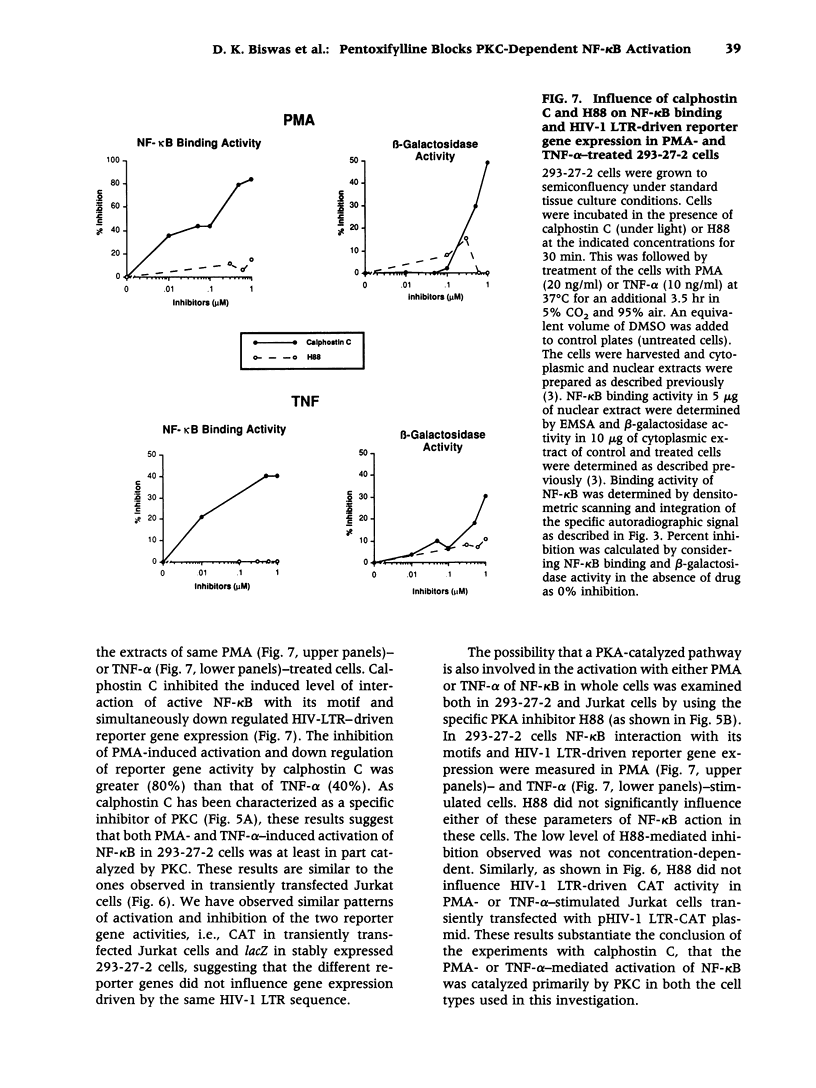




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baeuerle P. A., Baltimore D. Activation of DNA-binding activity in an apparently cytoplasmic precursor of the NF-kappa B transcription factor. Cell. 1988 Apr 22;53(2):211–217. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90382-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baeuerle P. A., Baltimore D. I kappa B: a specific inhibitor of the NF-kappa B transcription factor. Science. 1988 Oct 28;242(4878):540–546. doi: 10.1126/science.3140380. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biswas D. K., Ahlers C. M., Dezube B. J., Pardee A. B. Cooperative inhibition of NF-kappa B and Tat-induced superactivation of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 long terminal repeat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Dec 1;90(23):11044–11048. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.23.11044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biswas D. K., Dezube B. J., Ahlers C. M., Pardee A. B. Pentoxifylline inhibits HIV-1 LTR-driven gene expression by blocking NF-kappa B action. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1993 Jul;6(7):778–786. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruns R. F., Miller F. D., Merriman R. L., Howbert J. J., Heath W. F., Kobayashi E., Takahashi I., Tamaoki T., Nakano H. Inhibition of protein kinase C by calphostin C is light-dependent. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Apr 15;176(1):288–293. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)90922-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiao P. J., Miyamoto S., Verma I. M. Autoregulation of I kappa B alpha activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jan 4;91(1):28–32. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.1.28. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chijiwa T., Mishima A., Hagiwara M., Sano M., Hayashi K., Inoue T., Naito K., Toshioka T., Hidaka H. Inhibition of forskolin-induced neurite outgrowth and protein phosphorylation by a newly synthesized selective inhibitor of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase, N-[2-(p-bromocinnamylamino)ethyl]-5-isoquinolinesulfonamide (H-89), of PC12D pheochromocytoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 25;265(9):5267–5272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross S. L., Feinberg M. B., Wolf J. B., Holbrook N. J., Wong-Staal F., Leonard W. J. Regulation of the human interleukin-2 receptor alpha chain promoter: activation of a nonfunctional promoter by the transactivator gene of HTLV-I. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):47–56. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90754-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diaz-Meco M. T., Berra E., Municio M. M., Sanz L., Lozano J., Dominguez I., Diaz-Golpe V., Lain de Lera M. T., Alcamí J., Payá C. V. A dominant negative protein kinase C zeta subspecies blocks NF-kappa B activation. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Aug;13(8):4770–4775. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.8.4770. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duh E. J., Maury W. J., Folks T. M., Fauci A. S., Rabson A. B. Tumor necrosis factor alpha activates human immunodeficiency virus type 1 through induction of nuclear factor binding to the NF-kappa B sites in the long terminal repeat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(15):5974–5978. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.15.5974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fazely F., Dezube B. J., Allen-Ryan J., Pardee A. B., Ruprecht R. M. Pentoxifylline (Trental) decreases the replication of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells and in cultured T cells. Blood. 1991 Apr 15;77(8):1653–1656. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh S., Baltimore D. Activation in vitro of NF-kappa B by phosphorylation of its inhibitor I kappa B. Nature. 1990 Apr 12;344(6267):678–682. doi: 10.1038/344678a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grilli M., Chiu J. J., Lenardo M. J. NF-kappa B and Rel: participants in a multiform transcriptional regulatory system. Int Rev Cytol. 1993;143:1–62. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61873-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara M., Inagaki M., Hidaka H. Specific binding of a novel compound, N-[2-(methylamino)ethyl]-5-isoquinolinesulfonamide (H-8) to the active site of cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Mol Pharmacol. 1987 May;31(5):523–528. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbert J. M., Augereau J. M., Gleye J., Maffrand J. P. Chelerythrine is a potent and specific inhibitor of protein kinase C. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Nov 15;172(3):993–999. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91544-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hidaka H., Inagaki M., Kawamoto S., Sasaki Y. Isoquinolinesulfonamides, novel and potent inhibitors of cyclic nucleotide dependent protein kinase and protein kinase C. Biochemistry. 1984 Oct 9;23(21):5036–5041. doi: 10.1021/bi00316a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohmann H. P., Remy R., Scheidereit C., van Loon A. P. Maintenance of NF-kappa B activity is dependent on protein synthesis and the continuous presence of external stimuli. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jan;11(1):259–266. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.1.259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iida T., Kobayashi E., Yoshida M., Sano H. Calphostins, novel and specific inhibitors of protein kinase C. II. Chemical structures. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1989 Oct;42(10):1475–1481. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.42.1475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakobovits A., Rosenthal A., Capon D. J. Trans-activation of HIV-1 LTR-directed gene expression by tat requires protein kinase C. EMBO J. 1990 Apr;9(4):1165–1170. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08223.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinter A. L., Poli G., Maury W., Folks T. M., Fauci A. S. Direct and cytokine-mediated activation of protein kinase C induces human immunodeficiency virus expression in chronically infected promonocytic cells. J Virol. 1990 Sep;64(9):4306–4312. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.9.4306-4312.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kischel T., Harbers M., Stabel S., Borowski P., Müller K., Hilz H. Tumor promotion and depletion of protein kinase C in epidermal JB6 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Dec 29;165(3):981–987. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92699-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi E., Nakano H., Morimoto M., Tamaoki T. Calphostin C (UCN-1028C), a novel microbial compound, is a highly potent and specific inhibitor of protein kinase C. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Mar 15;159(2):548–553. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)90028-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krishnamurthi S., Joseph S. Arachidonate release in neutrophils: does a lack of effect of protein kinase C inhibitors imply no involvement of protein kinase C? Biochem J. 1989 Jul 15;261(2):687–688. doi: 10.1042/bj2610687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li S., Sedivy J. M. Raf-1 protein kinase activates the NF-kappa B transcription factor by dissociating the cytoplasmic NF-kappa B-I kappa B complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Oct 15;90(20):9247–9251. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.20.9247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meichle A., Schütze S., Hensel G., Brunsing D., Krönke M. Protein kinase C-independent activation of nuclear factor kappa B by tumor necrosis factor. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 15;265(14):8339–8343. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nabel G. J., Rice S. A., Knipe D. M., Baltimore D. Alternative mechanisms for activation of human immunodeficiency virus enhancer in T cells. Science. 1988 Mar 11;239(4845):1299–1302. doi: 10.1126/science.2830675. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nabel G., Baltimore D. An inducible transcription factor activates expression of human immunodeficiency virus in T cells. Nature. 1987 Apr 16;326(6114):711–713. doi: 10.1038/326711a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishikawa M., Uemura Y., Hidaka H., Shirakawa S. 1-(5-Isoquinolinesulfonyl)-2-methylpiperazine(H-7), a potent inhibitor of protein kinases, inhibits the differentiation of HL-60 cells induced by phorbol diester. Life Sci. 1986 Sep 22;39(12):1101–1107. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(86)90202-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. The role of protein kinase C in cell surface signal transduction and tumour promotion. Nature. 1984 Apr 19;308(5961):693–698. doi: 10.1038/308693a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn L., Kunkel S., Nabel G. J. Tumor necrosis factor alpha and interleukin 1 stimulate the human immunodeficiency virus enhancer by activation of the nuclear factor kappa B. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2336–2340. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qatsha K. A., Rudolph C., Marmé D., Schächtele C., May W. S. Gö 6976, a selective inhibitor of protein kinase C, is a potent antagonist of human immunodeficiency virus 1 induction from latent/low-level-producing reservoir cells in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 May 15;90(10):4674–4678. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.10.4674. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quick J., Ware J. A., Driedger P. E. The structure and biological activities of the widely used protein kinase inhibitor, H7, differ depending on the commercial source. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Sep 16;187(2):657–663. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)91245-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roederer M., Staal F. J., Raju P. A., Ela S. W., Herzenberg L. A., Herzenberg L. A. Cytokine-stimulated human immunodeficiency virus replication is inhibited by N-acetyl-L-cysteine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(12):4884–4888. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.12.4884. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schütze S., Scheurich P., Schlüter C., Ucer U., Pfizenmaier K., Krönke M. Tumor necrosis factor-induced changes of gene expression in U937 cells. Differentiation-dependent plasticity of the responsive state. J Immunol. 1988 May 1;140(9):3000–3005. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen R., Baltimore D. Inducibility of kappa immunoglobulin enhancer-binding protein Nf-kappa B by a posttranslational mechanism. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):921–928. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90807-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirakawa F., Chedid M., Suttles J., Pollok B. A., Mizel S. B. Interleukin 1 and cyclic AMP induce kappa immunoglobulin light-chain expression via activation of an NF-kappa B-like DNA-binding protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Mar;9(3):959–964. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.3.959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirakawa F., Mizel S. B. In vitro activation and nuclear translocation of NF-kappa B catalyzed by cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase and protein kinase C. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jun;9(6):2424–2430. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.6.2424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sompayrac L. M., Danna K. J. Efficient infection of monkey cells with DNA of simian virus 40. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7575–7578. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staal F. J., Roederer M., Herzenberg L. A., Herzenberg L. A. Intracellular thiols regulate activation of nuclear factor kappa B and transcription of human immunodeficiency virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(24):9943–9947. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.24.9943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaishnav Y. N., Wong-Staal F. The biochemistry of AIDS. Annu Rev Biochem. 1991;60:577–630. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.60.070191.003045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Visvanathan K. V., Goodbourn S. Double-stranded RNA activates binding of NF-kappa B to an inducible element in the human beta-interferon promoter. EMBO J. 1989 Apr;8(4):1129–1138. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03483.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]