Abstract
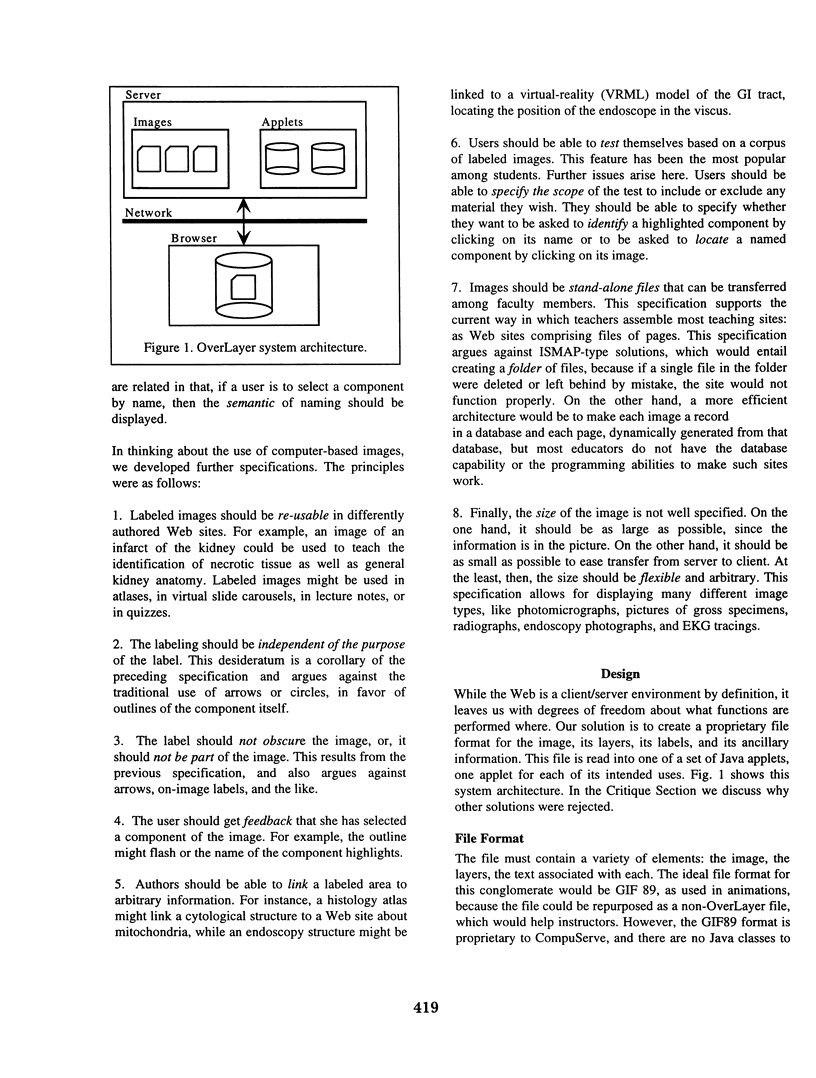
The Web provides educators with the best opportunity to date for distributing teaching images across the educational enterprise and within the clinical environment. Experience in the pre-Web era showed that labels and information linked to parts of the image are crucial to student learning. Standard Web technology does not enable the delivery of labeled images. We have developed an environment called OverLayer that succeeds in the authoring and delivering of such images in a variety of formats. OverLayer has a number of functional specifications, based on the literature and on our experience, among them, the following: Users should be able to find components by name or by image; to receive feedback about their choice to test themselves. The image should be of arbitrary size; should be reusable; should be linked to further information; should be stand-alone files. The labels should not obscure the image; should be linked to further information. Images should be stand-alone files that can be transferred among faculty members. Implemented in Java, OverLayer (http:/(/)omie.med.jhmi.edu/overlayer) has at its heart a set of object classes that have been reused in a number of applets for different teaching purposes and a file format for creating OverLayer images. We have created a 350-image histology library and a 500-image pathology library, and are working on a 400-image GI endoscopy library. We hope that the OverLayer suite of classes and implementations will help to further the gains made by previous image-based hyperlinked technologies.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradley S. W., Rosse C., Brinkley J. F. Web-based access to an online atlas of anatomy: the Digital Anatomist Common Gateway Interface. Proc Annu Symp Comput Appl Med Care. 1995:512–516. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McEnery K. W., Roth S. M., Kelley L. K., Hirsch K. R., Menton D. N., Kelly E. A. A method for interactive medical instruction utilizing the World Wide Web. Proc Annu Symp Comput Appl Med Care. 1995:502–507. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stensaas S. S. Animating the curriculum: integrating multimedia into teaching. Bull Med Libr Assoc. 1994 Apr;82(2):133–139. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



