Abstract
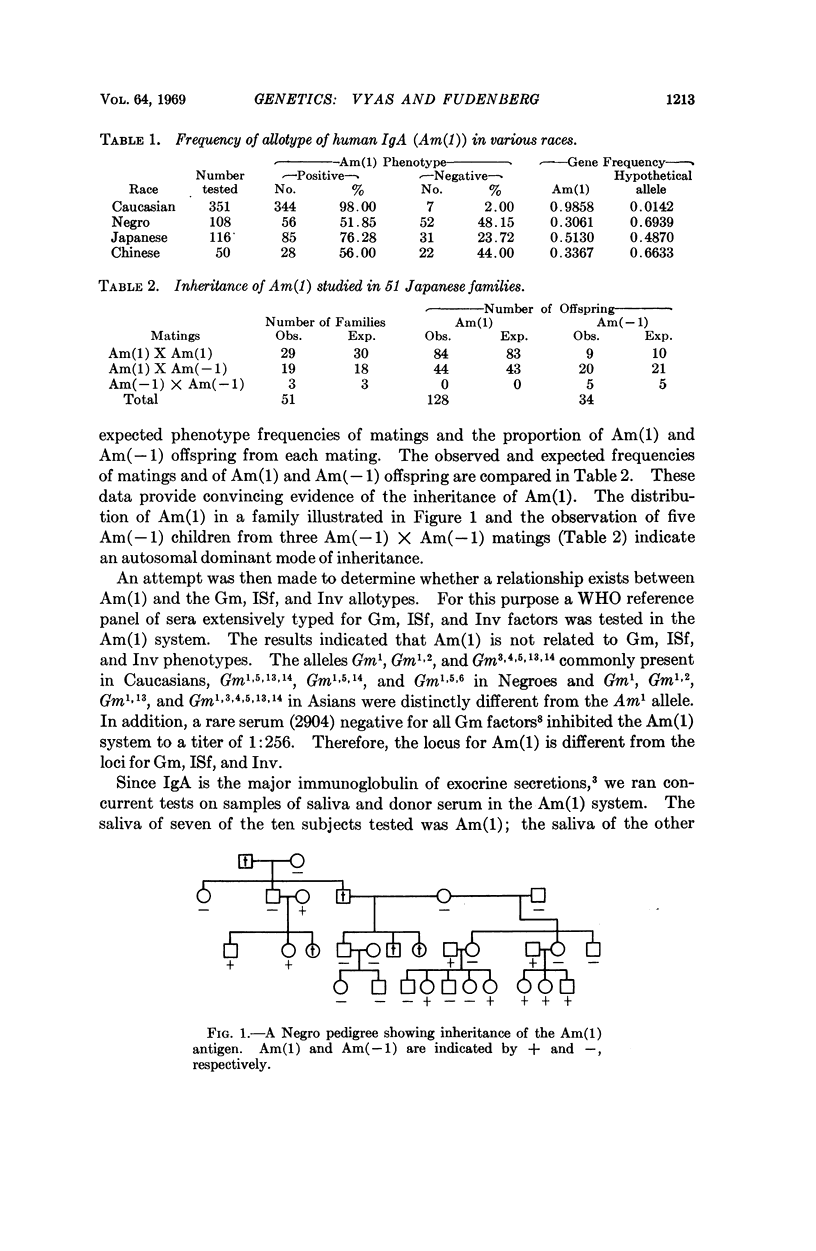
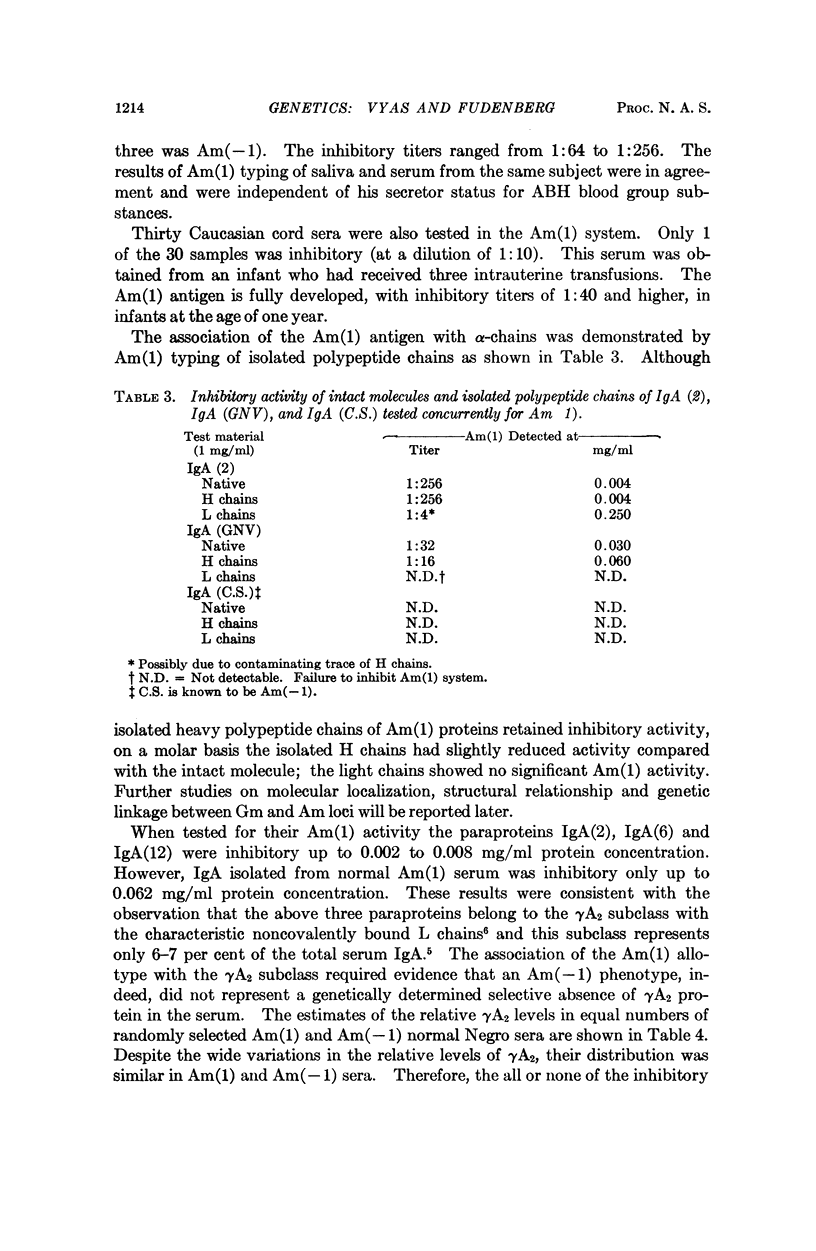
The genetic markers of human immunoglobulins have significantly contributed to the understanding of the molecular biology of antibody synthesis. Like the Gm markers of IgG, the first genetic marker of serum IgA, a major immunoglubulin of exocrine secretions, has now been defined and termed Am(1). It is inherited as a Mendelian dominant trait and is independent of the Gm and Inv allotypes. Am(1) is localized in the α-chains of the γA2 subclass and is independent of the serum γA2 levels. Its polymorphism makes it suitable for studies in population genetics and the molecular biology of IgA globulin.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Grey H. M., Abel C. A., Yount W. J., Kunkel H. G. A subclass of human gamma-A-globulins (gamma-A2) which lacks the disulfied bonds linking heavy and light chains. J Exp Med. 1968 Dec 1;128(6):1223–1236. doi: 10.1084/jem.128.6.1223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel H. G., Smith W. K., Joslin F. G., Natvig J. B., Litwin S. D. Genetic marker of the gamma-A2 subgroup of gamma-A immunoglobulins. Nature. 1969 Sep 20;223(5212):1247–1248. doi: 10.1038/2231247a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muir W. A., Steinberg A. G. On the genetics of the human allotypes, Gm and Inv. Semin Hematol. 1967 Apr;4(2):156–173. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Natvig J. B., Kunkel H. G. Detection of genetic antigens utilizing gamma globulins coupled to red blood cells. Nature. 1967 Jul 1;215(5096):68–69. doi: 10.1038/215068a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt A. P., Taswell H. F., Gleich G. J. Anaphylactic transfusion reactions associated with anti-IgA antibody. N Engl J Med. 1969 Jan 23;280(4):188–193. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196901232800404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg A. G., Muir W. A., McIntire S. A. Two unusual Gm alleles: their implications for the genetics of the Gm antigens. Am J Hum Genet. 1968 May;20(3):258–278. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomasi T. B., Jr, Bienenstock J. Secretory immunoglobulins. Adv Immunol. 1968;9:1–96. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60441-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaerman J. P., Heremans J. F., Laurell C. B. Distribution of alpha-chain subclasses in normal and pathological IgA-globulins. Immunology. 1968 Mar;14(3):425–432. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vyas G. N., Fudenberg H. H. Isoimmune anti-IgA causing anaphylactoid transfusion reactions. N Engl J Med. 1969 May 8;280(19):1073–1074. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196905082801912. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vyas G. N., Fudenberg H. H., Pretty H. M., Gold E. R. A new rapid method for genetic typing of human immunoglobulins. J Immunol. 1968 Feb;100(2):274–279. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vyas G. N., Holmdahl L., Perkins H. A., Fudenberg H. H. Serologic specificity of hun anti-IgA and its significance in transfusion. Blood. 1969 Nov;34(5):573–581. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vyas G. N., Perkins H. A., Fudenberg H. H. Anaphylactoid transfusion reactions associated with anti-IgA. Lancet. 1968 Aug 10;2(7563):312–315. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(68)90527-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


