Abstract
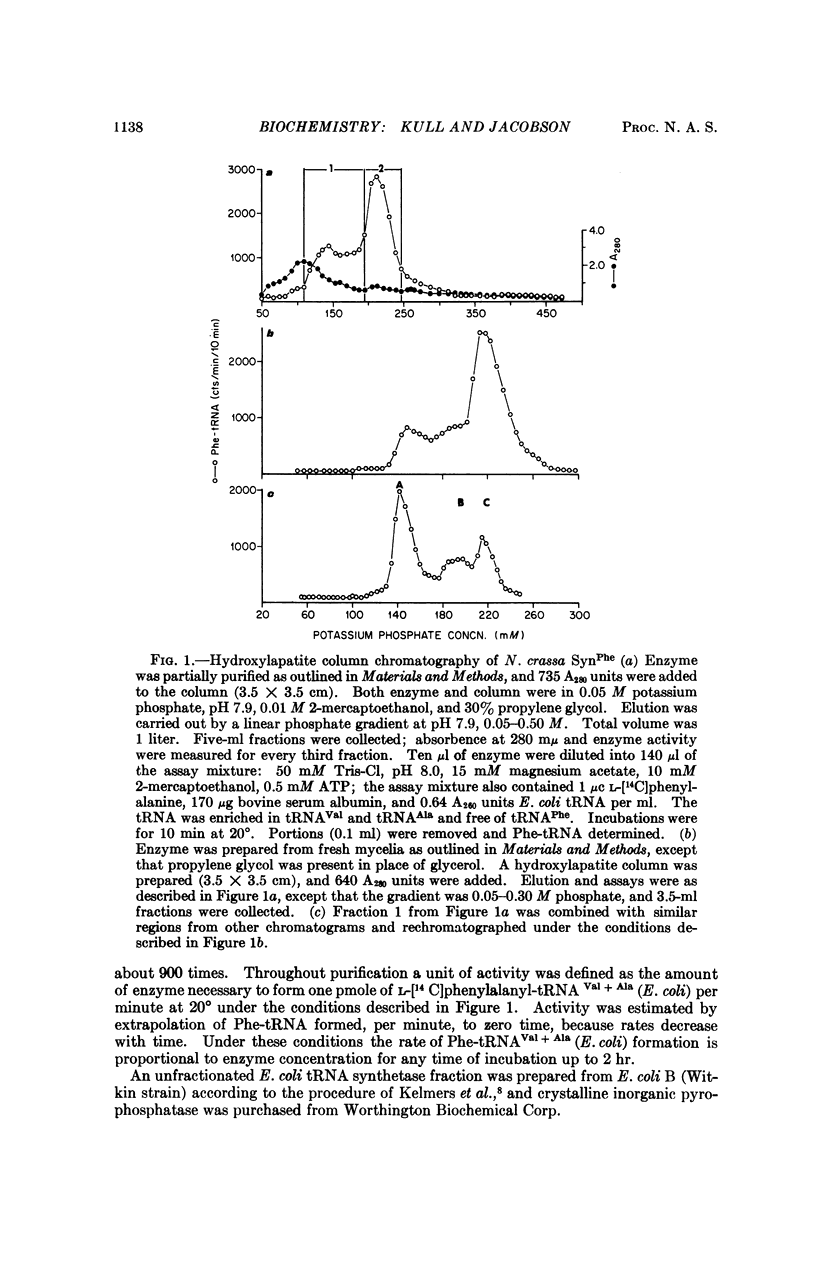
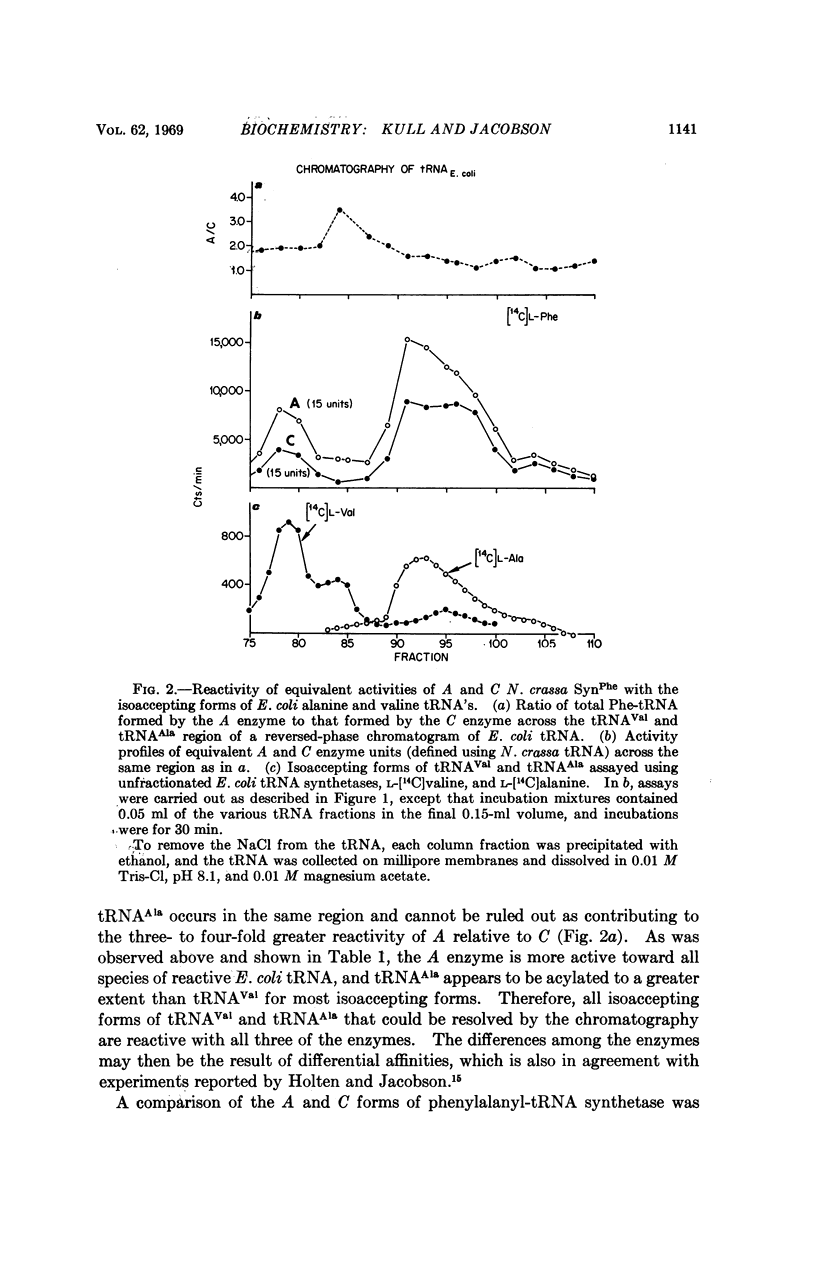
Several tRNA's specific for a particular amino acid have been shown to exist in multiple, or isoaccepting, forms. There is considerable interest in establishing whether multiple aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases also exist. We present evidence that the cytoplasm of Neurospora crassa contains three chromatographically separable phenylalanyl-tRNA synthetases distinct from mitochondrial phenylalanyl-tRNA synthetase. In addition to differences in chromatographic properties the three enzymes exhibit different affinities, in Tris-Cl buffer, toward purified species of valine and alanine tRNA's isolated from Escherichia coli. The two major chromatographic fractions have very similar sedimentation characteristics, which makes a monomer-dimer relationship unlikely.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BARNETT W. E., JACOBSON K. B. EVIDENCE FOR DEGENERACY AND AMBIGUITY IN INTERSPECIES AMINOACYL-SRNA FORMATION. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Apr;51:642–647. doi: 10.1073/pnas.51.4.642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOLLUM F. J. Thermal conversion of nonpriming deoxyribonucleic acid to primer. J Biol Chem. 1959 Oct;234:2733–2734. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnett W. E., Brown D. H., Epler J. L. Mitochondrial-specific aminoacyl-RNA synthetases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Jun;57(6):1775–1781. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.6.1775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnett W. E., Brown D. H. Mitochondrial transfer ribonucleic acids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Feb;57(2):452–458. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.2.452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnett W. E., Epler J. L. Fractionation and specificities of two aspartyl-ribonucleic acid and two phenylalanyl-ribonucleic acid synthetases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Jan;55(1):184–189. doi: 10.1073/pnas.55.1.184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnett W. E. Interspecies aminoacyl-sRNA formation: fractionation of Neurospora enzymes involved in anomalous aminoacylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Jun;53(6):1462–1467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.53.6.1462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böck A. Relation between subunit structure and temperature-sensitivity of mutant phenylalanyl RNA synthetases of Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1968 Apr;4(3):395–400. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1968.tb00225.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassio D., Waller J. P. Etude la méthionyl-tRNA synthétase d'Escherichia coli. 3. Dissociation en sous-unités actives par action d'un facteur extrinsèque. Eur J Biochem. 1968 Jun;5(1):33–41. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1968.tb00333.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holten V. Z., Jacobson K. B. Studies on the aminoacylation of valine- and alanine-specific transfer RNA of Escherichia coli by aminoacyl transfer RNA synthetases from Neurospora crassa and E. coli. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1969 Jan;129(1):283–289. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(69)90177-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imamoto F., Yamane T., Sueoka N. Existence of two phenylalanyl-sRNA synthetases in Neurospora crassa. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Jun;53(6):1456–1462. doi: 10.1073/pnas.53.6.1456. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelmers A. D., Novelli G. D., Stulberg M. P. Separation of transfer ribonucleic acids by reverse phase chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1965 Oct;240(10):3979–3983. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- National Academy of Sciences: Abstracts of papers presented at the autumn meeting, Durham, North Carolina, 17-19 October 1966. Science. 1966 Oct 21;154(3747):417–430. doi: 10.1126/science.154.3747.417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson R. L., Kelmers A. D. Separation of transfer ribonucleic acids by hydroxyapatite columns. J Biol Chem. 1966 Feb 10;241(3):767–769. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strehler B. L., Hendley D. D., Hirsch G. P. Evidence of a codon restriction hypothesis of cellular differentiation: multiplicity of mammalian leucyl-sRNA-specific synthetases and tissue-specific deficiency in an alanyl-sRNA synthetase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Jun;57(6):1751–1758. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.6.1751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stulberg M. P. The isolation and properties of phenylalanyl ribonucleic acid synthetase from Escherichia coli B. J Biol Chem. 1967 Mar 10;242(5):1060–1064. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sumner J. B. A METHOD FOR THE COLORIMETRIC DETERMINATION OF PHOSPHORUS. Science. 1944 Nov 3;100(2601):413–414. doi: 10.1126/science.100.2601.413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vescia A. Separation of two leucyl-ribonucleic acid synthetases from rat liver. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1967 Nov 30;29(4):496–500. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(67)90511-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss J. F., Kelmers A. D. A new chromatographic system for increased resolution of transfer ribonucleic acids. Biochemistry. 1967 Aug;6(8):2507–2513. doi: 10.1021/bi00860a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


