Abstract
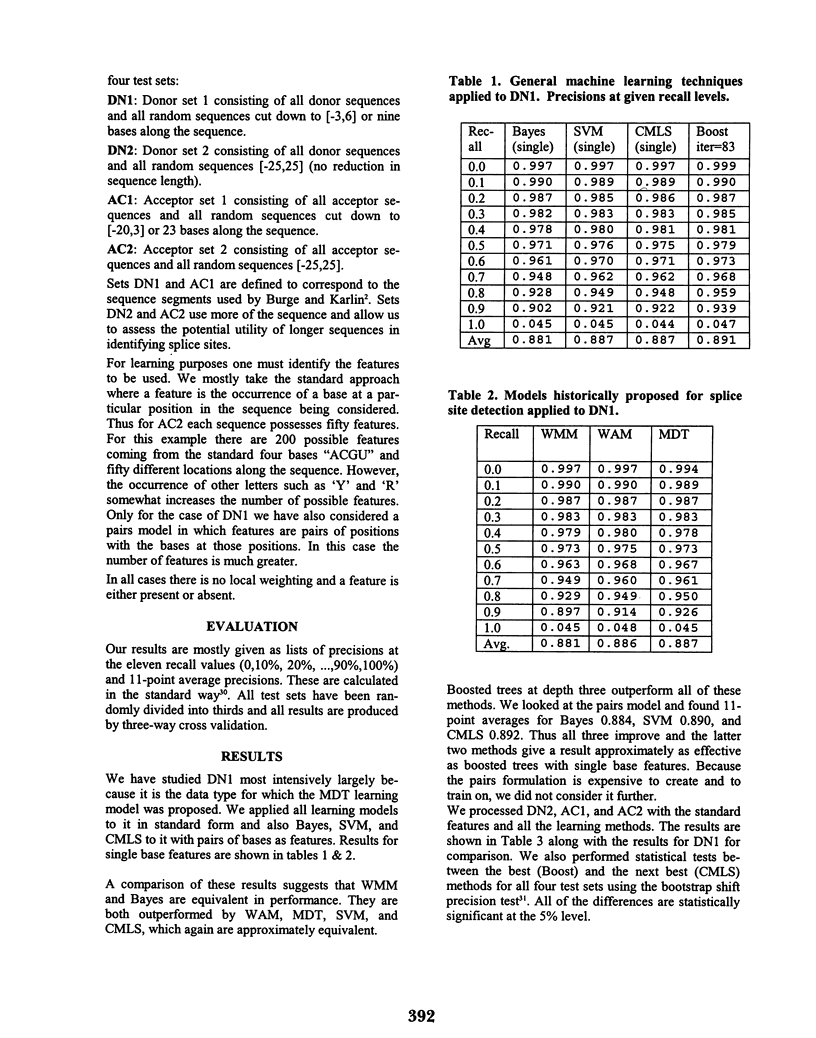
In an era when whole organism genomes are being routinely sequenced, the problem of gene finding has become a key issue on the road to understanding. For eukaryotic organisms a large part of locating the genes is accomplished by predicting the likely location of splice sites on a DNA strand. This problem of splice site location has been ap- proached using a number of machine learning or statistical methods tailored more or less specifically to the nature of the problem. Recently large margin classifiers and boosting methods have been found to give improvements over more traditional methods in a number of areas. Here we compare large margin classifiers (SVM and CMLS) and boosted decision trees with the three most common models used for splice site detection (WMM, WAM, and MDT). We find that the newer methods compare favorably in all cases and can yield significant improvement in some cases.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brunak S., Engelbrecht J., Knudsen S. Prediction of human mRNA donor and acceptor sites from the DNA sequence. J Mol Biol. 1991 Jul 5;220(1):49–65. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90380-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burge C., Karlin S. Prediction of complete gene structures in human genomic DNA. J Mol Biol. 1997 Apr 25;268(1):78–94. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1997.0951. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guigó R. Computational gene identification: an open problem. Comput Chem. 1997;21(4):215–222. doi: 10.1016/s0097-8485(97)00008-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parra G., Blanco E., Guigó R. GeneID in Drosophila. Genome Res. 2000 Apr;10(4):511–515. doi: 10.1101/gr.10.4.511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pertea M., Lin X., Salzberg S. L. GeneSplicer: a new computational method for splice site prediction. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001 Mar 1;29(5):1185–1190. doi: 10.1093/nar/29.5.1185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reese M. G., Eeckman F. H., Kulp D., Haussler D. Improved splice site detection in Genie. J Comput Biol. 1997 Fall;4(3):311–323. doi: 10.1089/cmb.1997.4.311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salzberg S., Chen X., Henderson J., Fasman K. Finding genes in DNA using decision trees and dynamic programming. Proc Int Conf Intell Syst Mol Biol. 1996;4:201–210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salzberg S., Delcher A. L., Fasman K. H., Henderson J. A decision tree system for finding genes in DNA. J Comput Biol. 1998 Winter;5(4):667–680. doi: 10.1089/cmb.1998.5.667. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solovyev V., Salamov A. The Gene-Finder computer tools for analysis of human and model organisms genome sequences. Proc Int Conf Intell Syst Mol Biol. 1997;5:294–302. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staden R. Computer methods to locate signals in nucleic acid sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 2):505–519. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part2.505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uberbacher E. C., Mural R. J. Locating protein-coding regions in human DNA sequences by a multiple sensor-neural network approach. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 15;88(24):11261–11265. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.24.11261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilbur W. J. Boosting naïve Bayesian learning on a large subset of MEDLINE. Proc AMIA Symp. 2000:918–922. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang M. Q. Identification of protein coding regions in the human genome by quadratic discriminant analysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997 Jan 21;94(2):565–568. doi: 10.1073/pnas.94.2.565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang M. Q., Marr T. G. A weight array method for splicing signal analysis. Comput Appl Biosci. 1993 Oct;9(5):499–509. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/9.5.499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


