Abstract
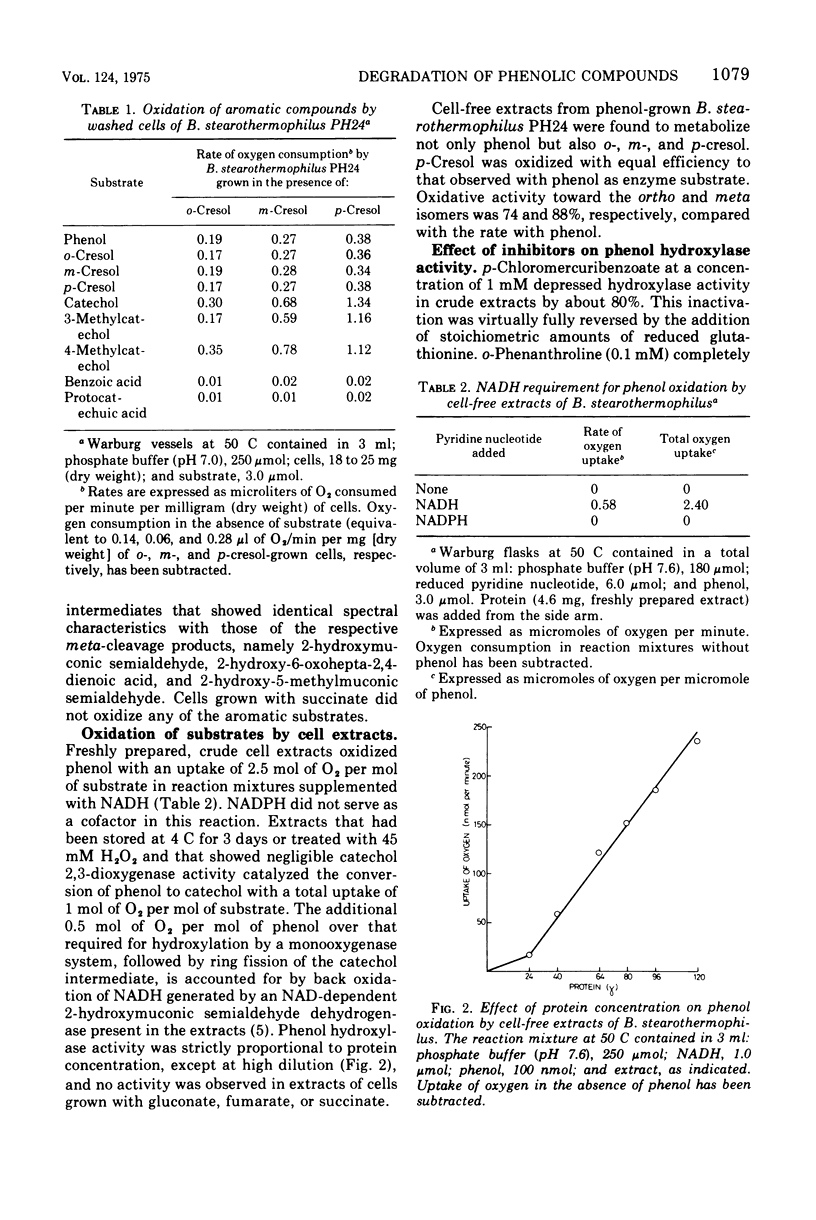
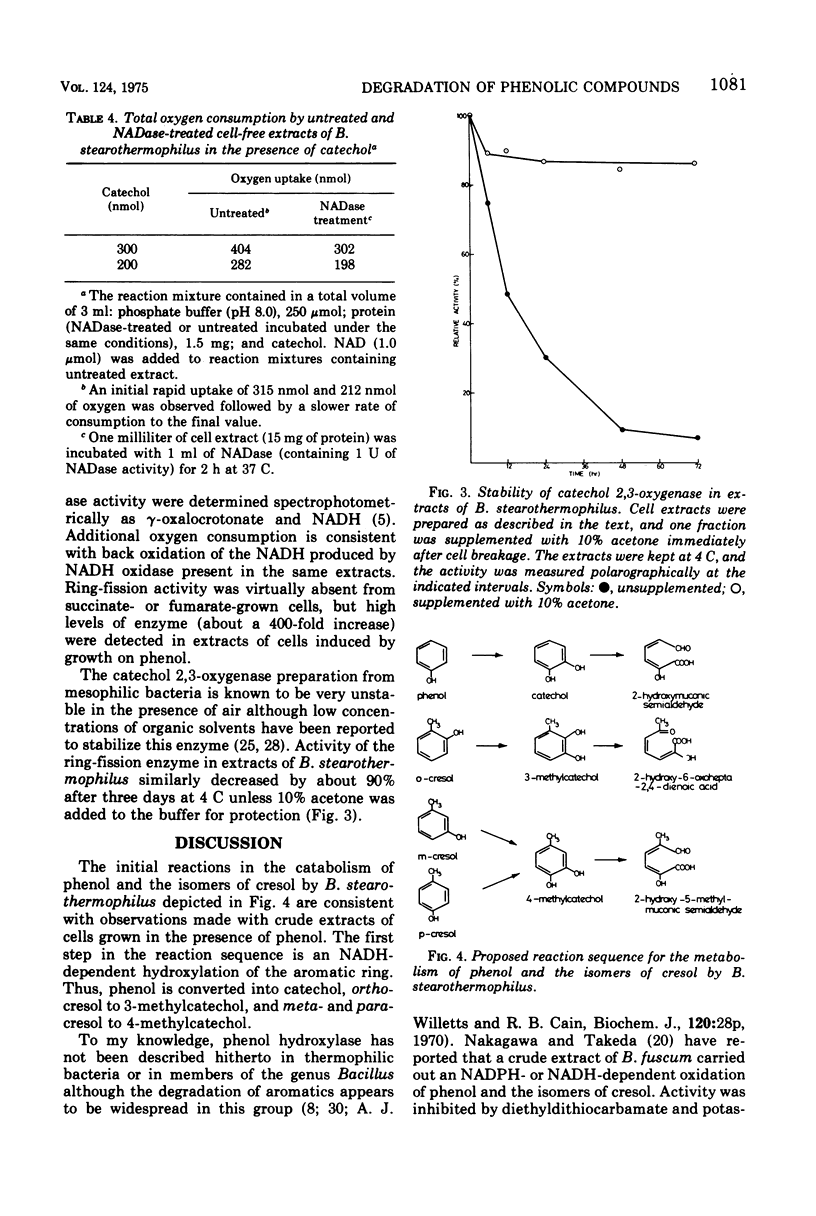
An obligate thermophilic strain of Bacillus stearothermophilus, strain PH24, isolated from industrial sediment by elective culture, grew readily at 55 C on phenol or on one of the isomers of cresol as the major carbon source. Intact cells grown in the presence of phenol, o-cresol, m-cresol, or p-cresol were induced to oxidize, without lag, these substrates together with catechol, 3-methylcatechol, and 4-methylcatechol. Cell extracts prepared from B. stearothermophilus PH24 after growth in the presence of phenol converted phenol to catechol with a concomitant uptake of 1 mol of oxygen per mol of substrate in reaction mixtures supplemented with reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide. These preparations also catalyzed the oxidation of o-cresol to 3-methylcatechol and of m-cresol and p-cresol to 4-methylcatechol. Enzyme activity was inhibited by 1 mM p-chloromercuribenzoate and by 0.1 mM 0-phenanthroline. Catechol and the corresponding methylcatechol intermediates were further dissimilated by cell extracts of phenol-grown cells via the meta-cleavage route to yield 2-hydroxymuconic semialdehyde and the respective methylated derivatives.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bayly R. C., Dagley S., Gibson D. T. The metabolism of cresols by species of Pseudomonas. Biochem J. 1966 Nov;101(2):293–301. doi: 10.1042/bj1010293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayly R. C., Wigmore G. J. Metabolism of phenol and cresols by mutants of Pseudomonas putida. J Bacteriol. 1973 Mar;113(3):1112–1120. doi: 10.1128/jb.113.3.1112-1120.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird J. A., Cain R. B. Microbial degradation of alkylbenzenesulphonates. Metabolism of homologues of short alkyl-chain length by an Alcaligenes sp. Biochem J. 1974 May;140(2):121–134. doi: 10.1042/bj1400121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buswell J. A. The meta-cleavage of catechol by a thermophilic Bacillus species. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Oct 8;60(3):934–941. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90404-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buswell J. A., Twomey D. G. Utilization of phenol and cresols by Bacillus stearothermophilus, strain PH24. J Gen Microbiol. 1975 Apr;87(2):377–379. doi: 10.1099/00221287-87-2-377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cain R. B., Bilton R. F., Darrah J. A. The metabolism of aromatic acids by micro-organisms. Metabolic pathways in the fungi. Biochem J. 1968 Aug;108(5):797–828. doi: 10.1042/bj1080797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford R. L. Novel pathway for degradation of protocatechuic acid in Bacillus species. J Bacteriol. 1975 Feb;121(2):531–536. doi: 10.1128/jb.121.2.531-536.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAGLEY S., GIBSON D. T. THE BACTERIAL DEGRADATION OF CATECHOL. Biochem J. 1965 May;95:466–474. doi: 10.1042/bj0950466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAGLEY S., PATEL M. D. Oxidation of p-cresol and related compounds by a Pseudomonas. Biochem J. 1957 Jun;66(2):227–233. doi: 10.1042/bj0660227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dagley S. Catabolism of aromatic compounds by micro-organisms. Adv Microb Physiol. 1971;6(0):1–46. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(08)60066-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HENDERSON M. E. The metabolism of aromatic compounds related to lignin by some hyphomycetes and yeast-like fungi of soil. J Gen Microbiol. 1961 Sep;26:155–165. doi: 10.1099/00221287-26-1-155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hegeman G. D., Rosenberg S. L. The evolution of bacterial enzyme systems. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1970;24:429–462. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.24.100170.002241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NAKAGAWA H., TAKEDA Y. Phenol hydroxylase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Aug 13;62:423–426. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90275-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NOZAKI M., KAGAMIYAMA H., HAYAISHI O. METAPYROCATECHASE. I. PURIFICATION, CRYSTALLIZATION AND SOME PROPERTIES. Biochem Z. 1963;338:582–590. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakazawa T., Yokota T. Benzoate metabolism in Pseudomonas putida(arvilla) mt-2: demonstration of two benzoate pathways. J Bacteriol. 1973 Jul;115(1):262–267. doi: 10.1128/jb.115.1.262-267.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neujahr H. Y., Gaal A. Phenol hydroxylase from yeast. Purification and properties of the enzyme from Trichosporon cutaneum. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Jun;35(2):386–400. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02851.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neujahr H. Y., Lindsjö S., Varga J. M. Oxidation of phenols by cells and cell-free enzymes from Candida tropicalis. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1974;40(2):209–216. doi: 10.1007/BF00394378. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neujahr H. Y., Varga J. M. Degradation of phenols by intact cells and cell-free preparations of Trichosporon cutaneum. Eur J Biochem. 1970 Mar 1;13(1):37–44. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb00896.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ornston L. N., Stanier R. Y. The conversion of catechol and protocatechuate to beta-ketoadipate by Pseudomonas putida. J Biol Chem. 1966 Aug 25;241(16):3776–3786. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribbons D. W. Metabolism of omicron-cresol by Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain T1. J Gen Microbiol. 1966 Aug;44(2):221–231. doi: 10.1099/00221287-44-2-221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sala-Trepat J. M., Evans W. C. The meta cleavage of catechol by Azotobacter species. 4-Oxalocrotonate pathway. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Jun 11;20(3):400–413. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01406.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willetts A. J., Cain R. B. Microbial metabolism of alkylbenzene sulphonates. Bacterial metabolism of undecylbenzene-p-sulphonate and dodecylbenzene-p-sulphonate. Biochem J. 1972 Sep;129(2):389–402. doi: 10.1042/bj1290389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


