Abstract
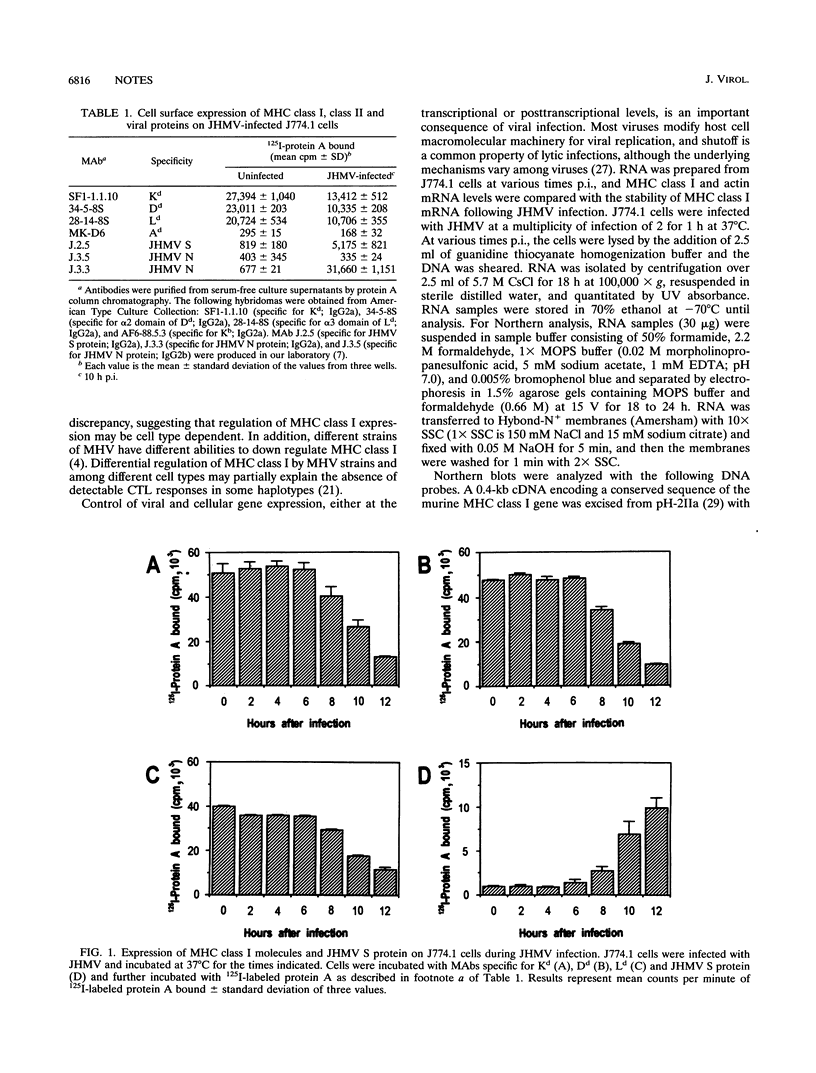
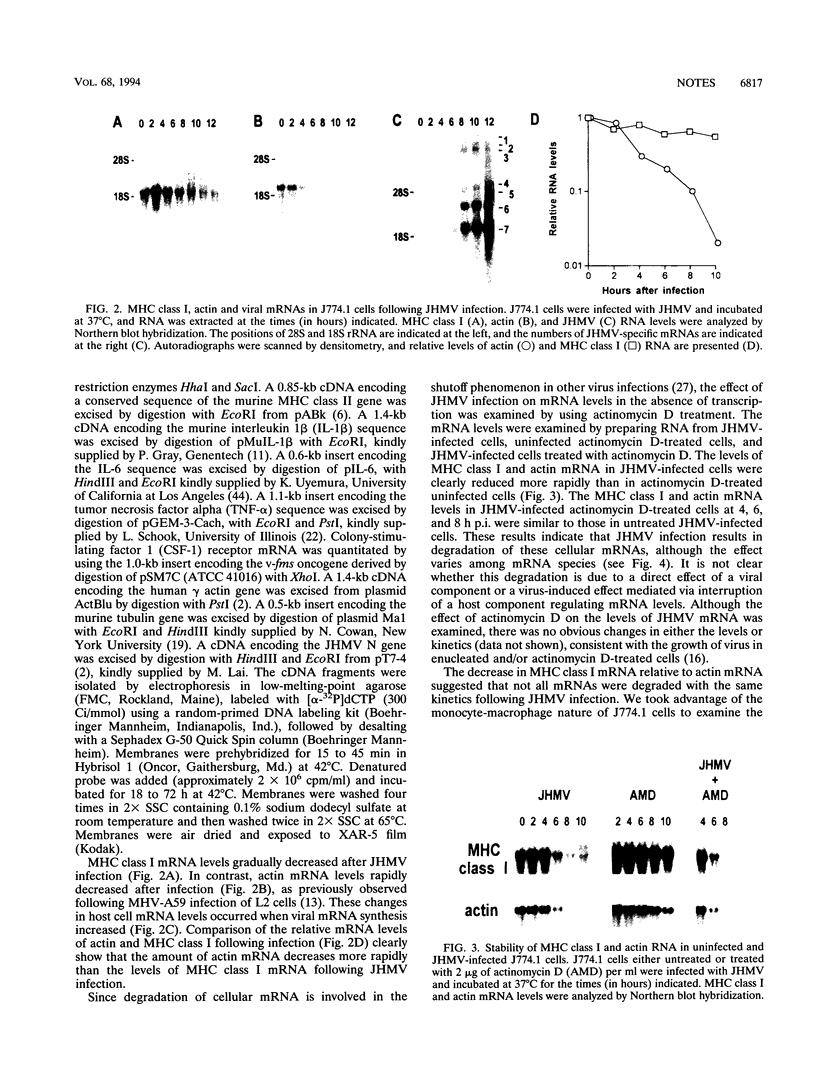
Infection with the murine coronavirus strain JHM decreases cell surface expression of major histocompatibility complex class I antigens. Northern blots showed that JHM virus infection rapidly reduced the level of actin mRNA, whereas the levels of major histocompatibility complex class I and tubulin mRNAs were reduced only slightly. By contrast, the mRNA levels of interleukin 1 beta, colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor, and tumor necrosis factor alpha increased following infection.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aharon T., Schneider R. J. Selective destabilization of short-lived mRNAs with the granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor AU-rich 3' noncoding region is mediated by a cotranslational mechanism. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Mar;13(3):1971–1980. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.3.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baric R. S., Nelson G. W., Fleming J. O., Deans R. J., Keck J. G., Casteel N., Stohlman S. A. Interactions between coronavirus nucleocapsid protein and viral RNAs: implications for viral transcription. J Virol. 1988 Nov;62(11):4280–4287. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.11.4280-4287.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benveniste E. N. Inflammatory cytokines within the central nervous system: sources, function, and mechanism of action. Am J Physiol. 1992 Jul;263(1 Pt 1):C1–16. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1992.263.1.C1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergmann C., McMillan M., Stohlman S. Characterization of the Ld-restricted cytotoxic T-lymphocyte epitope in the mouse hepatitis virus nucleocapsid protein. J Virol. 1993 Dec;67(12):7041–7049. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.12.7041-7049.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalziel R. G., Lampert P. W., Talbot P. J., Buchmeier M. J. Site-specific alteration of murine hepatitis virus type 4 peplomer glycoprotein E2 results in reduced neurovirulence. J Virol. 1986 Aug;59(2):463–471. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.2.463-471.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estess P., Begovich A. B., Koo M., Jones P. P., McDevitt H. O. Sequence analysis and structure-function correlations of murine q, k, u, s, and f haplotype I-A beta cDNA clones. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):3594–3598. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.3594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleming J. O., Stohlman S. A., Harmon R. C., Lai M. M., Frelinger J. A., Weiner L. P. Antigenic relationships of murine coronaviruses: analysis using monoclonal antibodies to JHM (MHV-4) virus. Virology. 1983 Dec;131(2):296–307. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90498-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleming J. O., Trousdale M. D., el-Zaatari F. A., Stohlman S. A., Weiner L. P. Pathogenicity of antigenic variants of murine coronavirus JHM selected with monoclonal antibodies. J Virol. 1986 Jun;58(3):869–875. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.3.869-875.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleming J. O., Wang F. I., Trousdale M. D., Hinton D. R., Stohlman S. A. Interaction of immune and central nervous systems: contribution of anti-viral Thy-1+ cells to demyelination induced by coronavirus JHM. Reg Immunol. 1993 Jan-Feb;5(1):37–43. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gombold J. L., Weiss S. R. Mouse hepatitis virus A59 increases steady-state levels of MHC mRNAs in primary glial cell cultures and in the murine central nervous system. Microb Pathog. 1992 Dec;13(6):493–505. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(92)90015-G. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray P. W., Glaister D., Chen E., Goeddel D. V., Pennica D. Two interleukin 1 genes in the mouse: cloning and expression of the cDNA for murine interleukin 1 beta. J Immunol. 1986 Dec 1;137(11):3644–3648. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauser S. L., Doolittle T. H., Lincoln R., Brown R. H., Dinarello C. A. Cytokine accumulations in CSF of multiple sclerosis patients: frequent detection of interleukin-1 and tumor necrosis factor but not interleukin-6. Neurology. 1990 Nov;40(11):1735–1739. doi: 10.1212/wnl.40.11.1735. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilton A., Mizzen L., MacIntyre G., Cheley S., Anderson R. Translational control in murine hepatitis virus infection. J Gen Virol. 1986 May;67(Pt 5):923–932. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-5-923. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joseph J., Knobler R. L., Lublin F. D., Hart M. N. Differential modulation of MHC class I antigen expression on mouse brain endothelial cells by MHV-4 infection. J Neuroimmunol. 1989 May;22(3):241–253. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(89)90022-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai M. M. Coronavirus: organization, replication and expression of genome. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1990;44:303–333. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.44.100190.001511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavi E., Suzumura A., Murray E. M., Silberberg D. H., Weiss S. R. Induction of MHC class I antigens on glial cells is dependent on persistent mouse hepatitis virus infection. J Neuroimmunol. 1989 Apr;22(2):107–111. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(89)90040-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lecomte J., Cainelli-Gebara V., Mercier G., Mansour S., Talbot P. J., Lussier G., Oth D. Protection from mouse hepatitis virus type 3-induced acute disease by an anti-nucleoprotein monoclonal antibody. Brief report. Arch Virol. 1987;97(1-2):123–130. doi: 10.1007/BF01310740. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis S. A., Lee M. G., Cowan N. J. Five mouse tubulin isotypes and their regulated expression during development. J Cell Biol. 1985 Sep;101(3):852–861. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.3.852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malter J. S., Hong Y. A redox switch and phosphorylation are involved in the post-translational up-regulation of the adenosine-uridine binding factor by phorbol ester and ionophore. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 15;266(5):3167–3171. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mobley J., Evans G., Dailey M. O., Perlman S. Immune response to a murine coronavirus: identification of a homing receptor-negative CD4+ T cell subset that responds to viral glycoproteins. Virology. 1992 Apr;187(2):443–452. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90446-V. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers M. J., Pullen J. K., Ghildyal N., Eustis-Turf E., Schook L. B. Regulation of IL-1 and TNF-alpha expression during the differentiation of bone marrow derived macrophage. J Immunol. 1989 Jan 1;142(1):153–160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakanaga K., Yamanouchi K., Fujiwara K. Protective effect of monoclonal antibodies on lethal mouse hepatitis virus infection in mice. J Virol. 1986 Jul;59(1):168–171. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.1.168-171.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakanaga K., Yamanouchi K., Fujiwara K. Protective effect of the F(ab')2 fragments of monoclonal antibodies to mouse hepatitis virus. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1987;218:365–371. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-1280-2_45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearce B. D., Hobbs M. V., McGraw T. S., Buchmeier M. J. Cytokine induction during T-cell-mediated clearance of mouse hepatitis virus from neurons in vivo. J Virol. 1994 Sep;68(9):5483–5495. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.9.5483-5495.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rötzschke O., Falk K., Deres K., Schild H., Norda M., Metzger J., Jung G., Rammensee H. G. Isolation and analysis of naturally processed viral peptides as recognized by cytotoxic T cells. Nature. 1990 Nov 15;348(6298):252–254. doi: 10.1038/348252a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider R. J., Shenk T. Impact of virus infection on host cell protein synthesis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:317–332. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.001533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selmaj K., Raine C. S., Cross A. H. Anti-tumor necrosis factor therapy abrogates autoimmune demyelination. Ann Neurol. 1991 Nov;30(5):694–700. doi: 10.1002/ana.410300510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinmetz M., Frelinger J. G., Fisher D., Hunkapiller T., Pereira D., Weissman S. M., Uehara H., Nathenson S., Hood L. Three cDNA clones encoding mouse transplantation antigens: homology to immunoglobulin genes. Cell. 1981 Apr;24(1):125–134. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90508-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stohlman S. A., Bergmann C., Cua D., Wege H., van der Veen R. Location of antibody epitopes within the mouse hepatitis virus nucleocapsid protein. Virology. 1994 Jul;202(1):146–153. doi: 10.1006/viro.1994.1330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stohlman S. A., Kyuwa S., Cohen M., Bergmann C., Polo J. M., Yeh J., Anthony R., Keck J. G. Mouse hepatitis virus nucleocapsid protein-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes are Ld restricted and specific for the carboxy terminus. Virology. 1992 Jul;189(1):217–224. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90697-N. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stohlman S. A., Kyuwa S., Polo J. M., Brady D., Lai M. M., Bergmann C. C. Characterization of mouse hepatitis virus-specific cytotoxic T cells derived from the central nervous system of mice infected with the JHM strain. J Virol. 1993 Dec;67(12):7050–7059. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.12.7050-7059.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoll G., Jung S., Jander S., van der Meide P., Hartung H. P. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha in immune-mediated demyelination and Wallerian degeneration of the rat peripheral nervous system. J Neuroimmunol. 1993 Jun;45(1-2):175–182. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(93)90178-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sussman M. A., Shubin R. A., Kyuwa S., Stohlman S. A. T-cell-mediated clearance of mouse hepatitis virus strain JHM from the central nervous system. J Virol. 1989 Jul;63(7):3051–3056. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.7.3051-3056.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzumura A., Lavi E., Weiss S. R., Silberberg D. H. Coronavirus infection induces H-2 antigen expression on oligodendrocytes and astrocytes. Science. 1986 May 23;232(4753):991–993. doi: 10.1126/science.3010460. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tahara S. M., Dietlin T. A., Bergmann C. C., Nelson G. W., Kyuwa S., Anthony R. P., Stohlman S. A. Coronavirus translational regulation: leader affects mRNA efficiency. Virology. 1994 Aug 1;202(2):621–630. doi: 10.1006/viro.1994.1383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Townsend A., Bodmer H. Antigen recognition by class I-restricted T lymphocytes. Annu Rev Immunol. 1989;7:601–624. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.07.040189.003125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Bleek G. M., Nathenson S. G. Isolation of an endogenously processed immunodominant viral peptide from the class I H-2Kb molecule. Nature. 1990 Nov 15;348(6298):213–216. doi: 10.1038/348213a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang F. I., Stohlman S. A., Fleming J. O. Demyelination induced by murine hepatitis virus JHM strain (MHV-4) is immunologically mediated. J Neuroimmunol. 1990 Nov;30(1):31–41. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(90)90050-W. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wege H., Winter J., Meyermann R. The peplomer protein E2 of coronavirus JHM as a determinant of neurovirulence: definition of critical epitopes by variant analysis. J Gen Virol. 1988 Jan;69(Pt 1):87–98. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-1-87. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson J. S., Stohlman S. A. Effective clearance of mouse hepatitis virus from the central nervous system requires both CD4+ and CD8+ T cells. J Virol. 1990 Sep;64(9):4589–4592. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.9.4589-4592.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi K., Goto N., Kyuwa S., Hayami M., Toyoda Y. Protection of mice from a lethal coronavirus infection in the central nervous system by adoptive transfer of virus-specific T cell clones. J Neuroimmunol. 1991 Apr;32(1):1–9. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(91)90065-F. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi K., Kyuwa S., Nakanaga K., Hayami M. Establishment of cytotoxic T-cell clones specific for cells infected with mouse hepatitis virus. J Virol. 1988 Jul;62(7):2505–2507. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.7.2505-2507.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamura M., Wang X. H., Ohmen J. D., Uyemura K., Rea T. H., Bloom B. R., Modlin R. L. Cytokine patterns of immunologically mediated tissue damage. J Immunol. 1992 Aug 15;149(4):1470–1475. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]