Abstract
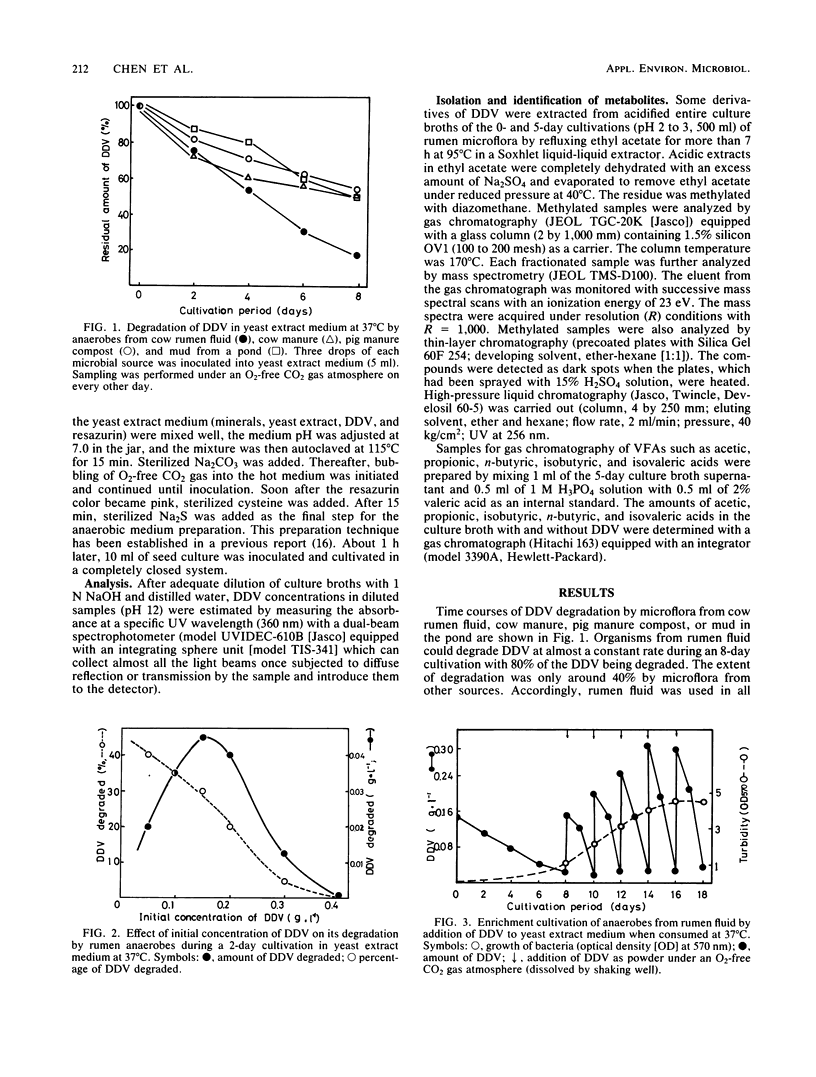
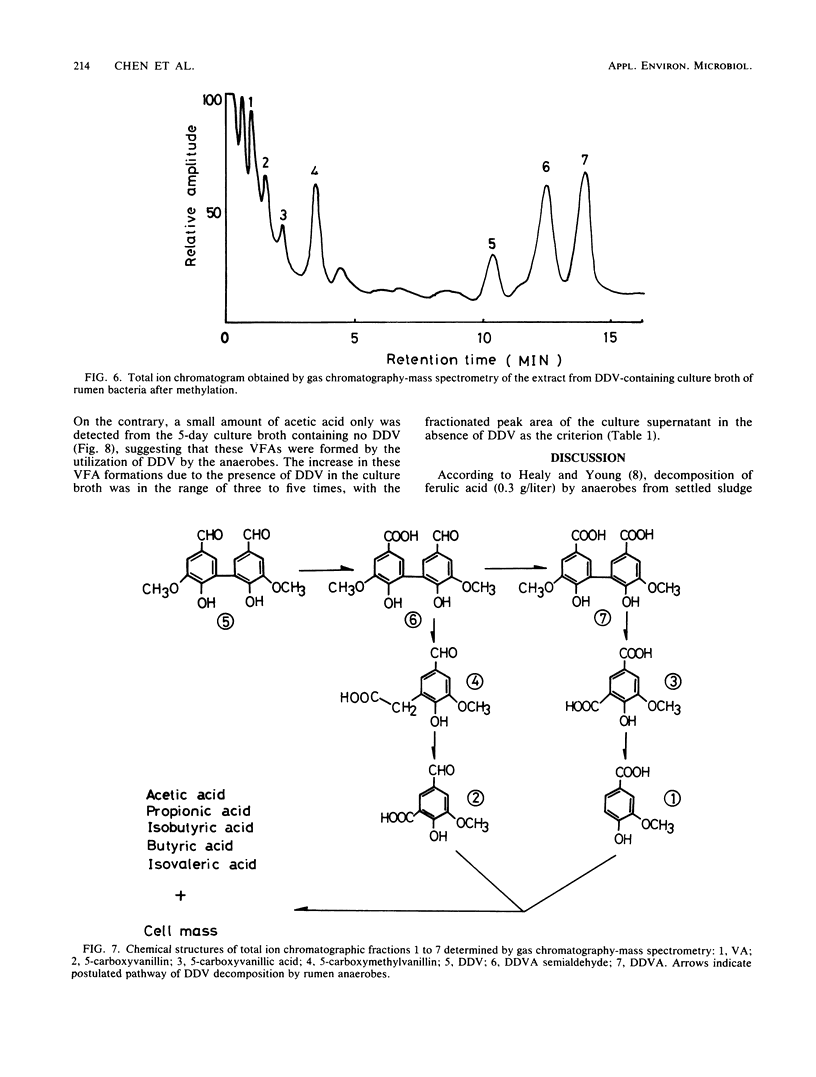
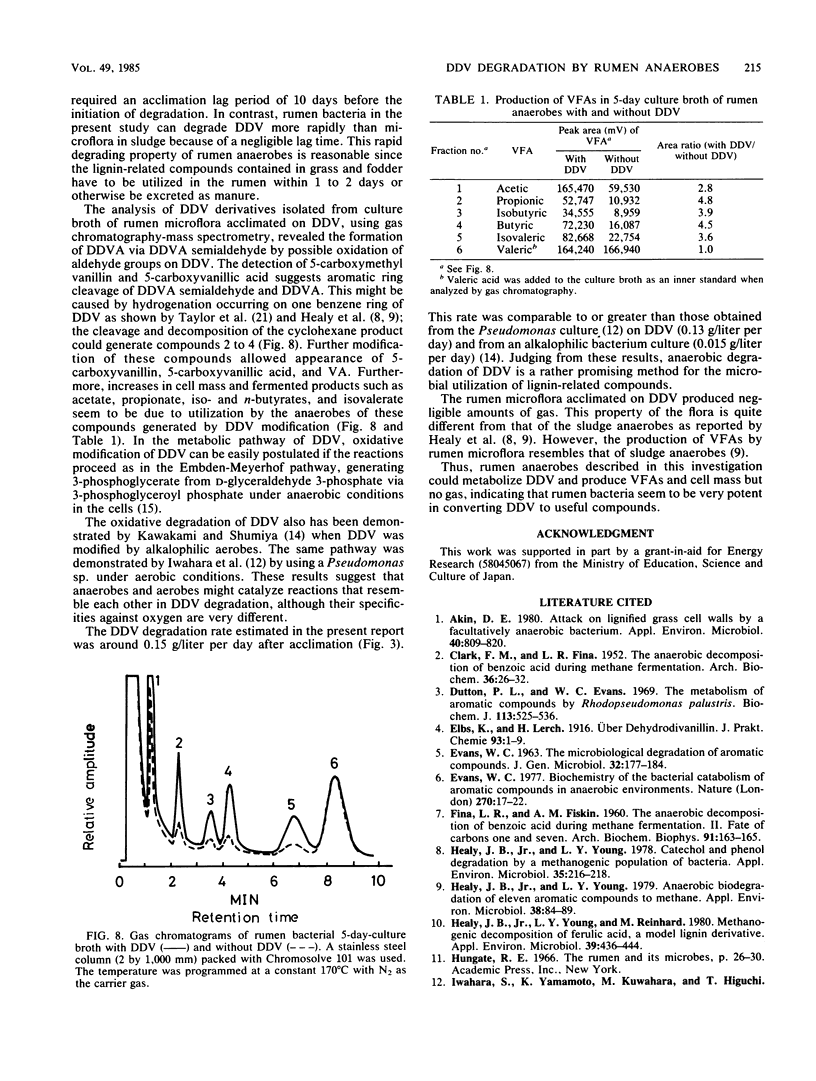
Dehydrodivanillin (DDV; 0.15 g/liter) was biodegradable at 37°C under strictly anaerobic conditions by microflora from cow rumen fluid to the extent of 25% within 2 days in a yeast extract medium. The anaerobes were acclimated on DDV for 2 weeks, leading to DDV-degrading microflora with rates of degradation eight times higher than those initially. Dehydrodivanillic acid and vanillic acid were detected in an ethylacetate extract of a DDV-enriched culture broth by thin-layer, gas, and high-performance liquid chromatographies and by mass spectrometry.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akin D. E. Attack on lignified grass cell walls by a facultatively anaerobic bacterium. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Oct;40(4):809–820. doi: 10.1128/aem.40.4.809-820.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLARK F. M., FINA L. R. The anaerobic decomposition of benzoic acid during methane fermentation. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1952 Mar;36(1):26–32. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(52)90374-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutton P. L., Evans W. C. The metabolism of aromatic compounds by Rhodopseudomonas palustris. A new, reductive, method of aromatic ring metabolism. Biochem J. 1969 Jul;113(3):525–536. doi: 10.1042/bj1130525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EVANS W. C. THE MICROBIOLOGICAL DEGRADATION OF AROMATIC COMPOUNDS. J Gen Microbiol. 1963 Aug;32:177–184. doi: 10.1099/00221287-32-2-177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans W. C. Biochemistry of the bacterial catabolism of aromatic compounds in anaerobic environments. Nature. 1977 Nov 3;270(5632):17–22. doi: 10.1038/270017a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FINA L. R., FISKIN A. M. The anaerobic decomposition of benzoic acid during methane fermentation. II. Fate of carbons one and seven. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1960 Dec;91:163–165. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(60)90483-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Healy J. B., Jr, Young L. Y. Catechol and phenol degradation by a methanogenic population of bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Jan;35(1):216–218. doi: 10.1128/aem.35.1.216-218.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Healy J. B., Young L. Y. Anaerobic biodegradation of eleven aromatic compounds to methane. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Jul;38(1):84–89. doi: 10.1128/aem.38.1.84-89.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Healy J. B., Young L. Y., Reinhard M. Methanogenic decomposition of ferulic Acid, a model lignin derivative. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Feb;39(2):436–444. doi: 10.1128/aem.39.2.436-444.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janshekar H., Fiechter A. Lignin: biosynthesis, application, and biodegradation. Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol. 1983;27:119–178. doi: 10.1007/BFb0009107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohmiya Y., Angevine L. S., Mehendale H. M. Effect of drug-induced phospholipidosis on pulmonary disposition of pneumophilic drugs. Drug Metab Dispos. 1983 Jan-Feb;11(1):25–30. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter P., Singleton A. G. The degradation of lignin and quantitative aspects of ruminant digestion. Br J Nutr. 1971 Jan;25(1):3–14. doi: 10.1079/bjn19710061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor B. F., Campbell W. L., Chinoy I. Anaerobic degradation of the benzene nucleus by a facultatively anaerobic microorganism. J Bacteriol. 1970 May;102(2):430–437. doi: 10.1128/jb.102.2.430-437.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


