Abstract
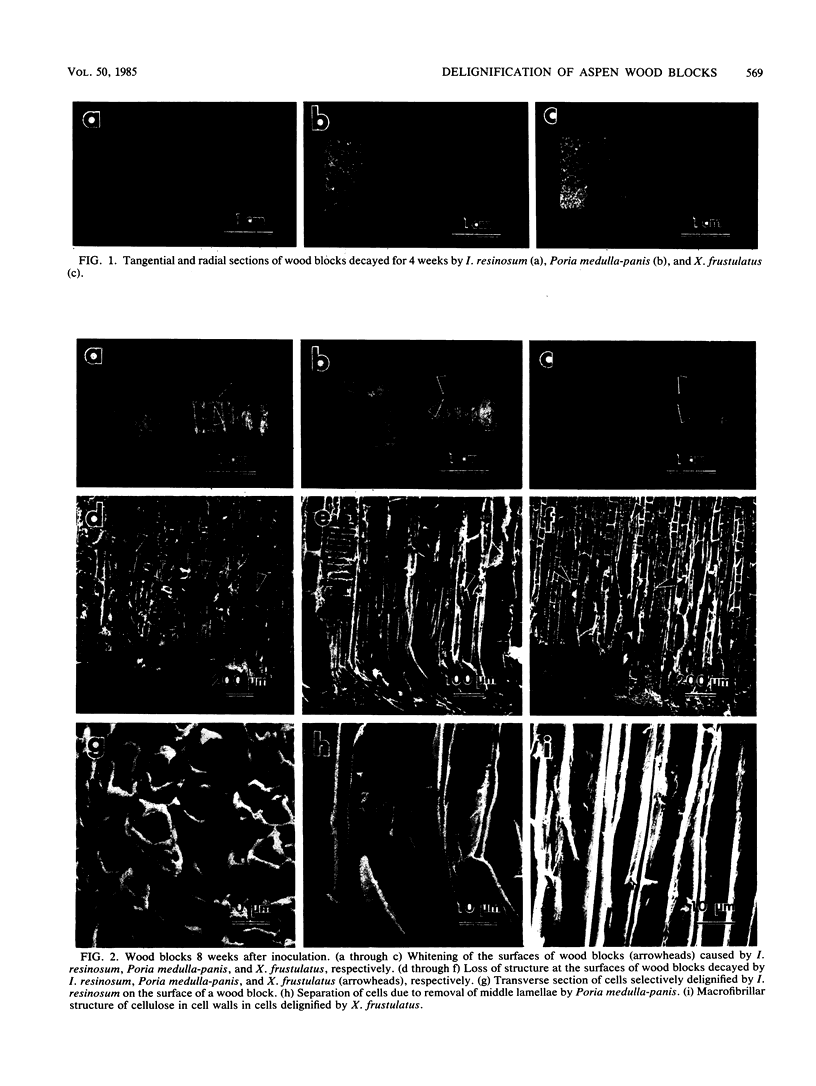
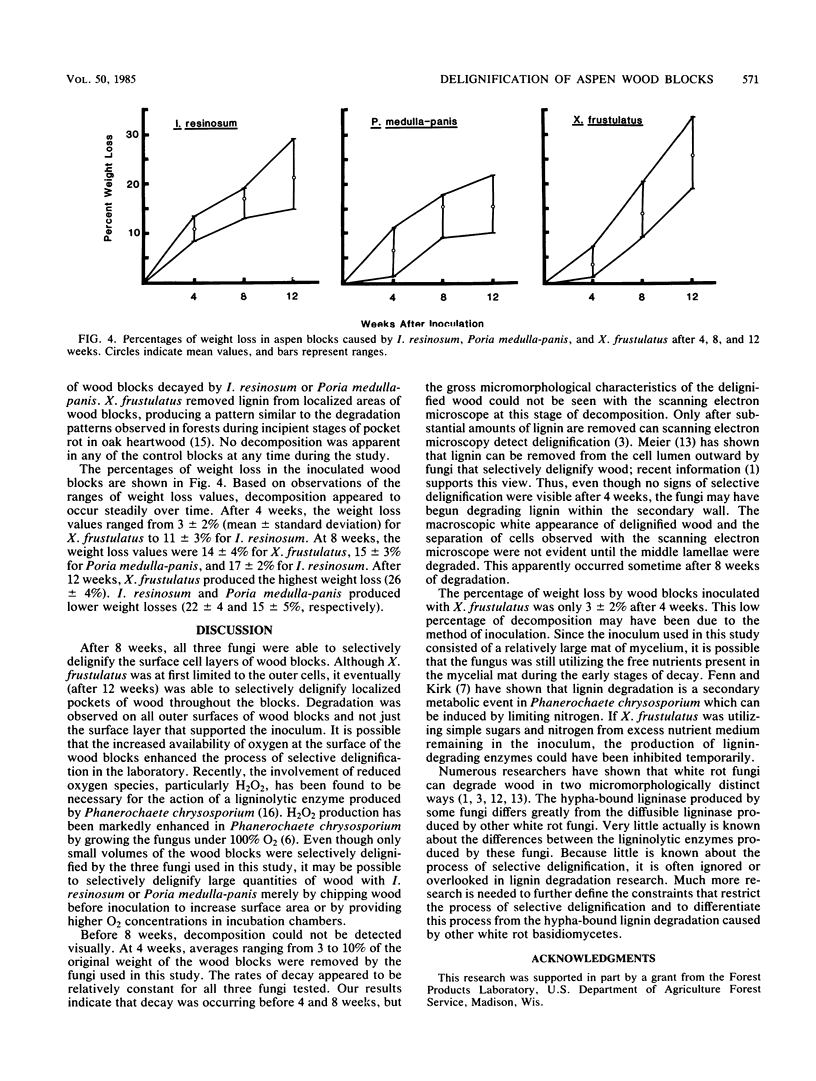
Aspen wood blocks were selectively delignified in the laboratory by Ischnoderma resinosum, Poria medulla-panis, and Xylobolus frustulatus. After 8 weeks only the outer surfaces of wood blocks were selectively delignified. The percentages of weight loss obtained after 4, 8, and 12 weeks showed that decay occurred at a relatively constant rate. Selectively delignified wood could be identified by using scanning electron microscopy only when lignin had been extensively removed from cell walls. X. frustulatus was able to form pockets of delignified wood throughout blocks after 12 weeks.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blanchette R. A. Screening wood decayed by white rot fungi for preferential lignin degradation. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Sep;48(3):647–653. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.3.647-653.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faison B. D., Kirk T. K. Relationship Between Lignin Degradation and Production of Reduced Oxygen Species by Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Nov;46(5):1140–1145. doi: 10.1128/aem.46.5.1140-1145.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otjen L., Blanchette R. A. Xylobolus frustulatus Decay of Oak: Patterns of Selective Delignification and Subsequent Cellulose Removal. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Apr;47(4):670–676. doi: 10.1128/aem.47.4.670-676.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tien M., Kirk T. K. Lignin-Degrading Enzyme from the Hymenomycete Phanerochaete chrysosporium Burds. Science. 1983 Aug 12;221(4611):661–663. doi: 10.1126/science.221.4611.661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]