Abstract
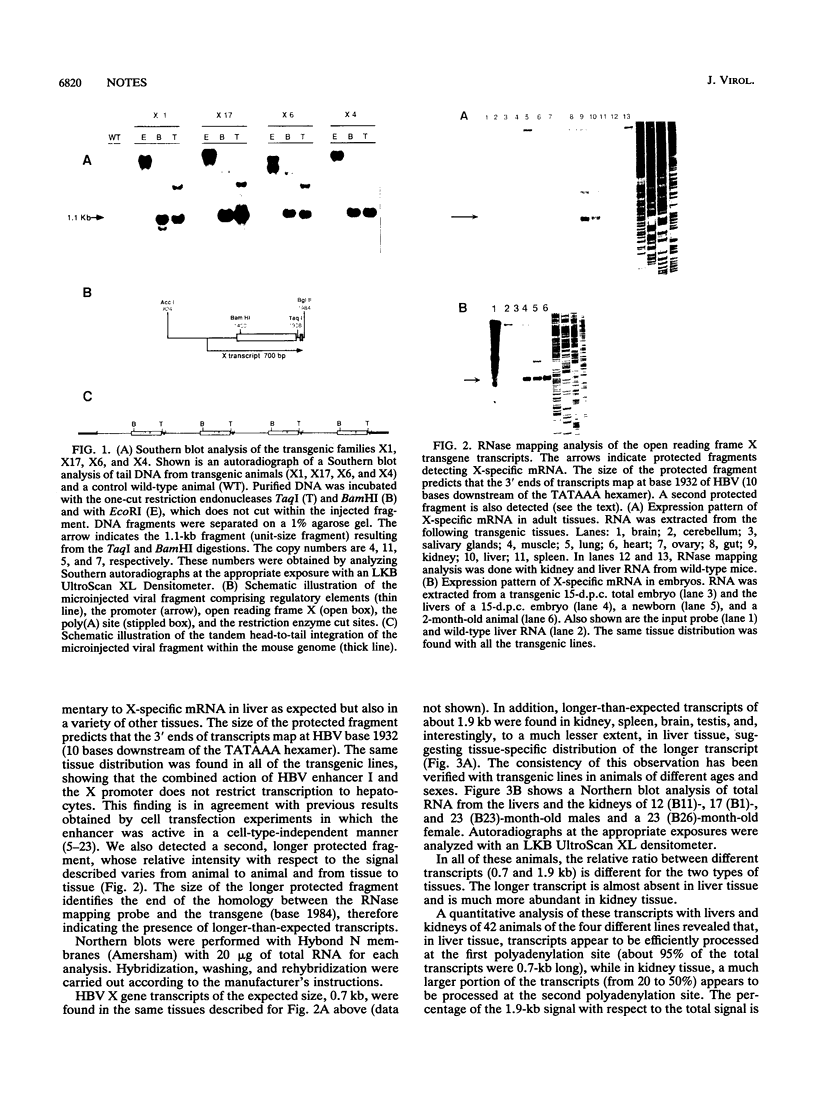
The hepatitis B virus genome contains a unique polyadenylation (TATAAA) signal which is differentially utilized in the formation of the various hepatitis B virus transcripts. A head-to-tail multiple-copy insertion of a viral fragment comprising the viral enhancer, the X promoter, the X open reading frame, and the viral poly(A) signal in transgenic mice allowed us to monitor tissue-specific differences in the expression of transcripts initiating from the X promoter. These transcripts are efficiently processed at the first polyadenylation site in the liver, while in the kidney, the brain, and the testis, a portion of the transcripts covers two copies of the transgene, since only the second polyadenylation site is properly recognized. As discussed in this article, this observation suggests a tissue-specific distribution of cellular factors involved in polyadenylation.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bartenschlager R., Junker-Niepmann M., Schaller H. The P gene product of hepatitis B virus is required as a structural component for genomic RNA encapsidation. J Virol. 1990 Nov;64(11):5324–5332. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.11.5324-5332.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown P. H., Tiley L. S., Cullen B. R. Effect of RNA secondary structure on polyadenylation site selection. Genes Dev. 1991 Jul;5(7):1277–1284. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.7.1277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang L. J., Pryciak P., Ganem D., Varmus H. E. Biosynthesis of the reverse transcriptase of hepatitis B viruses involves de novo translational initiation not ribosomal frameshifting. Nature. 1989 Jan 26;337(6205):364–368. doi: 10.1038/337364a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elfassi E. Broad specificity of the hepatitis B enhancer function. Virology. 1987 Sep;160(1):259–262. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90069-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galibert F., Mandart E., Fitoussi F., Tiollais P., Charnay P. Nucleotide sequence of the hepatitis B virus genome (subtype ayw) cloned in E. coli. Nature. 1979 Oct 25;281(5733):646–650. doi: 10.1038/281646a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganem D., Varmus H. E. The molecular biology of the hepatitis B viruses. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:651–693. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmartin G. M., Nevins J. R. An ordered pathway of assembly of components required for polyadenylation site recognition and processing. Genes Dev. 1989 Dec;3(12B):2180–2190. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.12b.2180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guo W. T., Wang J., Tam G., Yen T. S., Ou J. S. Leaky transcription termination produces larger and smaller than genome size hepatitis B virus X gene transcripts. Virology. 1991 Apr;181(2):630–636. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90896-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitt N., Briggs D., Gil A., Proudfoot N. J. Definition of an efficient synthetic poly(A) site. Genes Dev. 1989 Jul;3(7):1019–1025. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.7.1019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahé Y., Mukaida N., Kuno K., Akiyama M., Ikeda N., Matsushima K., Murakami S. Hepatitis B virus X protein transactivates human interleukin-8 gene through acting on nuclear factor kB and CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein-like cis-elements. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 25;266(21):13759–13763. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russnak R., Ganem D. Sequences 5' to the polyadenylation signal mediate differential poly(A) site use in hepatitis B viruses. Genes Dev. 1990 May;4(5):764–776. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.5.764. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeger C., Ganem D., Varmus H. E. Biochemical and genetic evidence for the hepatitis B virus replication strategy. Science. 1986 Apr 25;232(4749):477–484. doi: 10.1126/science.3961490. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seto E., Mitchell P. J., Yen T. S. Transactivation by the hepatitis B virus X protein depends on AP-2 and other transcription factors. Nature. 1990 Mar 1;344(6261):72–74. doi: 10.1038/344072a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siddiqui A., Jameel S., Mapoles J. Transcriptional control elements of hepatitis B surface antigen gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(3):566–570. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.3.566. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simonsen C. C., Levinson A. D. Analysis of processing and polyadenylation signals of the hepatitis B virus surface antigen gene by using simian virus 40-hepatitis B virus chimeric plasmids. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Dec;3(12):2250–2258. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.12.2250. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spandau D. F., Lee C. H. trans-activation of viral enhancers by the hepatitis B virus X protein. J Virol. 1988 Feb;62(2):427–434. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.2.427-434.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treinin M., Laub O. Identification of a promoter element located upstream from the hepatitis B virus X gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):545–548. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Twu J. S., Schloemer R. H. Transcription of the human beta interferon gene is inhibited by hepatitis B virus. J Virol. 1989 Jul;63(7):3065–3071. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.7.3065-3071.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vannice J. L., Levinson A. D. Properties of the human hepatitis B virus enhancer: position effects and cell-type nonspecificity. J Virol. 1988 Apr;62(4):1305–1313. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.4.1305-1313.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varmus H. Retroviruses. Science. 1988 Jun 10;240(4858):1427–1435. doi: 10.1126/science.3287617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Vegvar H. E., Lund E., Dahlberg J. E. 3' end formation of U1 snRNA precursors is coupled to transcription from snRNA promoters. Cell. 1986 Oct 24;47(2):259–266. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90448-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]