Abstract
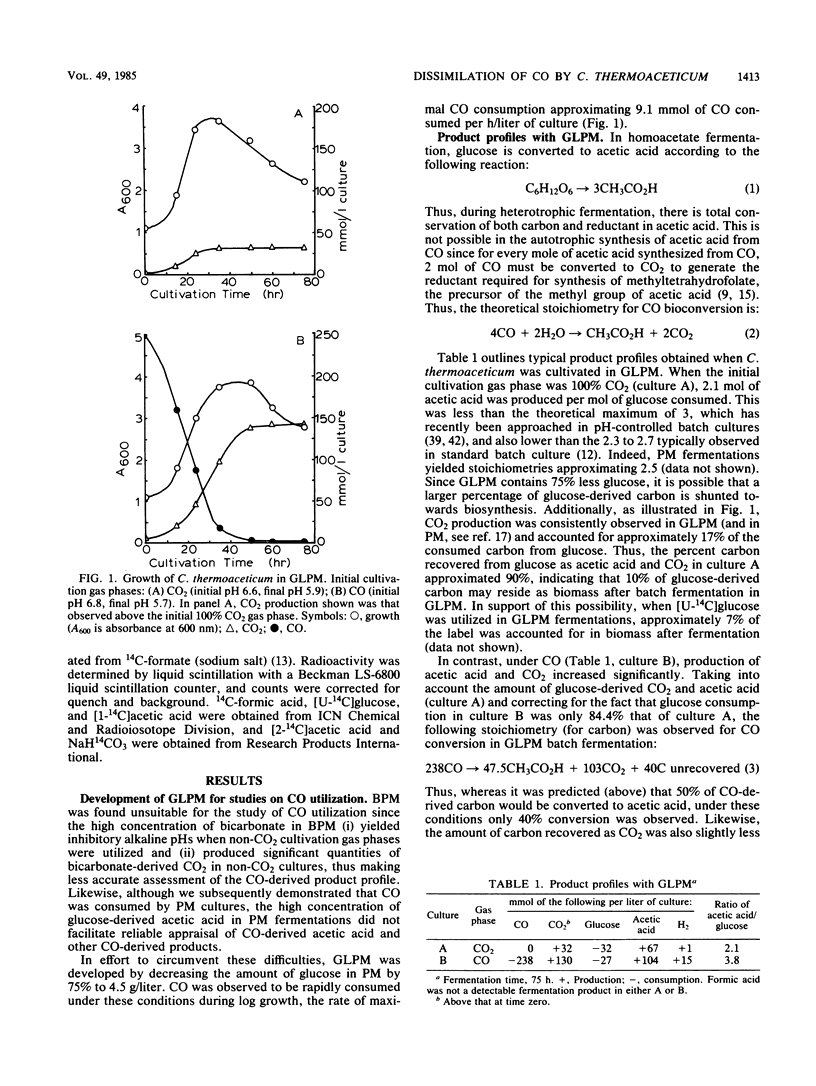
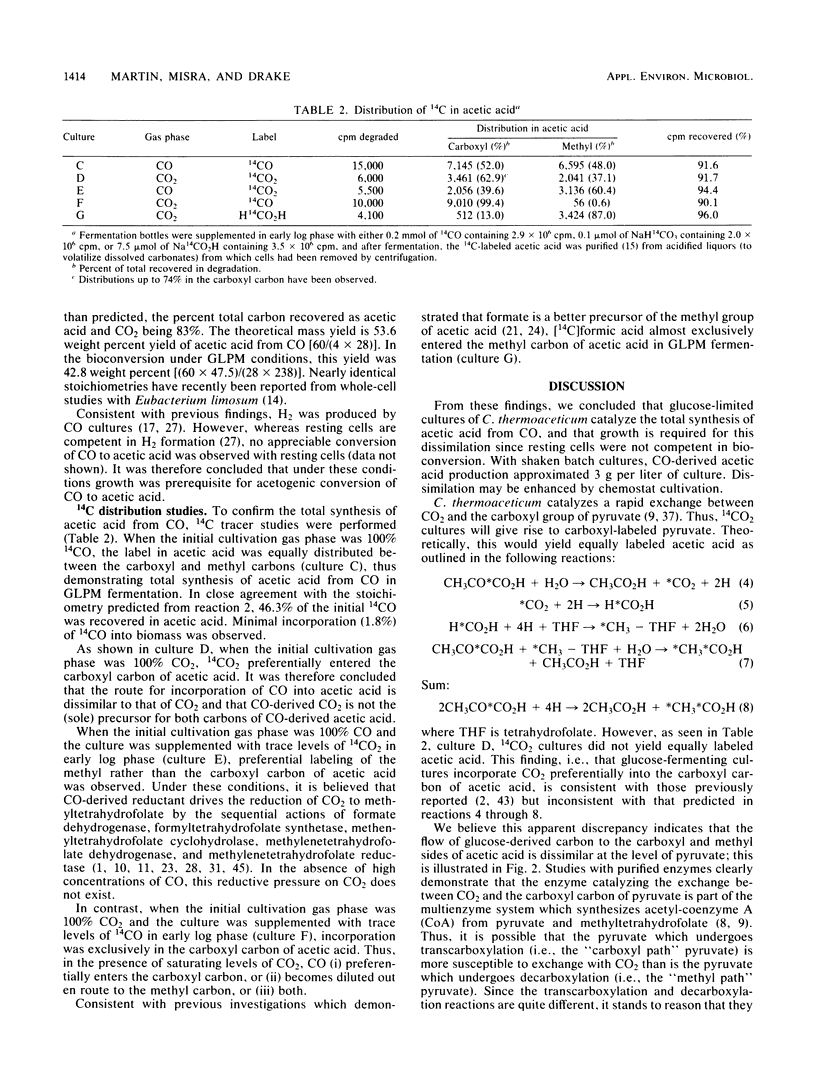
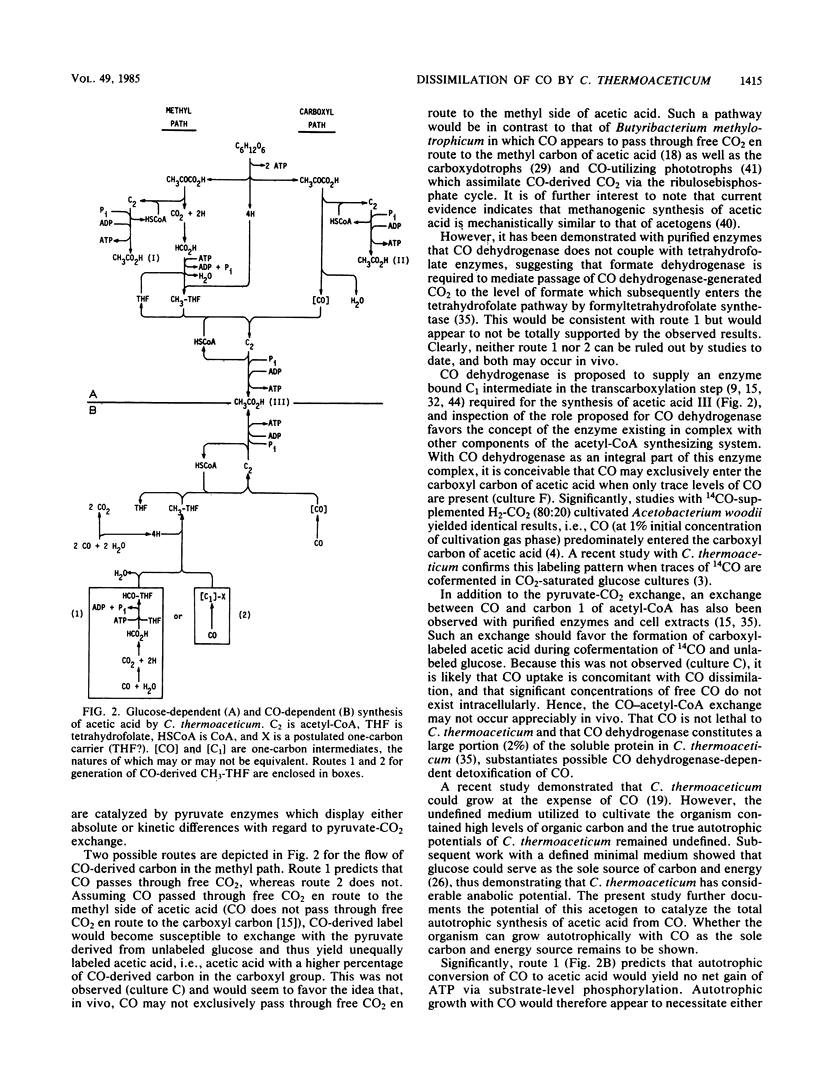
Clostridium thermoaceticum was cultivated in glucose-limited media, and the dissimilation of CO to acetic acid was evaluated. We found that cultures catalyzed the rapid dissimilation of CO to acetic acid and CO2, with the stoichiometry obtained for conversion approximating that predicted from the following reaction: 4CO + 2H2O → CH3CO2H + 2CO2. Growing cultures formed approximately 50 mmol (3 g) of CO-derived acetic acid per liter of culture, with the rate of maximal consumption approximating 9.1 mmol of CO consumed/h per liter of culture. In contrast, resting cells were found not to dissimilate CO to acetic acid. 14CO was incorporated, with equal distribution between the carboxyl and methyl carbons of acetic acid when the initial cultivation gas phase was 100% CO, whereas 14CO2 preferentially entered the carboxyl carbon when the initial gas phase was 100% CO2. Significantly, in the presence of saturating levels of CO, 14CO2 preferentially entered the methyl carbon, whereas saturating levels of CO2 yielded 14CO-derived labeling predominantly in the carboxyl carbon. These findings are discussed in relation to the path of carbon flow to acetic acid.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andreesen J. R., Schaupp A., Neurauter C., Brown A., Ljungdahl L. G. Fermentation of glucose, fructose, and xylose by Clostridium thermoaceticum: effect of metals on growth yield, enzymes, and the synthesis of acetate from CO 2 . J Bacteriol. 1973 May;114(2):743–751. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.2.743-751.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker H. A., Kamen M. D. Carbon Dioxide Utilization in the Synthesis of Acetic Acid by Clostridium Thermoaceticum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1945 Aug;31(8):219–225. doi: 10.1073/pnas.31.8.219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diekert G. B., Thauer R. K. Carbon monoxide oxidation by Clostridium thermoaceticum and Clostridium formicoaceticum. J Bacteriol. 1978 Nov;136(2):597–606. doi: 10.1128/jb.136.2.597-606.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drake H. L. Demonstration of hydrogenase in extracts of the homoacetate-fermenting bacterium Clostridium thermoaceticum. J Bacteriol. 1982 May;150(2):702–709. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.2.702-709.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drake H. L., Goss N. H., Wood H. G. A new, convenient method for the rapid analysis of inorganic pyrophosphate. Anal Biochem. 1979 Apr 1;94(1):117–120. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90800-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drake H. L., Hu S. I., Wood H. G. Purification of carbon monoxide dehydrogenase, a nickel enzyme from Clostridium thermocaceticum. J Biol Chem. 1980 Aug 10;255(15):7174–7180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drake H. L., Hu S. I., Wood H. G. Purification of five components from Clostridium thermoaceticum which catalyze synthesis of acetate from pyruvate and methyltetrahydrofolate. Properties of phosphotransacetylase. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 10;256(21):11137–11144. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durfor C. N., Wetherbee P. J., Deaton J. C., Solomon E. I. Characterization and spectroscopic properties of reduced Mo and W formate dehydrogenase from C. thermoaceticum. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Aug 30;115(1):61–67. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)90968-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott J. I., Ljungdahl L. G. Chemical modification of cysteine and tyrosine residues in formyltetrahydrofolate synthetase from Clostridium thermoaceticum. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1982 Apr 15;215(1):245–252. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(82)90301-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fontaine F. E., Peterson W. H., McCoy E., Johnson M. J., Ritter G. J. A New Type of Glucose Fermentation by Clostridium thermoaceticum. J Bacteriol. 1942 Jun;43(6):701–715. doi: 10.1128/jb.43.6.701-715.1942. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs G., Schnitker U., Thauer R. K. Carbon monoxide oxidation by growing cultures of Clostridium pasteurianum. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Nov 1;49(1):111–115. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03816.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Genthner B. R., Bryant M. P. Growth of Eubacterium limosum with Carbon Monoxide as the Energy Source. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Jan;43(1):70–74. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.1.70-74.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu S. I., Drake H. L., Wood H. G. Synthesis of acetyl coenzyme A from carbon monoxide, methyltetrahydrofolate, and coenzyme A by enzymes from Clostridium thermoaceticum. J Bacteriol. 1982 Feb;149(2):440–448. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.2.440-448.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu S. I., Pezacka E., Wood H. G. Acetate synthesis from carbon monoxide by Clostridium thermoaceticum. Purification of the corrinoid protein. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 25;259(14):8892–8897. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellum R., Drake H. L. Effects of cultivation gas phase on hydrogenase of the acetogen Clostridium thermoaceticum. J Bacteriol. 1984 Oct;160(1):466–469. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.1.466-469.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerby R., Niemczura W., Zeikus J. G. Single-carbon catabolism in acetogens: analysis of carbon flow in Acetobacterium woodii and Butyribacterium methylotrophicum by fermentation and 13C nuclear magnetic resonance measurement. J Bacteriol. 1983 Sep;155(3):1208–1218. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.3.1208-1218.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LENTZ K., WOOD H. G. Synthesis of acetate from formate and carbon dioxide by Clostridium thermoaceticum. J Biol Chem. 1955 Aug;215(2):645–654. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ljungdahl L. G. Total synthesis of acetate from CO2 by heterotrophic bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1969;23:515–538. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.23.100169.002503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundie L. L., Jr, Drake H. L. Development of a minimally defined medium for the acetogen Clostridium thermoaceticum. J Bacteriol. 1984 Aug;159(2):700–703. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.2.700-703.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer F., Elliott J. I., Sherod D., Ljungdahl L. G. Formyltetrahydrofolate synthase from Clostridium thermoaceticum. An electron microscopic study and specific interaction of the enzyme with ATP and ADP. Eur J Biochem. 1982 May 17;124(2):397–404. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer O., Schlegel H. G. Biology of aerobic carbon monoxide-oxidizing bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1983;37:277–310. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.37.100183.001425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ng T. K., Busche R. M., McDonald C. C., Hardy R. W. Production of feedstock chemicals. Science. 1983 Feb 11;219(4585):733–740. doi: 10.1126/science.219.4585.733. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien W. E., Brewer J. M., Ljungdahl L. G. Purification and characterization of thermostable 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate dehydrogenase from Clostridium thermoaceticum. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jan 25;248(2):403–408. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PHARES E. F. Degradation of labeled propionic and acetic acids. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1951 Sep;33(2):173–178. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(51)90094-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pezacka E., Wood H. G. The synthesis of acetyl-CoA by Clostridium thermoaceticum from carbon dioxide, hydrogen, coenzyme A and methyltetrahydrofolate. Arch Microbiol. 1984 Jan;137(1):63–69. doi: 10.1007/BF00425809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pruett R. L. Synthesis gas: a raw material for industrial chemicals. Science. 1981 Jan 2;211(4477):11–16. doi: 10.1126/science.211.4477.11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ragsdale S. W., Clark J. E., Ljungdahl L. G., Lundie L. L., Drake H. L. Properties of purified carbon monoxide dehydrogenase from Clostridium thermoaceticum, a nickel, iron-sulfur protein. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 25;258(4):2364–2369. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulman M., Ghambeer R. K., Ljungdahl L. G., Wood H. G. Total synthesis of acetate from CO2. VII. Evidence with Clostridium thermoaceticum that the carboxyl of acetate is derived from the carboxyl of pyruvate by transcarboxylation and not by fixation of CO2. J Biol Chem. 1973 Sep 25;248(18):6255–6261. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz R. D., Keller F. A. Acetic Acid Production by Clostridium thermoaceticum in pH-Controlled Batch Fermentations at Acidic pH. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Jun;43(6):1385–1392. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.6.1385-1392.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz R. D., Keller F. A. Isolation of a Strain of Clostridium thermoaceticum Capable of Growth and Acetic Acid Production at pH 4.5. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Jan;43(1):117–123. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.1.117-123.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uffen R. L. Metabolism of carbon monoxide by Rhodopseudomonas gelatinosa: cell growth and properties of the oxidation system. J Bacteriol. 1983 Sep;155(3):956–965. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.3.956-965.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOOD H. G. A study of carbon dioxide fixation by mass determination of the types of C13-acetate. J Biol Chem. 1952 Feb;194(2):905–931. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang G., Wang D. I. Elucidation of Growth Inhibition and Acetic Acid Production by Clostridium thermoaceticum. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Feb;47(2):294–298. doi: 10.1128/aem.47.2.294-298.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto I., Saiki T., Liu S. M., Ljungdahl L. G. Purification and properties of NADP-dependent formate dehydrogenase from Clostridium thermoaceticum, a tungsten-selenium-iron protein. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 10;258(3):1826–1832. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeikus J. G. Chemical and fuel production by anaerobic bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1980;34:423–464. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.34.100180.002231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeikus J. G. Metabolism of one-carbon compounds by chemotrophic anaerobes. Adv Microb Physiol. 1983;24:215–299. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(08)60387-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


