Abstract
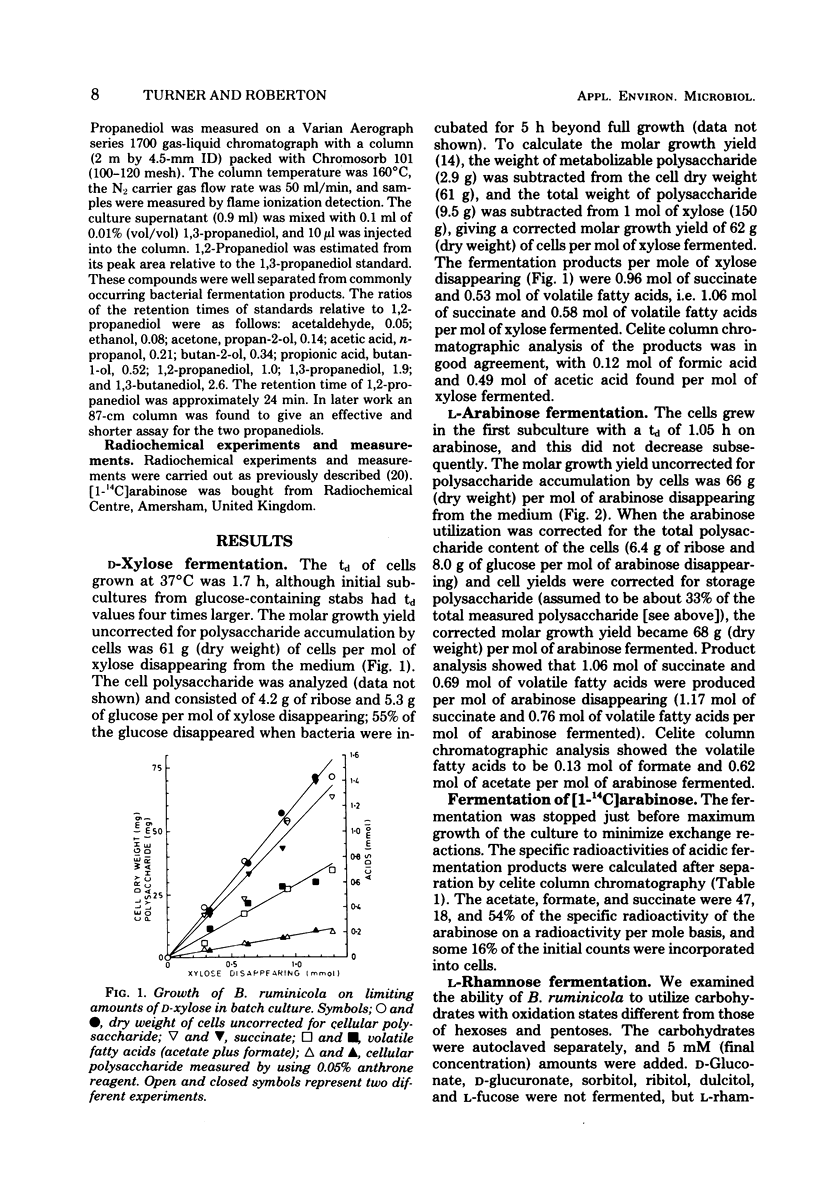
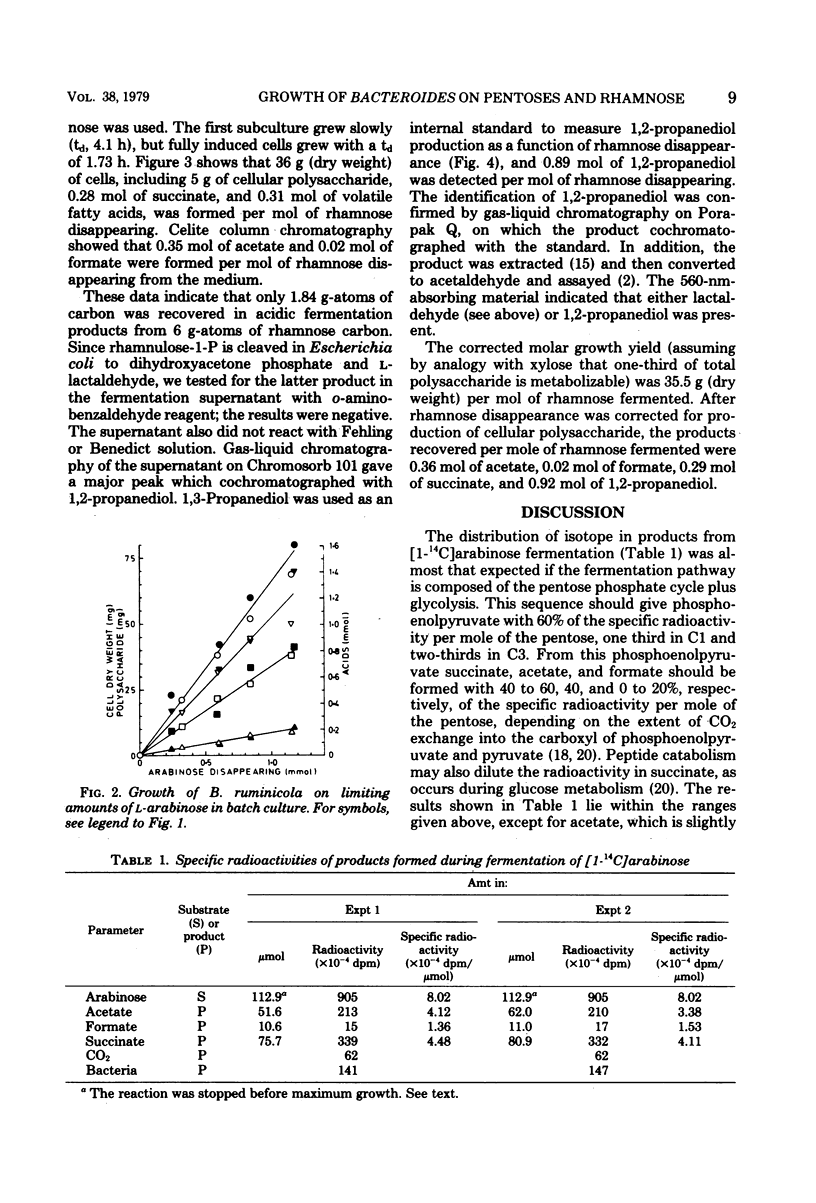
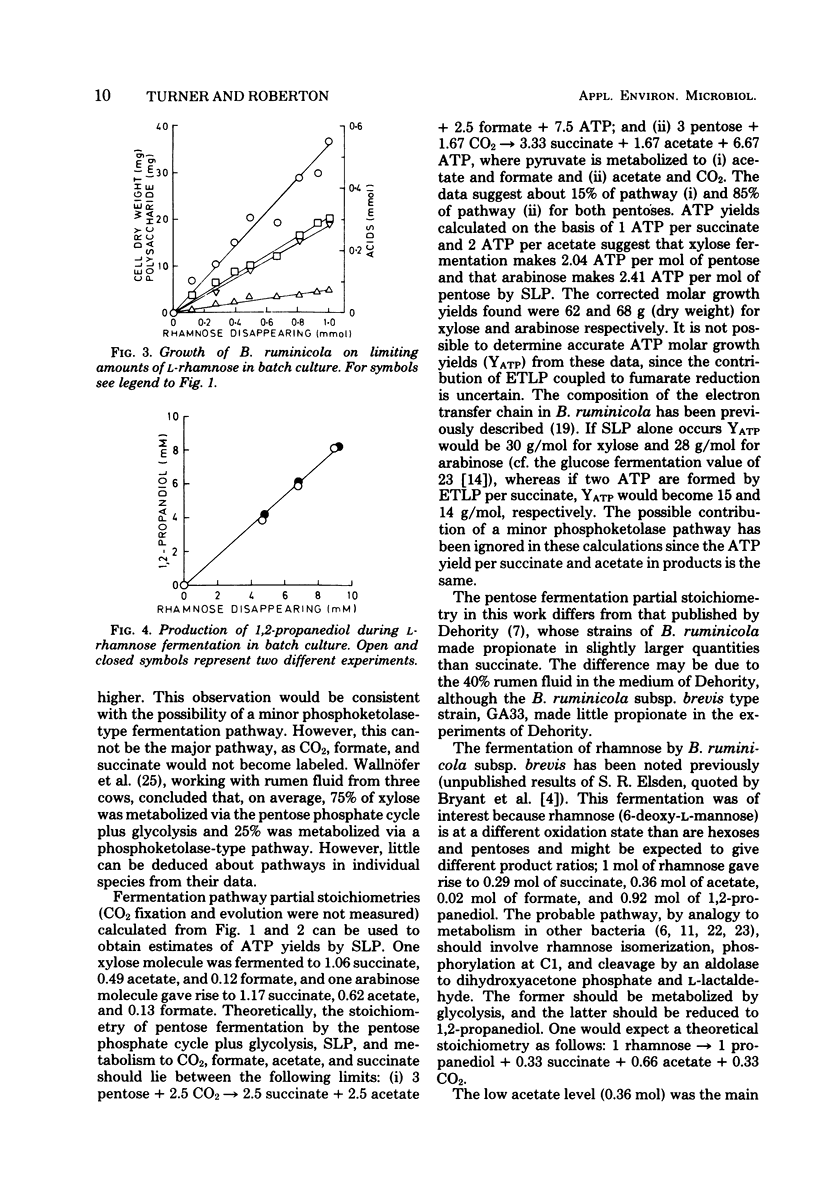
Metabolism and growth yields of Bacteroides ruminicola grown on d-xylose, l-arabinose, and l-rhamnose were studied. Growth yields were 62, 68, and 35.5 g (dry weight) per mol of carbohydrate fermented after correction for storage polysaccharide. Experiments with [1-14C]arabinose indicated that pentose was fermented by a pentose phosphate cycle plus glycolysis, with some indication of a minor phosphoketolase-type pathway. The product ratios from pentose were similar to those previously described for hexose. Rhamnose was fermented mainly to 1,2-propanediol, succinate, and acetate, although the latter was quantitatively less than expected. Estimates of adenosine 5′-triphosphate (ATP) molar growth yields could not be calculated with any certainty, as ATP generation by electron transport-linked phosphorylation cannot yet be assessed. If ATP were generated by substrate-level phosphorylation reactions alone, ATP molar growth yields for xylose, arabinose, and rhamnose would be 30, 28, and 35 g/mol. If calculations are based on an assumption that two ATP are generated by electron transport-linked phosphorylation per succinate, ATP molar growth yields become 15, 14, and 22 g/mol; if the assumption is also made that the pathway of lactaldehyde reduction is coupled to production of one ATP per 1,2-propanediol by electron transport-linked phosphorylation, the ATP molar growth yield for rhamnose fermentation becomes 14 g/mol. No preference can be expressed between these alternatives at present.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BAILEY R. W. The reaction of pentoses with anthrone. Biochem J. 1958 Apr;68(4):669–672. doi: 10.1042/bj0680669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BAUCHOP T., ELSDEN S. R. The growth of micro-organisms in relation to their energy supply. J Gen Microbiol. 1960 Dec;23:457–469. doi: 10.1099/00221287-23-3-457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRYANT M. P., SMALL N., BOUMA C., CHU H. Bacteroides ruminicola n. sp. and Succinimonas amylolytica; the new genus and species; species of succinic acid-producing anaerobic bacteria of the bovine rumen. J Bacteriol. 1958 Jul;76(1):15–23. doi: 10.1128/jb.76.1.15-23.1958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchanan B. B., Pine L. Path of glucose breakdown and cell yields of a facultative anaerobe, Actinomyces naeslundii. J Gen Microbiol. 1967 Feb;46(2):225–236. doi: 10.1099/00221287-46-2-225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czerkawski J. W., Breckenridge G. Fermentation of various glycolytic intermediates and other compounds by rumen micro-organisms, with particular reference to methane production. Br J Nutr. 1972 Jan;27(1):131–146. doi: 10.1079/bjn19720077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dehority B. A. Characterization of several bovine rumen bacteria isolated with a xylan medium. J Bacteriol. 1966 May;91(5):1724–1729. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.5.1724-1729.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dehority B. A., Grubb J. A. Basal medium for the selective enumeration of rumen bacteria utilizing specific energy sources. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Nov;32(5):703–710. doi: 10.1128/aem.32.5.703-710.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FETERIS W. A. A SERUM GLUCOSE METHOD WITHOUT PROTEIN PRECIPITATION. Am J Med Technol. 1965 Jan-Feb;31:17–21. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUGGINS C. G., MILLER O. N. A microcolorimetric method for the determination of 1, 2-propanediol phosphate. J Biol Chem. 1956 Jul;221(1):377–383. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henning P. A., van der Walt A. E. Inclusion of xylan in a medium for the enumeration of total culturable rumen bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Jun;35(6):1008–1011. doi: 10.1128/aem.35.6.1008-1011.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howlett M. R., Mountfort D. O., Turner K. W., Roberton A. M. Metabolism and growth yields in Bacteroides ruminicola strain b14. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Aug;32(2):274–283. doi: 10.1128/aem.32.2.274-283.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kröger A. Electron-transport phosphorylation coupled to fumarate reduction in anaerobically grown Proteus rettgeri. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 May 22;347(2):273–289. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(74)90051-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macy J., Probst I., Gottschalk G. Evidence for cytochrome involvement in fumarate reduction and adenosine 5'-triphosphate synthesis by Bacteroides fragilis grown in the presence of hemin. J Bacteriol. 1975 Aug;123(2):436–442. doi: 10.1128/jb.123.2.436-442.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller T. L. The pathway of formation of acetate and succinate from pyruvate by Bacteroides succinogenes. Arch Microbiol. 1978 May 30;117(2):145–152. doi: 10.1007/BF00402302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mountfort D. O., Roberton A. M. Origins of fermentation products formed during growth of Bacteroides ruminicola on glucose. J Gen Microbiol. 1978 Jun;106(2):353–360. doi: 10.1099/00221287-106-2-353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pirt S. J. The maintenance energy of bacteria in growing cultures. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1965 Oct 12;163(991):224–231. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1965.0069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAWADA H., TAKAGI Y. THE METABOLISM OF L-RHAMNOSE IN ESCHERICHIA COLI. 3. L-RHAMULOSE-PHOSPHATE ALDOLASE. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Oct 23;92:26–32. doi: 10.1016/0926-6569(64)90265-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stouthamer A. H. A theoretical study on the amount of ATP required for synthesis of microbial cell material. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1973;39(3):545–565. doi: 10.1007/BF02578899. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallnöfer P., Baldwin R. L., Stagno E. Conversion of C-labeled substrates to volatile Fatty acids by the rumen microbiota. Appl Microbiol. 1966 Nov;14(6):1004–1010. doi: 10.1128/am.14.6.1004-1010.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Vries W., van Wyck-Kapteyn W. M., Stouthamer A. H. Generation of ATP during cytochrome-linked anaerobic electron transport in propionic acid bacteria. J Gen Microbiol. 1973 May;76(1):31–41. doi: 10.1099/00221287-76-1-31. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


