Abstract
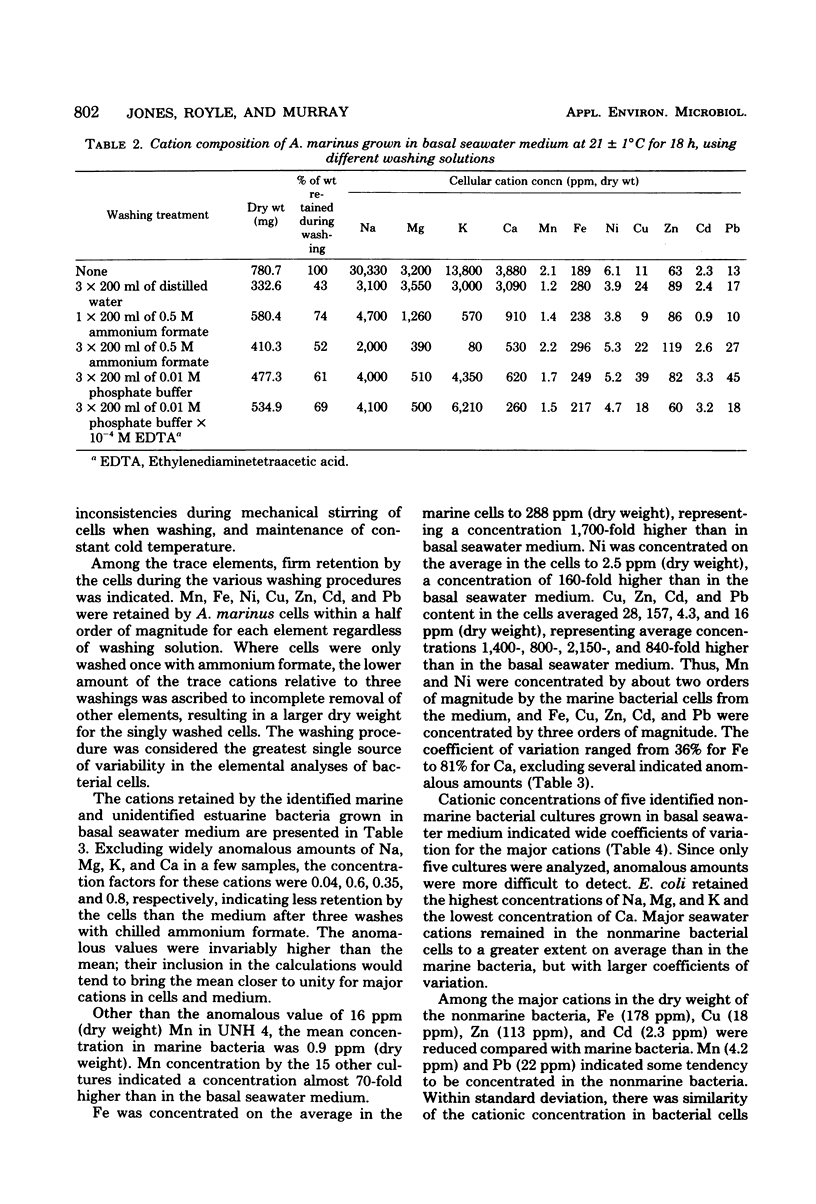
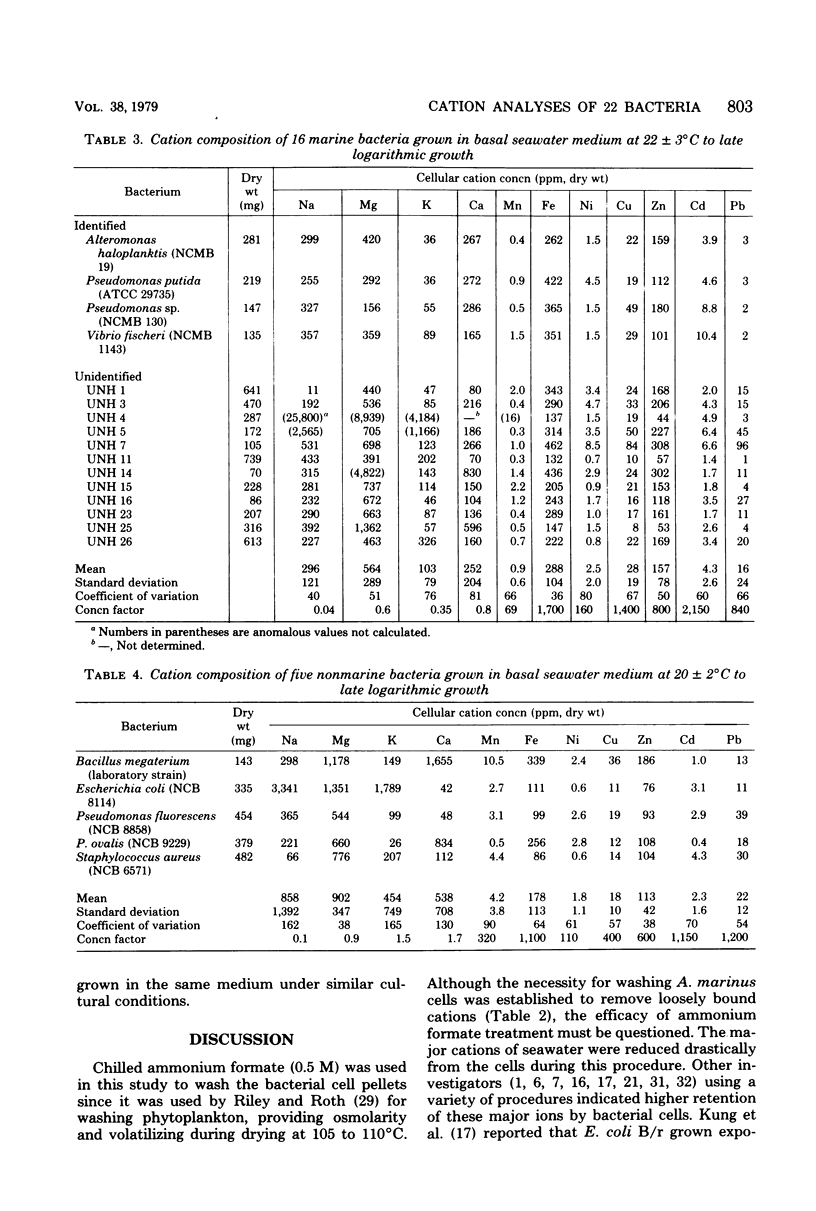
Twenty-two species of bacteria of marine, estuarine, and terrestrial origin were analyzed for cationic content by atomic absorption spectrophotometry after growth in a basal seawater medium. Alcaligenes marinus was analyzed from eight separate but replicate determinations yielding the following cationic concentrations: Na, 5,600 +/- 2,260; Mg 1,580 +/- 740; K, 700 +/- 360; Ca, 790 +/- 390; Mn, 1.7 +/- 0.5; Fe, 256 +/- 57; Ni, 1.7 +/- 0.7; Cu, 14 +/- 4; Zn, 122 +/- 27; Cd, 2.8 +/- 0.7; and Pb, 10 +/- 3 ppm/(dry weight). Washing A. marinus cells before analyses was necessary due to interstitial medium within the cell pellets after centrifugation and loose cationic retention by the cells. The principal source of error in the procedure was ascribed to variability due to washing cells with 0.5 M ammonium formate. The mean cationic concentrations for trace elements in the 22 bacterial cultures grown in the basal seawater medium to constant optical density and washed three times with 0.5 M ammonium formate were: Mn, 2.4 +/- 3.8; Fe, 262 +/- 112; Ni, 2.3 +/- 1.8; Cu, 24 +/- 17; Zn, 146 +/- 72; Cd, 3.8 +/- 2.5; and Pb, 17 +/- 21 ppm (dry weight). Major ions were concentrated only occasionally by the cells after washing, whereas Mn, Fe, Ni, Cu, Zn, Cd, and Pb were concentrated from the medium by the following factors on the average: 180, 1,600, 140, 1,200, 750, 1,900, and 900, respectively.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beveridge T. J., Murray R. G. Uptake and retention of metals by cell walls of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1976 Sep;127(3):1502–1518. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.3.1502-1518.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COLWELL R. R., MANDEL M. BASE COMPOSITION OF DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACID OF MARINE AND NONMARINE VIBRIOS DEDUCED FROM BUOYANT-DENSITY MEASUREMENTS IN CESIUM CHLORIDE. J Bacteriol. 1964 Dec;88:1816–1817. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.6.1816-1817.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COLWELL R. R., MORITA R. Y. REISOLATION AND EMENDATION OF DESCRIPTION OF VIBRIO MARINUS (RUSSELL) FORD. J Bacteriol. 1964 Oct;88:831–837. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.4.831-837.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cobet A. B., Wirsen C., Jr, Jones G. E. The effect of nickel on a marine bacterium, Arthrobacter marinus sp.nov. J Gen Microbiol. 1970 Aug;62(2):159–169. doi: 10.1099/00221287-62-2-159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curran H. R., Brunstetter B. C., Myers A. T. Spectrochemical Analysis of Vegetative Cells and Spores of Bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1943 May;45(5):485–494. doi: 10.1128/jb.45.5.485-494.1943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jernelöv A., Martin A. L. Ecological implications of metal metabolism by microorganisms. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1975;29:61–77. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.29.100175.000425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kung F. C., Raymond J., Glaser D. A. Metal ion content of Escherichia coli versus cell age. J Bacteriol. 1976 Jun;126(3):1089–1095. doi: 10.1128/jb.126.3.1089-1095.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lusk J. E., Williams R. J., Kennedy E. P. Magnesium and the growth of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1968 May 25;243(10):2618–2624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACLEOD R. A., ONOFREY E., NORRIS M. E. Nutrition and metabolism of marine bacteria. I. Survey of nutritional requirements. J Bacteriol. 1954 Dec;68(6):680–686. doi: 10.1128/jb.68.6.680-686.1954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEYLAND M., DUNKEL P., SCHADE A. L. The uptake of cobalt by Proteus vulgaris. J Gen Microbiol. 1952 Nov;7(3-4):409–416. doi: 10.1099/00221287-7-3-4-409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlman D. Microbial production of metal-organic compounds and complexes. Adv Appl Microbiol. 1965;7:103–138. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2164(08)70385-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROUF M. A. SPECTROCHEMICAL ANALYSIS OF INORGANIC ELEMENTS IN BACTERIA. J Bacteriol. 1964 Dec;88:1545–1549. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.6.1545-1549.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saxena J., Howard P. H. Environmental transformation of alkylated and inorganic forms of certain metals. Adv Appl Microbiol. 1977;21:185–226. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2164(08)70042-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skriabin G. K., Starovoitov I. I., Borisoglebskaia A. N., Borodin A. M. Okislenie naftalina shtammom Pseduomonas putida, nesushchim mutantnuiu plazmidu. Mikrobiologiia. 1978 Mar-Apr;47(2):273–277. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers A. O., Silver S. Microbial transformations of metals. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1978;32:637–672. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.32.100178.003225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAKACS F. P., MATULA T. I., MACLEOD R. A. NUTRITION AND METABOLISM OF MARINE BACTERIA. XIII. INTRACELLULAR CONCENTRATIONS OF SODIUM AND POTASSIUM IONS IN A MARINE PSEUDOMONAD. J Bacteriol. 1964 Mar;87:510–518. doi: 10.1128/jb.87.3.510-518.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tornabene T. G., Edwards H. W. Microbial uptake of lead. Science. 1972 Jun 23;176(4041):1334–1335. doi: 10.1126/science.176.4041.1334. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


