Abstract
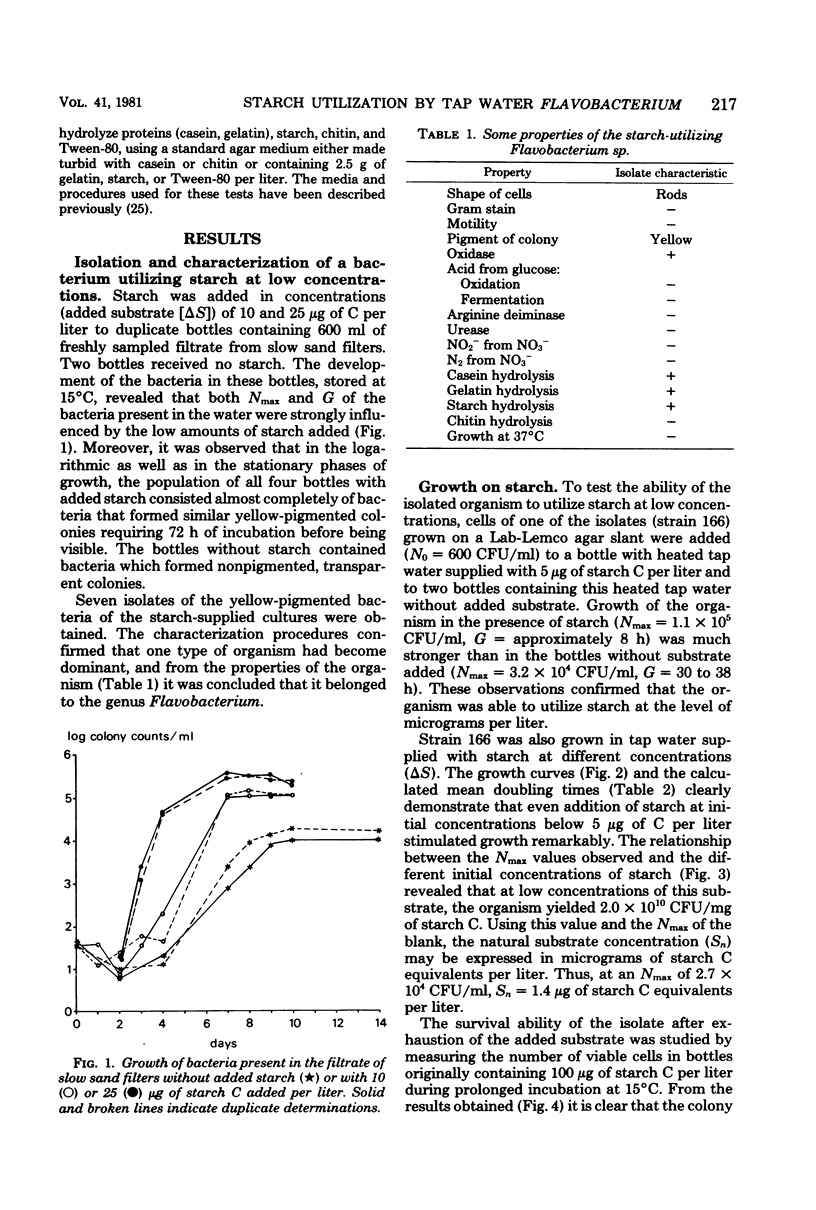
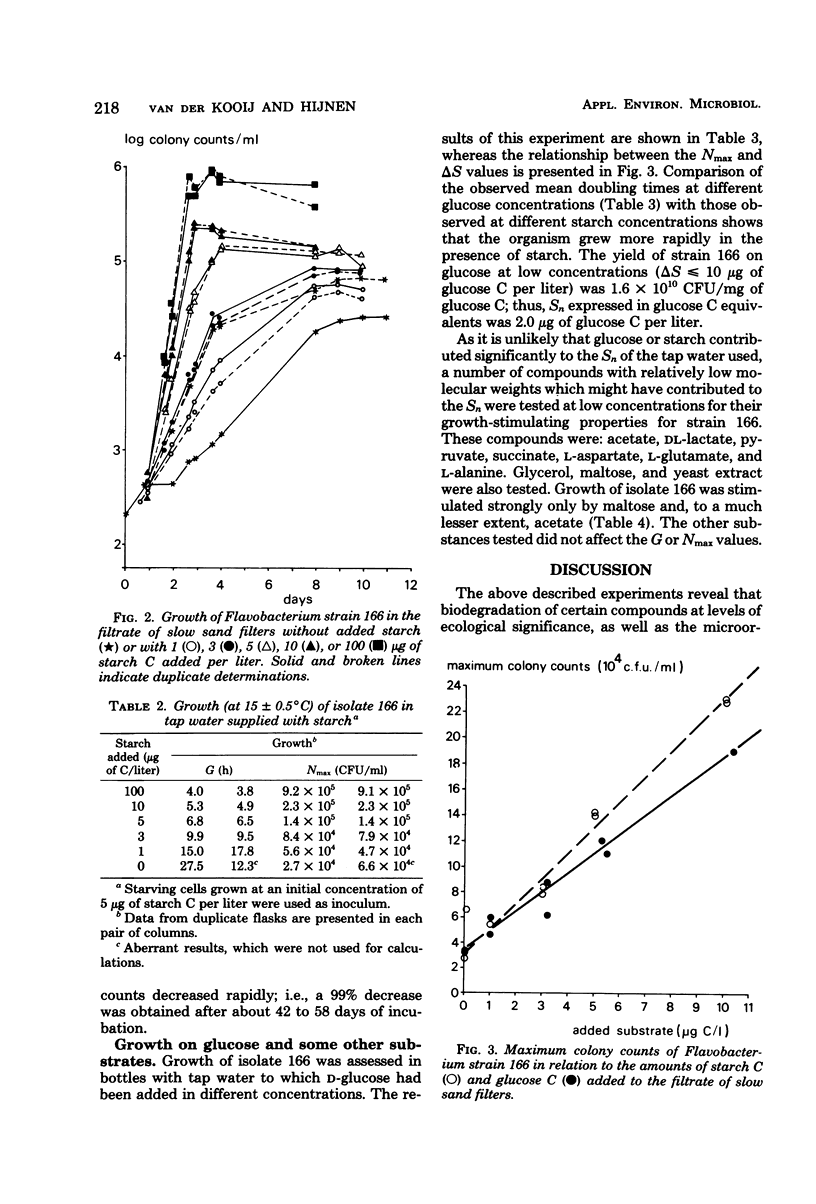
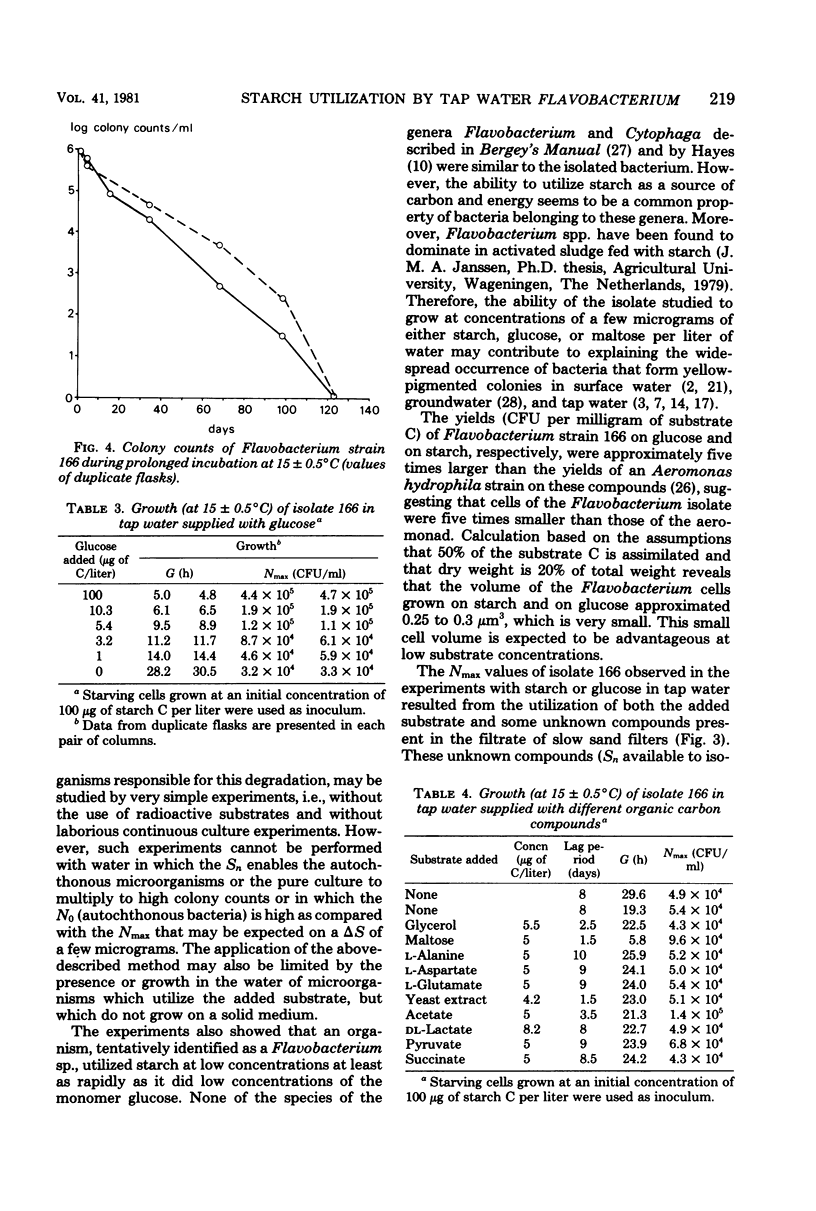
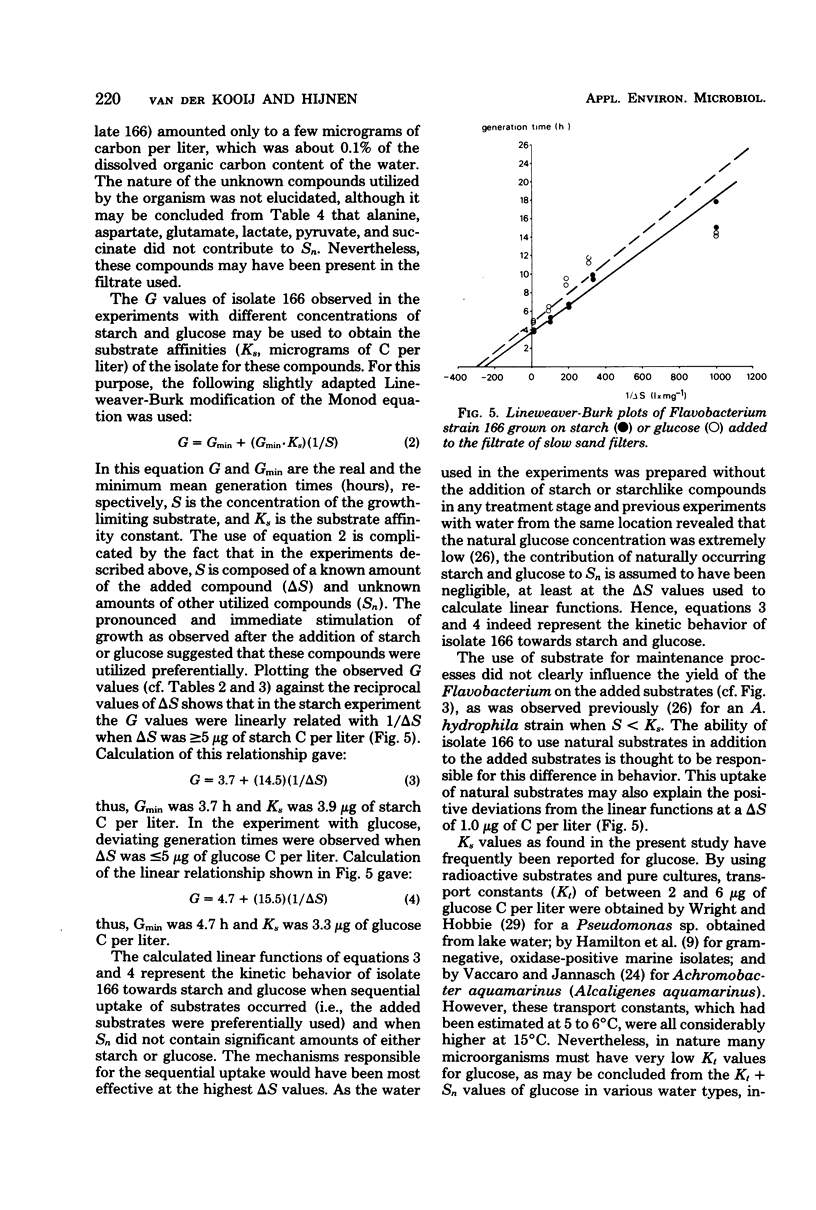
Experiments in well-cleaned glass flasks revealed that addition of starch in concentrations of 10 and 25 μg of substrate C per liter to the filtrate of slow sand filters stimulated the development of a yellow-pigmented bacterium which was identified as a Flavobacterium species. The isolate was able to multiply in tap water without substrates added, but addition of starch and glucose in amounts as low as 1 μg of substrate C per liter clearly enhanced growth. The substrate affinities of the Flavobacterium for these compounds were 3.9 μg of starch C and 3.3 μg of glucose C per liter. The results of this study indicate that microorganisms which rapidly utilize starch at a level of a few micrograms per liter commonly occur in water.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boethling R. S., Alexander M. Effect of concentration of organic chemicals on their biodegradation by natural microbial communities. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Jun;37(6):1211–1216. doi: 10.1128/aem.37.6.1211-1216.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnison B. K., Morita R. Y. Heterotrophic potential for amino acid uptake in a naturally eutrophic lake. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Mar;27(3):488–495. doi: 10.1128/am.27.3.488-495.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geesey G. G., Morita R. Y. Capture of arginine at low concentrations by a marine psychrophilic bacterium. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Dec;38(6):1092–1097. doi: 10.1128/aem.38.6.1092-1097.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths R. P., Hanus F. J., Morita R. Y. The effects of various water-sample treatments on the apparent uptake of glutamic acid by natural marine microbial populations. Can J Microbiol. 1974 Sep;20(9):1261–1266. doi: 10.1139/m74-194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUGH R., LEIFSON E. The taxonomic significance of fermentative versus oxidative metabolism of carbohydrates by various gram negative bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1953 Jul;66(1):24–26. doi: 10.1128/jb.66.1.24-26.1953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton R. D., Morgan K. M., Strickland J. D. The glucose uptake kinetics of some marine bacteria. Can J Microbiol. 1966 Oct;12(5):995–1003. doi: 10.1139/m66-134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOVACS N. Identification of Pseudomonas pyocyanea by the oxidase reaction. Nature. 1956 Sep 29;178(4535):703–703. doi: 10.1038/178703a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morita R. Y. Psychrophilic bacteria. Bacteriol Rev. 1975 Jun;39(2):144–167. doi: 10.1128/br.39.2.144-167.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanier R. Y., Palleroni N. J., Doudoroff M. The aerobic pseudomonads: a taxonomic study. J Gen Microbiol. 1966 May;43(2):159–271. doi: 10.1099/00221287-43-2-159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart D. J. The urease activity of fluorescent pseudomonads. J Gen Microbiol. 1965 Nov;41(2):169–174. doi: 10.1099/00221287-41-2-169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Kooij D. The occurrence of Pseudomonas spp. in surface water and in tap water as determined on citrate media. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1977;43(2):187–197. doi: 10.1007/BF00395673. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Kooij D., Visser A., Hijnen W. A. Growth of Aeromonas hydrophila at Low Concentrations of Substrates Added to Tap Water. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Jun;39(6):1198–1204. doi: 10.1128/aem.39.6.1198-1204.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


