Abstract
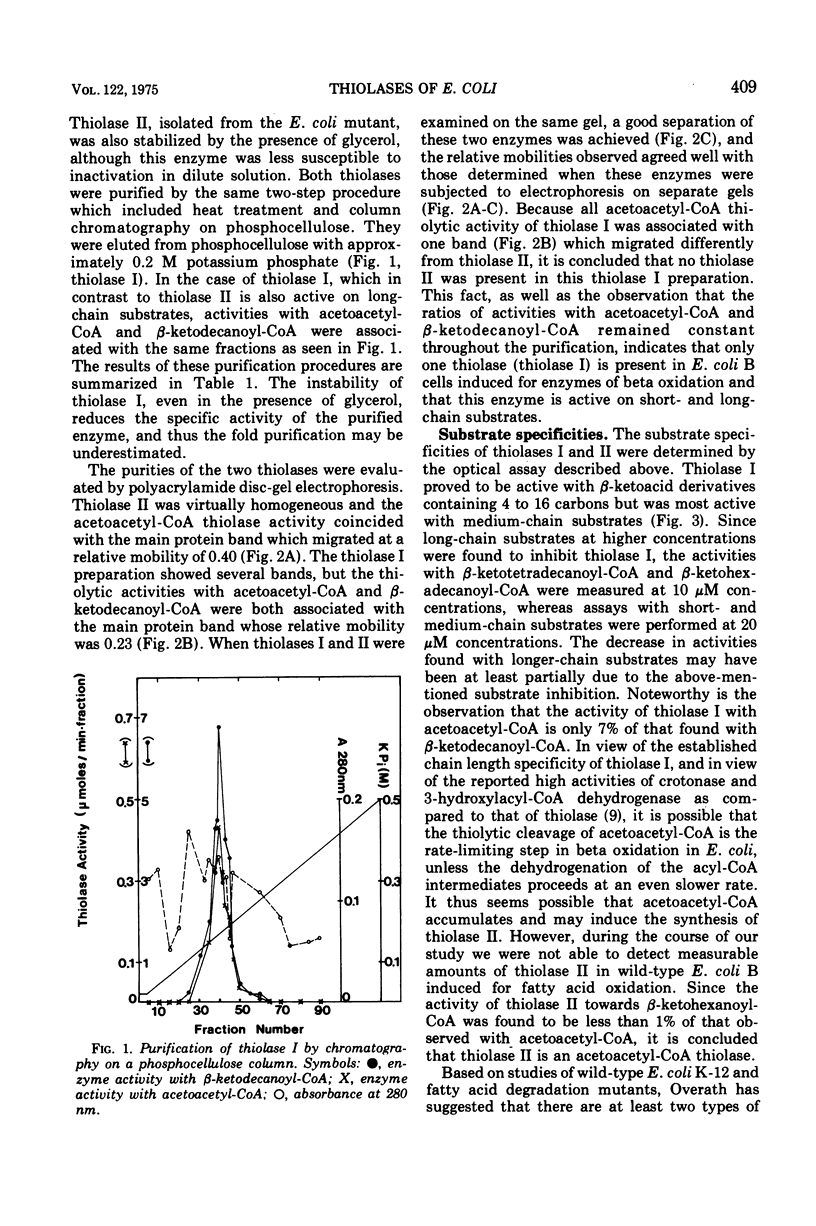
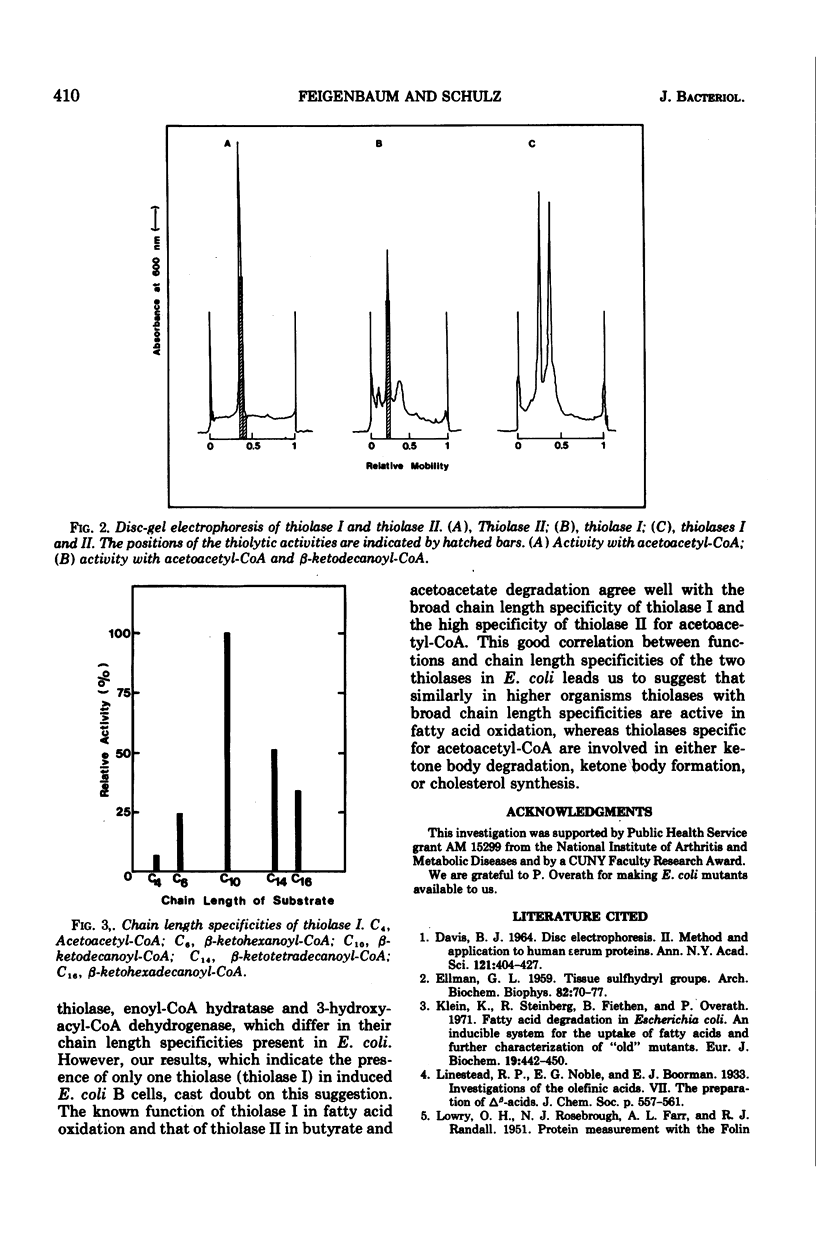
The presence of only one thiolase (EC 2.3.1.9) in wild-type Escherichia coli induced for enzymes of beta oxidation was demonstrated. A different thiolase was shown to be present in a mutant constitutive for the enzymes of butyrate degradation. The two thiolases were purified to near homogeneity by a simple two-step procedure and were found to be associated with different proteins as shown by gel electrophoresis. The thiolase isolated from induced wild-type Escherichia coli cell was active on beta-ketoacyl-coenzyme A derivatives containing 4 to 16 carbons, but exhibited optimal activity with medium-chain substrates. In contrast, the thiolase isolated from the constitutive mutant was shown to be specific for acetoacetyl-coenzyme A.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELLMAN G. L. Tissue sulfhydryl groups. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1959 May;82(1):70–77. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(59)90090-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein K., Steinberg R., Fiethen B., Overath P. Fatty acid degradation in Escherichia coli. An inducible system for the uptake of fatty acids and further characterization of old mutants. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Apr;19(3):442–450. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01334.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazzei Y., Negrel R., Ailhaud G. Purification and some properties of thiolase from Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Oct 14;220(1):129–131. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(70)90238-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Middleton B. The existence of ketoacyl-CoA thiolases of differing properties and intracellular localization in ox liver. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Jan 31;46(2):508–515. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(72)80168-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Middleton B. The oxoacyl-coenzyme A thiolases of animal tissues. Biochem J. 1973 Apr;132(4):717–730. doi: 10.1042/bj1320717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Overath P., Pauli G., Schairer H. U. Fatty acid degradation in Escherichia coli. An inducible acyl-CoA synthetase, the mapping of old-mutations, and the isolation of regulatory mutants. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Feb;7(4):559–574. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Overath P., Raufuss E. M. The induction of the enzymes of fatty acid degradation in Escherichia coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1967 Oct 11;29(1):28–33. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(67)90535-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pauli G., Overath P. ato Operon: a highly inducible system for acetoacetate and butyrate degradation in Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Sep 25;29(3):553–562. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb02021.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STERN J. R., DEL CAMPILLO A., RAW I. Enzymes of fatty acid metabolism. I. General introduction; crystalline crotonase. J Biol Chem. 1956 Feb;218(2):971–983. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulz H. Long chain enoyl coenzyme A hydratase from pig heart. J Biol Chem. 1974 May 10;249(9):2704–2709. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seubert W., Lamberts I., Kramer R., Ohly B. On the mechanism of malonyl-CoA-independent fatty acid synthesis. I. The mechanism of elongation of long-chain fatty acids by acetyl-CoA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Dec 18;164(3):498–517. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(68)90180-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeks G., Shapiro M., Burns R. O., Wakil S. J. Control of fatty acid metabolism. I. Induction of the enzymes of fatty acid oxidation in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1969 Feb;97(2):827–836. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.2.827-836.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


