Abstract
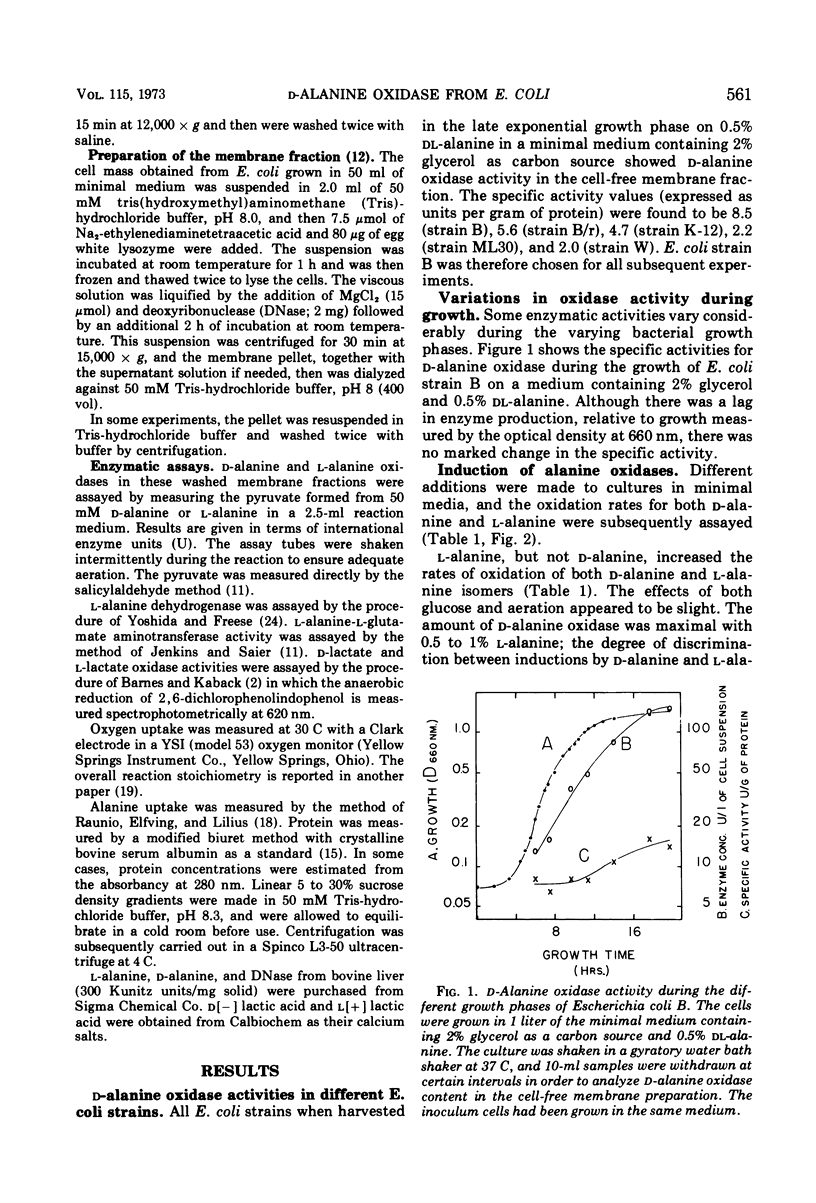
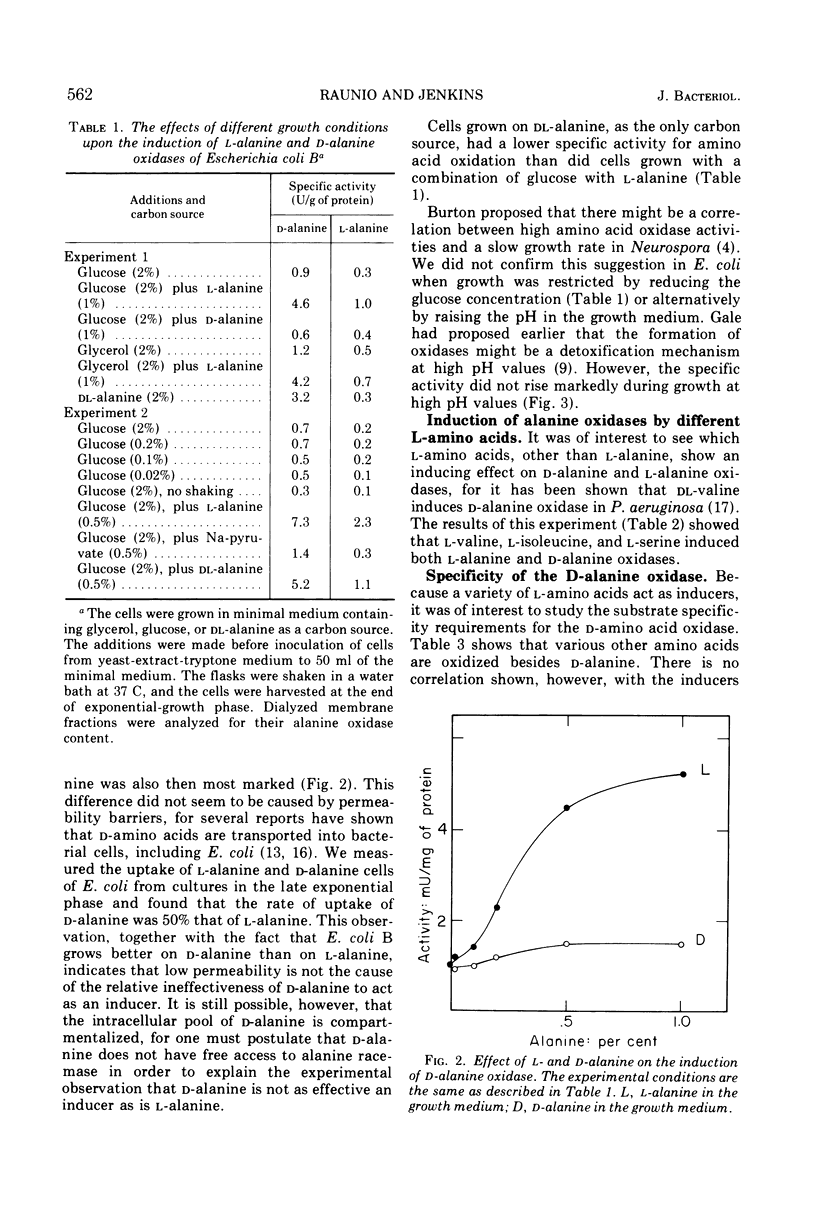
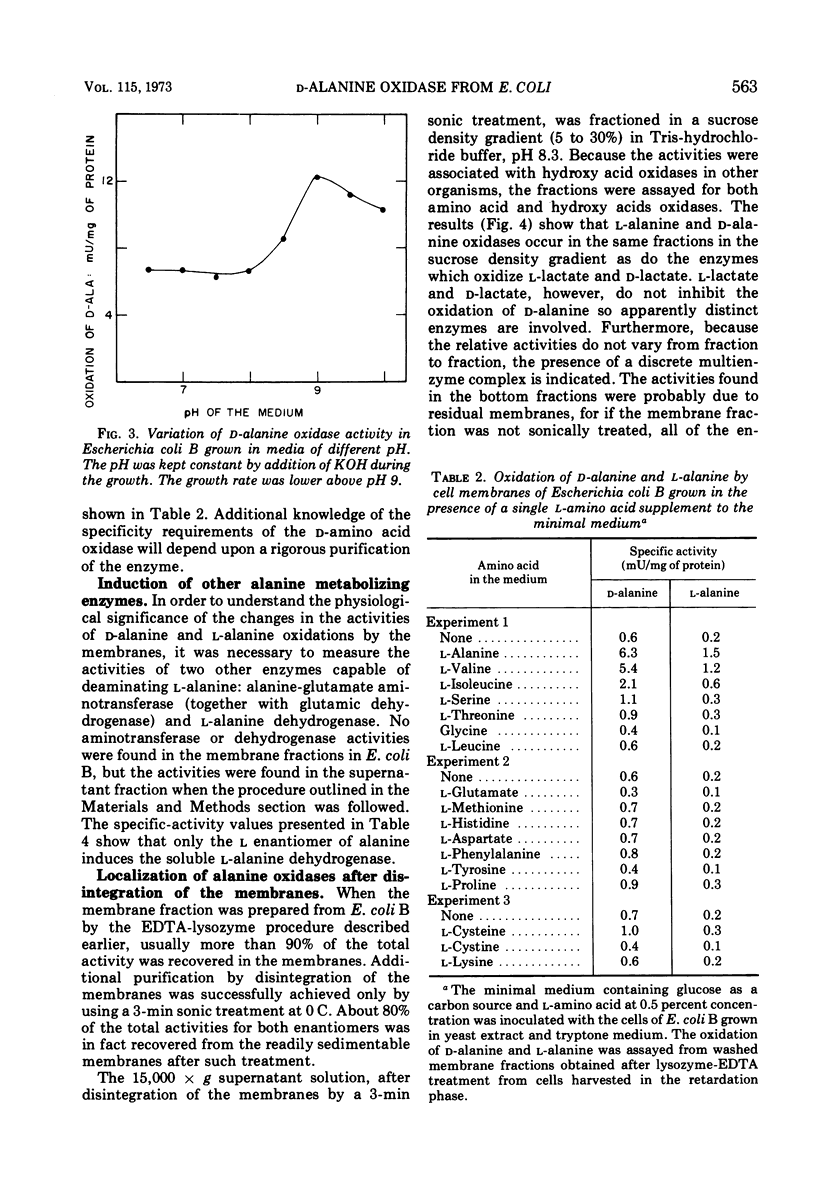
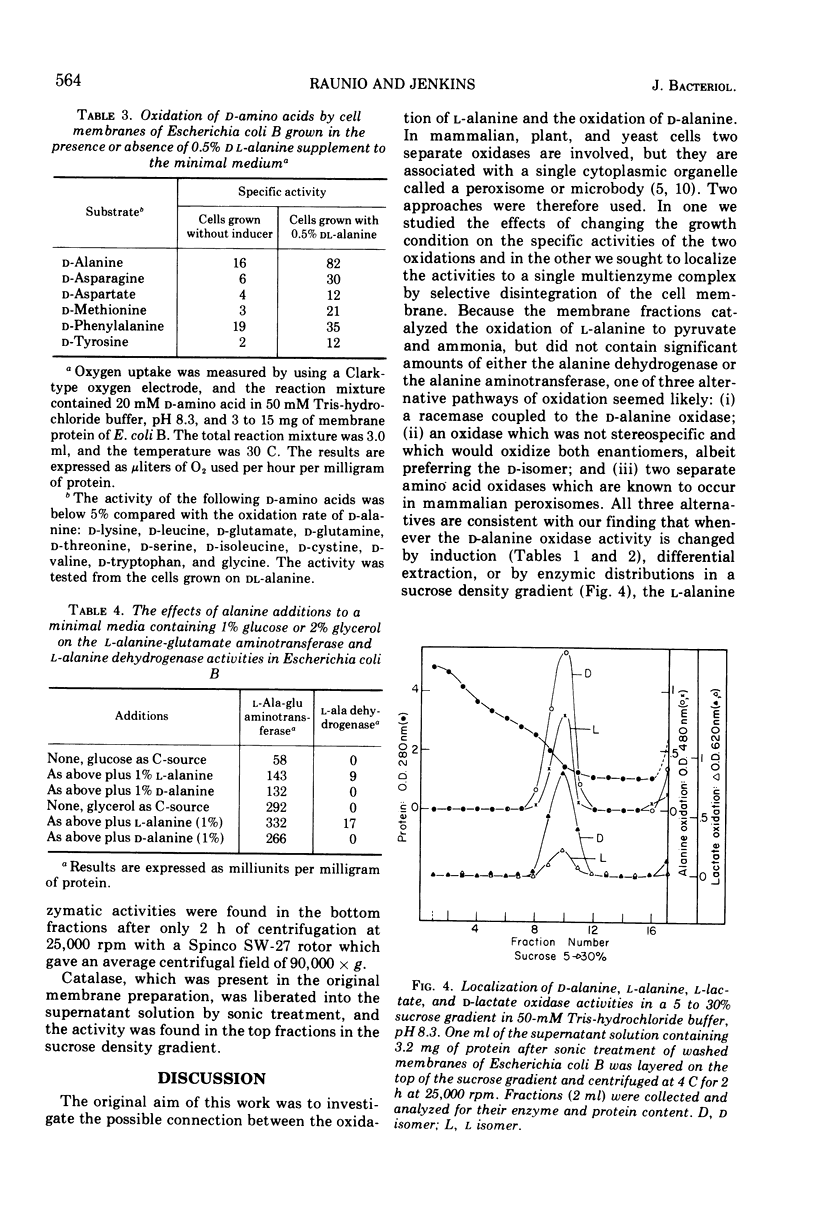
Dialyzed membranes of Escherichia coli prepared by an ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid-lysozyme method catalyze the oxidation of both l-alanine and d-alanine. The specific activities for the oxidations of both d-alanine and l-alanine are increased fivefold when the cells are grown in the presence of either l-alanine or dl-alanine, but are increased only slightly when grown in the presence of d-alanine. In the dl-alanine-induced system, the specific activities for the oxidations of some other d-amino acids are also raised. dl-alanine also induces two other alanine catabolizing enzymes, alanine dehydrogenase and alanine-glutamate aminotransferase which are found in the “soluble” fraction of lysozyme-treated cells. The oxidations of both l-alanine and d-alanine were associated with the membranes of induced cells. After the membranes were disintegrated by sonic treatment, both l-alanine and d-alanine oxidation catalysts sedimented in a sucrose density gradient together with d-lactate and l-lactate dehydrogenases, apparently as a single multienzyme complex.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ADELBERG E. A., UMBARGER H. E. Isoleucine and valine metabolism in Escherichia coli. V. alpha-Ketoisovaleric acid accumulation. J Biol Chem. 1953 Nov;205(1):475–482. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURTON K. The L-amino-acid oxidase of Neurospora. Biochem J. 1951 Dec;50(2):258–268. doi: 10.1042/bj0500258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes E. M., Jr, Kaback H. R. Mechanisms of active transport in isolated membrane vesicles. I. The site of energy coupling between D-lactic dehydrogenase and beta-galactoside transport in Escherichia coli membrane vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1971 Sep 10;246(17):5518–5522. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berberich R., Kaback M., Freese E. D-amino acids as inducers of L-alanine dehydrogenase in Bacillus subtilis. J Biol Chem. 1968 Mar 10;243(5):1006–1011. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DE LEY J., DOCHY R. Intermittent ultrasonic disruption and localisation of enzymes in acetic acid bacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1960 Aug 26;42:538–541. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(60)90837-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DE LEY J., DOCHY R. On the localisation of oxidase systems in Acetobacter cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1960 May 20;40:277–289. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(60)91352-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DE LEY J., SCHEL J. Studies on the metabolism of Acetobacter peroxydans. II. The enzymic mechanism of lactate metabolism. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1959 Sep;35:154–165. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(59)90344-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Duve C., Baudhuin P. Peroxisomes (microbodies and related particles). Physiol Rev. 1966 Apr;46(2):323–357. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1966.46.2.323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert M. P., Neuhaus F. C. Factors affecting the level of alanine racemase in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1972 Mar;109(3):1156–1161. doi: 10.1128/jb.109.3.1156-1161.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCGILVERY R. W., MOKRASCH L. C. Purification and properties of fructose-1, 6-diphosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1956 Aug;221(2):909–917. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NORTON J. E., BULMER G. S., SOKATCH J. R. THE OXIDATION OF D-ALANINE BY CELL MEMBRANES OF PSEUDOMONAS AERUGINOSA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Oct 8;78:136–147. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)91619-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUDMAN D., MEISTER A. Transamination in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1953 Feb;200(2):591–604. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raunio R. P., Straus L. D., Jenkins W. T. D-alanine oxidase from Escherichia coli: participation in the oxidation of L-alanine. J Bacteriol. 1973 Aug;115(2):567–573. doi: 10.1128/jb.115.2.567-573.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosso G., Takashima K., Adams E. Coenzyme content of purified alanine racemase from Pseudomonas. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 Jan 6;34(1):134–140. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90539-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephenson M., Gale E. F. Factors influencing bacterial deamination: The deamination of glycine, dl-alanine and l-glutamic acid by Bacterium coli. Biochem J. 1937 Aug;31(8):1316–1322.1. doi: 10.1042/bj0311316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


