Abstract
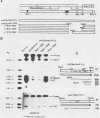
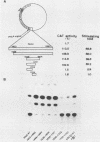
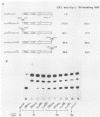
Previous studies have identified an enhancer (enhancer I) at nucleotides (nt) 1074 to 1234 in the genome of the human hepatitis B virus (HBV), which locates immediately upstream from the X gene. By analysis of the expression of the chloramphenicol acetyltransferase gene driven by a heterologous simian virus 40 early promoter, we describe the identification of a second enhancer (enhancer II) at nt 1636 to 1741, which locates downstream of enhancer I and immediately upstream of the core gene. With various deletions at the 5' end of enhancer II, a positive regulatory element was identified at nt 1636 to 1690 (the II-A element), with the 5' boundary between nt 1636 and 1671. The II-A element alone did not have an enhancer function, but the enhancer activity was achieved by the concomitant presence of the sequence from nt 1704 to 1741 (the II-B element). The II-B element alone did not have enhancer activity. These results indicate that cooperation between the II-A and II-B elements is required to exhibit the enhancer activity of enhancer II. We also show that enhancer II stimulates the transcriptional activity of both the SPI and SPII promoters of the surface gene. Therefore, the SPI promoter activity is regulated by the proximal HNF-1 binding element and the distal enhancers I and II. These results indicate that multiple regulatory elements scattered over the whole viral genome are involved in the regulation of expression of each individual HBV gene and that the same regulatory element controls the expression of different HBV genes. The relative positions of these regulatory elements in the HBV genome suggest that they may control the expression of HBV genes in a coordinate and cooperative manner.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aden D. P., Fogel A., Plotkin S., Damjanov I., Knowles B. B. Controlled synthesis of HBsAg in a differentiated human liver carcinoma-derived cell line. Nature. 1979 Dec 6;282(5739):615–616. doi: 10.1038/282615a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Agre P., Johnson P. F., McKnight S. L. Cognate DNA binding specificity retained after leucine zipper exchange between GCN4 and C/EBP. Science. 1989 Nov 17;246(4932):922–926. doi: 10.1126/science.2530632. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Antonucci T. K., Rutter W. J. Hepatitis B virus (HBV) promoters are regulated by the HBV enhancer in a tissue-specific manner. J Virol. 1989 Feb;63(2):579–583. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.2.579-583.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Araki K., Miyazaki J., Hino O., Tomita N., Chisaka O., Matsubara K., Yamamura K. Expression and replication of hepatitis B virus genome in transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(1):207–211. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.1.207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beasley R. P., Hwang L. Y., Lin C. C., Chien C. S. Hepatocellular carcinoma and hepatitis B virus. A prospective study of 22 707 men in Taiwan. Lancet. 1981 Nov 21;2(8256):1129–1133. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)90585-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cattaneo R., Will H., Hernandez N., Schaller H. Signals regulating hepatitis B surface antigen transcription. Nature. 1983 Sep 22;305(5932):336–338. doi: 10.1038/305336a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cattaneo R., Will H., Schaller H. Hepatitis B virus transcription in the infected liver. EMBO J. 1984 Sep;3(9):2191–2196. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02113.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C., Lin Y., O-Lee T. W., Chou C. K., Lee T. S., Liu T. J., P'eng F. K., Chen T. Y., Hu C. P. Induction of plasma protein secretion in a newly established human hepatoma cell line. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Jun;3(6):1133–1137. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.6.1133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang H. K., Chou C. K., Chang C., Su T. S., Hu C., Yoshida M., Ting L. P. The enhancer sequence of human hepatitis B virus can enhance the activity of its surface gene promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Mar 11;15(5):2261–2268. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.5.2261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang H. K., Ting L. P. The surface gene promoter of the human hepatitis B virus displays a preference for differentiated hepatocytes. Virology. 1989 May;170(1):176–183. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90364-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang H. K., Wang B. Y., Yuh C. H., Wei C. L., Ting L. P. A liver-specific nuclear factor interacts with the promoter region of the large surface protein gene of human hepatitis B virus. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):5189–5197. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.5189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De-Medina T., Faktor O., Shaul Y. The S promoter of hepatitis B virus is regulated by positive and negative elements. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jun;8(6):2449–2455. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.6.2449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elfassi E., Romet-Lemonne J. L., Essex M., Frances-McLane M., Haseltine W. A. Evidence of extrachromosomal forms of hepatitis B viral DNA in a bone marrow culture obtained from a patient recently infected with hepatitis B virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(11):3526–3528. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.11.3526. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farza H., Hadchouel M., Scotto J., Tiollais P., Babinet C., Pourcel C. Replication and gene expression of hepatitis B virus in a transgenic mouse that contains the complete viral genome. J Virol. 1988 Nov;62(11):4144–4152. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.11.4144-4152.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feuerman M. H., Godbout R., Ingram R. S., Tilghman S. M. Tissue-specific transcription of the mouse alpha-fetoprotein gene promoter is dependent on HNF-1. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Oct;9(10):4204–4212. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.10.4204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman A. D., Landschulz W. H., McKnight S. L. CCAAT/enhancer binding protein activates the promoter of the serum albumin gene in cultured hepatoma cells. Genes Dev. 1989 Sep;3(9):1314–1322. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.9.1314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fromental C., Kanno M., Nomiyama H., Chambon P. Cooperativity and hierarchical levels of functional organization in the SV40 enhancer. Cell. 1988 Sep 23;54(7):943–953. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90109-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galibert F., Chen T. N., Mandart E. Nucleotide sequence of a cloned woodchuck hepatitis virus genome: comparison with the hepatitis B virus sequence. J Virol. 1982 Jan;41(1):51–65. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.1.51-65.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godbout R., Ingram R. S., Tilghman S. M. Fine-structure mapping of the three mouse alpha-fetoprotein gene enhancers. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Mar;8(3):1169–1178. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.3.1169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heermann K. H., Goldmann U., Schwartz W., Seyffarth T., Baumgarten H., Gerlich W. H. Large surface proteins of hepatitis B virus containing the pre-s sequence. J Virol. 1984 Nov;52(2):396–402. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.2.396-402.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herr W., Clarke J. The SV40 enhancer is composed of multiple functional elements that can compensate for one another. Cell. 1986 May 9;45(3):461–470. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90332-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honigwachs J., Faktor O., Dikstein R., Shaul Y., Laub O. Liver-specific expression of hepatitis B virus is determined by the combined action of the core gene promoter and the enhancer. J Virol. 1989 Feb;63(2):919–924. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.2.919-924.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P. F., Landschulz W. H., Graves B. J., McKnight S. L. Identification of a rat liver nuclear protein that binds to the enhancer core element of three animal viruses. Genes Dev. 1987 Apr;1(2):133–146. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.2.133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones N. C., Rigby P. W., Ziff E. B. Trans-acting protein factors and the regulation of eukaryotic transcription: lessons from studies on DNA tumor viruses. Genes Dev. 1988 Mar;2(3):267–281. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.3.267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karpen S., Banerjee R., Zelent A., Price P., Acs G. Identification of protein-binding sites in the hepatitis B virus enhancer and core promoter domains. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;8(12):5159–5165. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.12.5159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malpièce Y., Michel M. L., Carloni G., Revel M., Tiollais P., Weissenbach J. The gene S promoter of hepatitis B virus confers constitutive gene expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jul 11;11(13):4645–4654. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.13.4645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer K. B., Neuberger M. S. The immunoglobulin kappa locus contains a second, stronger B-cell-specific enhancer which is located downstream of the constant region. EMBO J. 1989 Jul;8(7):1959–1964. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03601.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. H., Robinson W. S. Common evolutionary origin of hepatitis B virus and retroviruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2531–2535. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakabayashi H., Taketa K., Miyano K., Yamane T., Sato J. Growth of human hepatoma cells lines with differentiated functions in chemically defined medium. Cancer Res. 1982 Sep;42(9):3858–3863. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomiyama H., Fromental C., Xiao J. H., Chambon P. Cell-specific activity of the constituent elements of the simian virus 40 enhancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(22):7881–7885. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.22.7881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ondek B., Gloss L., Herr W. The SV40 enhancer contains two distinct levels of organization. Nature. 1988 May 5;333(6168):40–45. doi: 10.1038/333040a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ondek B., Shepard A., Herr W. Discrete elements within the SV40 enhancer region display different cell-specific enhancer activities. EMBO J. 1987 Apr;6(4):1017–1025. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04854.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfaff E., Klinkert M. Q., Theilmann L., Schaller H. Characterization of large surface proteins of hepatitis B virus by antibodies to preS-S encoded amino acids. Virology. 1986 Jan 15;148(1):15–22. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90399-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rall L. B., Standring D. N., Laub O., Rutter W. J. Transcription of hepatitis B virus by RNA polymerase II. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Oct;3(10):1766–1773. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.10.1766. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raney A. K., Milich D. R., McLachlan A. Characterization of hepatitis B virus major surface antigen gene transcriptional regulatory elements in differentiated hepatoma cell lines. J Virol. 1989 Sep;63(9):3919–3925. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.9.3919-3925.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schirm S., Jiricny J., Schaffner W. The SV40 enhancer can be dissected into multiple segments, each with a different cell type specificity. Genes Dev. 1987 Mar;1(1):65–74. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.1.65. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeger C., Ganem D., Varmus H. E. Biochemical and genetic evidence for the hepatitis B virus replication strategy. Science. 1986 Apr 25;232(4749):477–484. doi: 10.1126/science.3961490. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeger C., Ganem D., Varmus H. E. Nucleotide sequence of an infectious molecularly cloned genome of ground squirrel hepatitis virus. J Virol. 1984 Aug;51(2):367–375. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.2.367-375.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaul Y., Ben-Levy R., De-Medina T. High affinity binding site for nuclear factor I next to the hepatitis B virus S gene promoter. EMBO J. 1986 Aug;5(8):1967–1971. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04451.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaul Y., Ben-Levy R. Multiple nuclear proteins in liver cells are bound to hepatitis B virus enhancer element and its upstream sequences. EMBO J. 1987 Jul;6(7):1913–1920. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02451.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaul Y., Rutter W. J., Laub O. A human hepatitis B viral enhancer element. EMBO J. 1985 Feb;4(2):427–430. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03646.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stibbe W., Gerlich W. H. Structural relationships between minor and major proteins of hepatitis B surface antigen. J Virol. 1983 May;46(2):626–628. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.2.626-628.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers J., Mason W. S. Replication of the genome of a hepatitis B--like virus by reverse transcription of an RNA intermediate. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):403–415. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90157-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tiollais P., Pourcel C., Dejean A. The hepatitis B virus. Nature. 1985 Oct 10;317(6037):489–495. doi: 10.1038/317489a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tur-Kaspa R., Burk R. D., Shaul Y., Shafritz D. A. Hepatitis B virus DNA contains a glucocorticoid-responsive element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1627–1631. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tur-Kaspa R., Shaul Y., Moore D. D., Burk R. D., Okret S., Poellinger L., Shafritz D. A. The glucocorticoid receptor recognizes a specific nucleotide sequence in hepatitis B virus DNA causing increased activity of the HBV enhancer. Virology. 1988 Dec;167(2):630–633. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaginuma K., Koike K. Identification of a promoter region for 3.6-kilobase mRNA of hepatitis B virus and specific cellular binding protein. J Virol. 1989 Jul;63(7):2914–2920. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.7.2914-2920.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaginuma K., Shirakata Y., Kobayashi M., Koike K. Hepatitis B virus (HBV) particles are produced in a cell culture system by transient expression of transfected HBV DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(9):2678–2682. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.9.2678. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yee J. K. A liver-specific enhancer in the core promoter region of human hepatitis B virus. Science. 1989 Nov 3;246(4930):658–661. doi: 10.1126/science.2554495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zenke M., Grundström T., Matthes H., Wintzerith M., Schatz C., Wildeman A., Chambon P. Multiple sequence motifs are involved in SV40 enhancer function. EMBO J. 1986 Feb;5(2):387–397. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04224.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]