Abstract
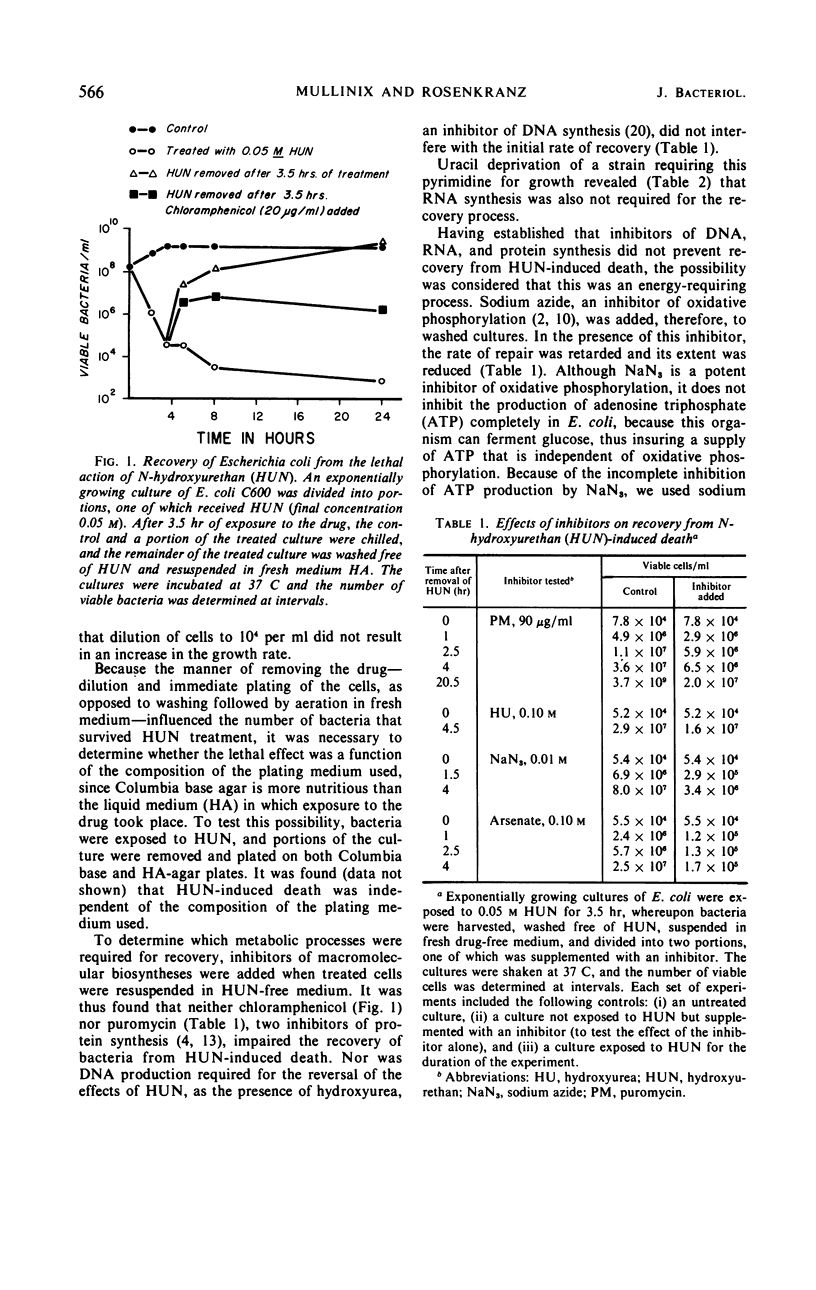
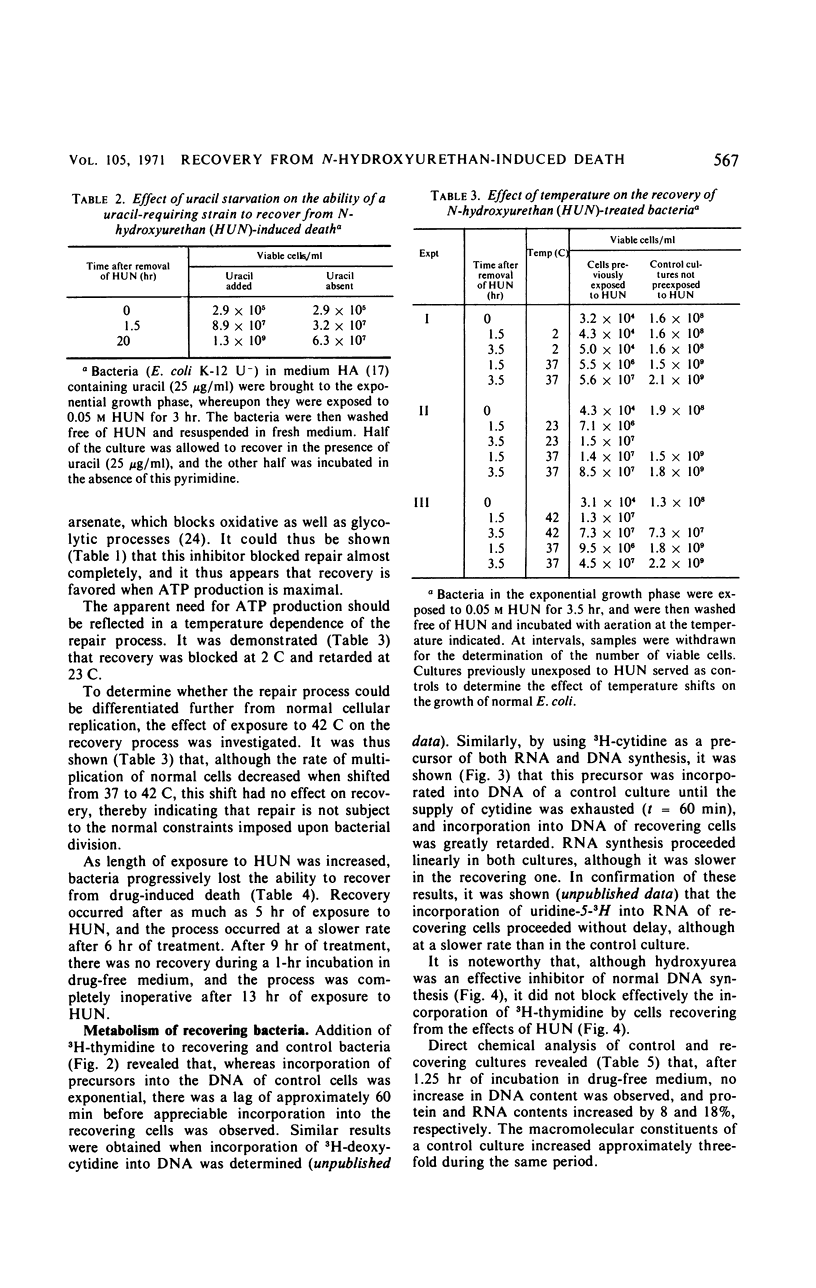
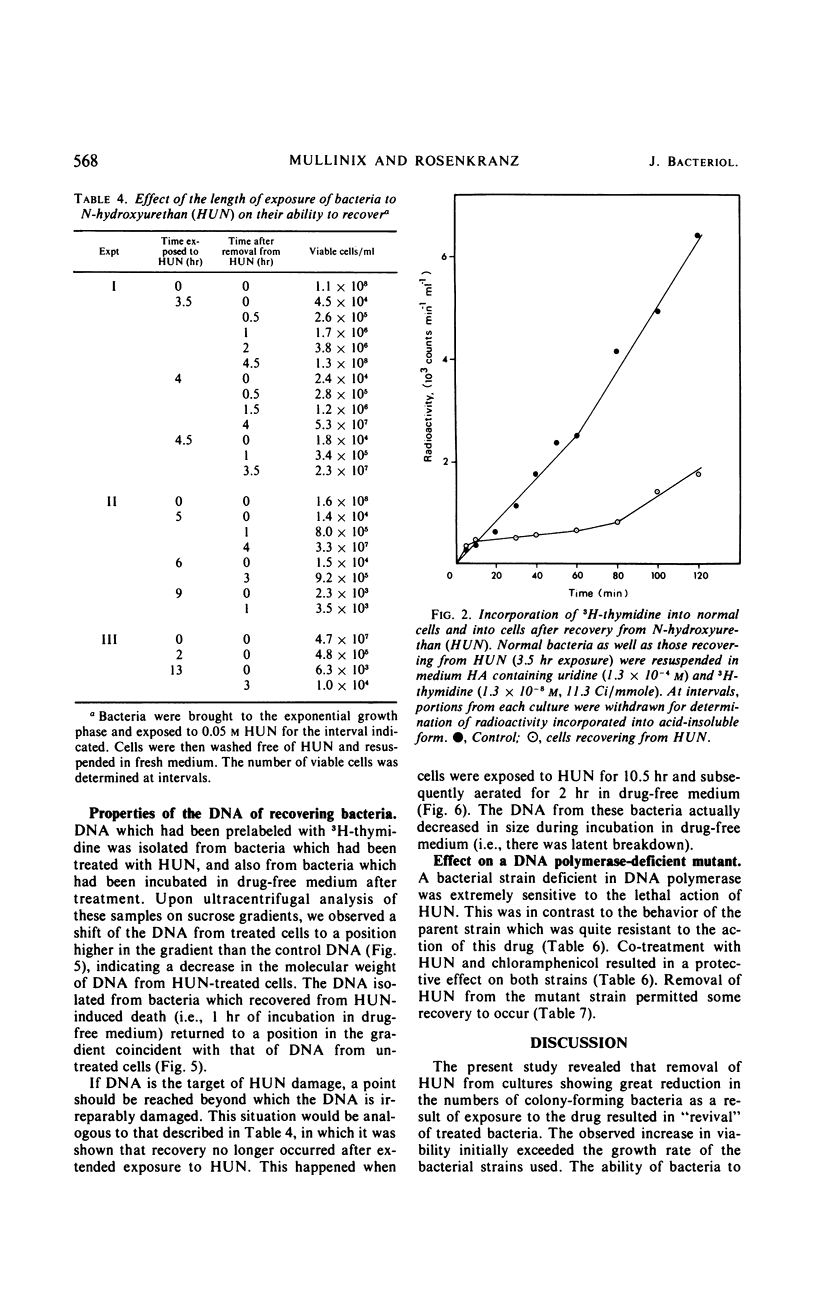
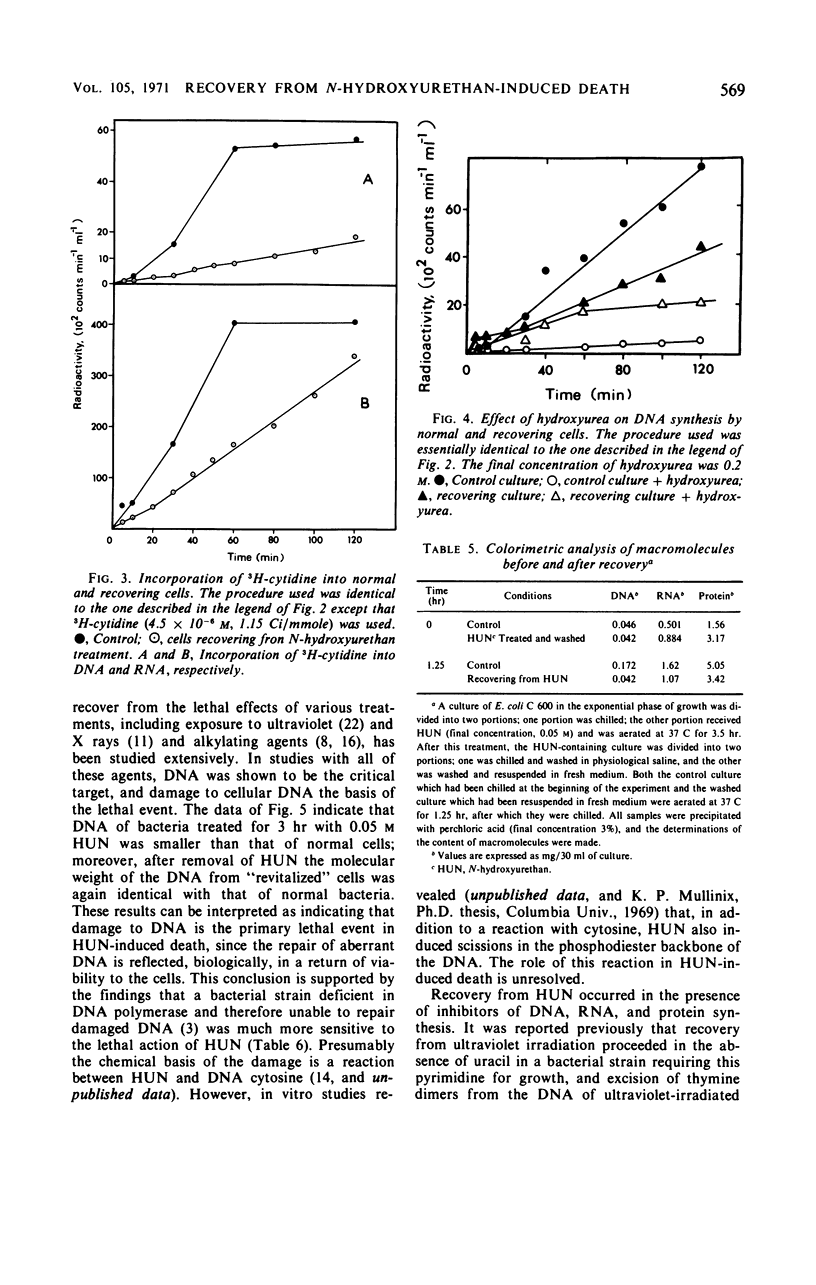
Bacteria (Escherichia coli) can recover from the lethal action of N-hydroxyurethan when they are incubated in drug-free liquid medium. This recovery, which is dependent upon energy metabolism, does not occur on solid medium. Recovery is accompanied by repair of the cellular deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA). A bacterial mutant deficient in DNA polymerase was extremely sensitive to the lethal action of hydroxyurethan. Data are presented which support the concept that DNA replication and DNA repair are mediated by different enzymes and that only the former process is inhibited by hydroxyurea.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Achey P., Billen D. Saturation of dark repair synthesis: accumulation of strand breaks. Biophys J. 1969 May;9(5):647–653. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(69)86409-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clifton C. E., Logan W. A. On the Relation between Assimilation and Respiration in Suspensions and in Cultures of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1939 May;37(5):523–540. doi: 10.1128/jb.37.5.523-540.1939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Lucia P., Cairns J. Isolation of an E. coli strain with a mutation affecting DNA polymerase. Nature. 1969 Dec 20;224(5225):1164–1166. doi: 10.1038/2241164a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GALE E. F., FOLKES J. P. The assimilation of amino-acids by bacteria. XV. Actions of antibiotics on nucleic acid and protein synthesis in Staphylococcus aureus. Biochem J. 1953 Feb;53(3):493–498. doi: 10.1042/bj0530493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanawalt P. C., Pettijohn D. E., Pauling E. C., Brunk C. F., Smith D. W., Kanner L. C., Couch J. L. Repair replication of DNA in vivo. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1968;33:187–194. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1968.033.01.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kos E., Drakulić M., Brdar B. Responses of various strains of Escherichia coli to inhibition of some biosynthetic processes after ultra-violet irradiation. Nature. 1965 Mar 13;205(976):1125–1126. doi: 10.1038/2051125a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawley P. D., Brookes P. Molecular mechanism of the cytotoxic action of difunctional alkylating agents and of resistance to this action. Nature. 1965 May 1;206(983):480–483. doi: 10.1038/206480a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGrath R. A., Williams R. W. Reconstruction in vivo of irradiated Escherichia coli deoxyribonucleic acid; the rejoining of broken pieces. Nature. 1966 Oct 29;212(5061):534–535. doi: 10.1038/212534a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullinix K. P., Rosenkranz H. S. Effects of N-hydroxyurethan on viability and metabolism of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1971 Feb;105(2):556–564. doi: 10.1128/jb.105.2.556-564.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NATHANS D. PUROMYCIN INHIBITION OF PROTEIN SYNTHESIS: INCORPORATION OF PUROMYCIN INTO PEPTIDE CHAINS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Apr;51:585–592. doi: 10.1073/pnas.51.4.585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nery R. Acylation of cystosine by ethyl N-hydroxycarbamate and its acyl derivatives and the binding of these agents to nucleic acids and proteins. J Chem Soc Perkin 1. 1969;14:1860–1865. doi: 10.1039/j39690001860. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierucci O., Helmstetter C. E. Chromosome replication, protein synthesis and cell division in Escherichia coli. Fed Proc. 1969 Nov-Dec;28(6):1755–1760. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSENKRANZ H. S., CARR H. S., ROSE H. M. PHENETHYL ALCOHOL. I. EFFECT ON MACROMOLECULAR SYNTHESIS OF ESCHERICHIA COLI. J Bacteriol. 1965 May;89:1354–1369. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.5.1354-1369.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSENKRANZ H. S., LEVY J. A. HYDROXYUREA: A SPECIFIC INHIBITOR OF DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACID SYNTHESIS. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Jan 11;95:181–183. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(65)90225-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiter H., Strauss B. Repair of damage induced by a monofunctional alkylating agent in a transformable, ultraviolet-sensitive strain of Bacillus subtilis. J Mol Biol. 1965 Nov;14(1):179–194. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80239-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenkranz H. S., Garro A. J., Levy J. A., Carr H. S. Studies with hydroxyurea. I. The reversible inhibition of bacterial DNA synthesis and the effect of hydroxyurea on the bactericidal action of streptomycin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Mar 21;114(3):501–515. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SETLOW R. B., CARRIER W. L. THE DISAPPEARANCE OF THYMINE DIMERS FROM DNA: AN ERROR-CORRECTING MECHANISM. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Feb;51:226–231. doi: 10.1073/pnas.51.2.226. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SUSSMAN M., SPIEGELMAN S. The use of arsenate in the analysis of energy relations amongst synthetic reactions. Arch Biochem. 1950 Nov;29(1):85–100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Searashi T., Strauss B. Glucose requirement for DNA breakdown resulting from treatment of Bacillus subtilis with ultraviolet radiation or methyl methanesulfonate. Mutat Res. 1967 May-Jun;4(3):372–375. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(67)90032-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Setlow R. B. The photochemistry, photobiology, and repair of polynucleotides. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1968;8:257–295. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60548-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swenson P. A., Setlow R. B. Effects of ultraviolet radiation on macromolecular synthesis in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1966 Jan;15(1):201–219. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80221-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


