Abstract
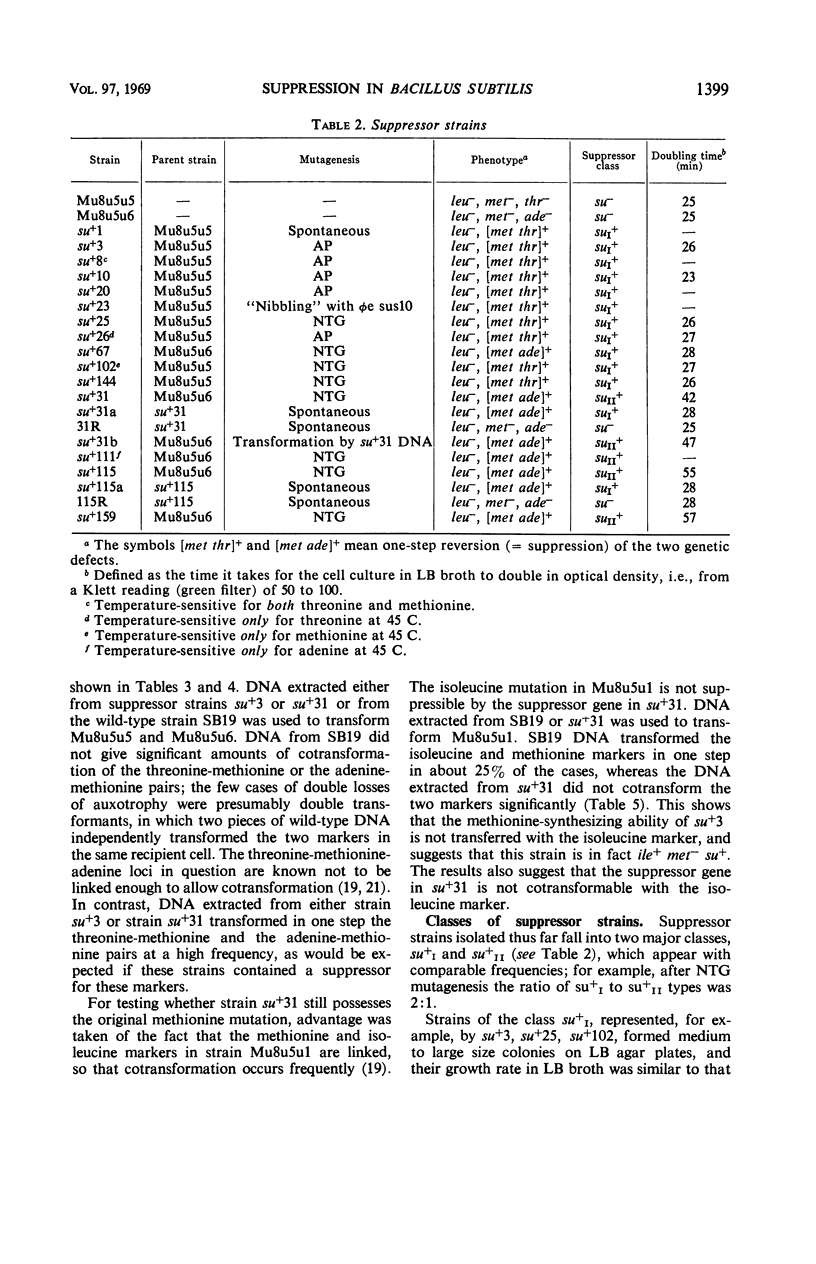
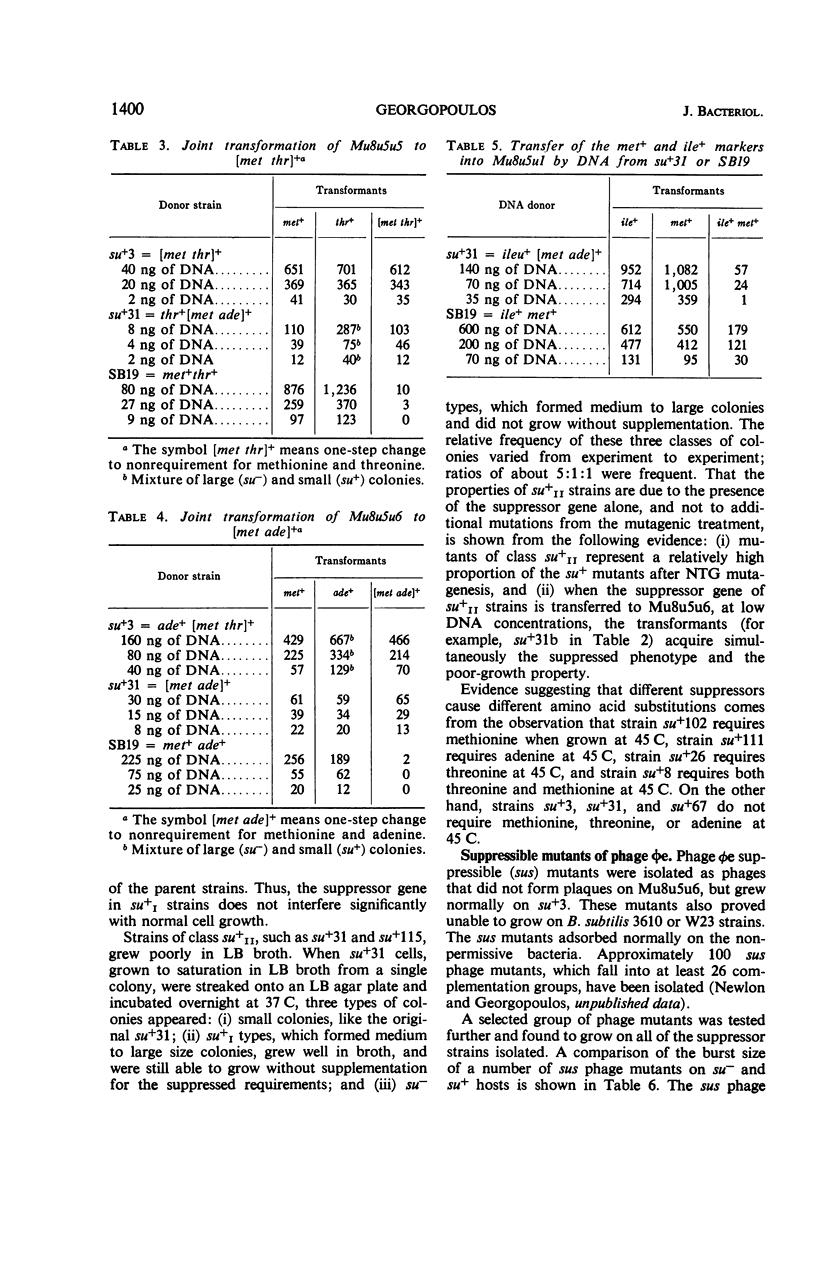
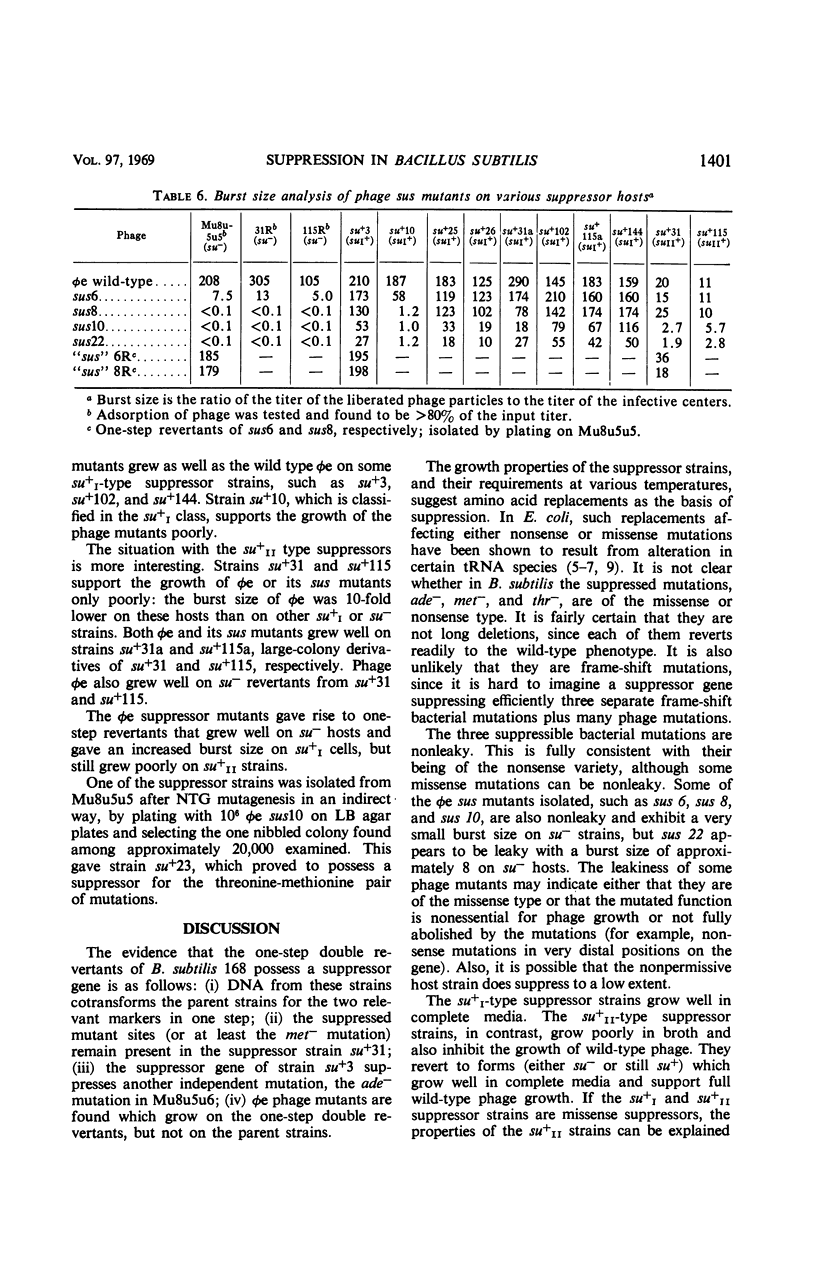
Multiple auxotrophic strains of Bacillus subtilis 168 were tested for joint one-step reversion of two or more auxotrophic markers to the wild-type phenotype. Mu8u5u5, a strain requiring leucine, methionine, and threonine, yielded revertants that grew without added methionine or threonine and proved to have a suppressor gene. When transferred by transformation with deoxyribonucleic acid, this suppressor gene also suppressed the adenine mutation in another strain, Mu8u5u6. The one-step double revertants fell into two distinct classes: strains of class su+I grow well in broth; strains of class su+II grow poorly. Strains su+II tend to revert frequently to the su+I or su− state. Conditional lethal mutants of phage φe were isolated which can grow on the su+ and not on the su− strains.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BENZER S., CHAMPE S. P. A change from nonsense to sense in the genetic code. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1962 Jul 15;48:1114–1121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.48.7.1114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRODY S., YANOFSKY C. Suppressor gene alteration of protein primary structure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Jul;50:9–16. doi: 10.1073/pnas.50.1.9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cahn F. H., Fox M. S. Fractionation of transformable bacteria from ocompetent cultures of Bacillus subtilis on renografin gradients. J Bacteriol. 1968 Mar;95(3):867–875. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.3.867-875.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capecchi M. R., Gussin G. N. Suppression in vitro: Identification of a Serine-sRNA as a "Nonsense" Suppressor. Science. 1965 Jul 23;149(3682):417–422. doi: 10.1126/science.149.3682.417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carbon J., Berg P., Yanofsky C. Missense suppression due to a genetically altered tRNA. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1966;31:487–497. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1966.031.01.063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelhardt D. L., Webster R. E., Wilhelm R. C., Zinder N. In vitro studies on the mechanism of suppression of a nonsense mutation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Dec;54(6):1791–1797. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.6.1791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorini L., Beckwith J. R. Suppression. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1966;20:401–422. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.20.100166.002153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta N. K., RajBhandary U. L., Khorana H. G. Missense suppression in tryptophan synthetase. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1966;31:499–500. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1966.031.01.064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAWTHORNE D. C., MORTIMER R. K. Super-suppressors in yeast. Genetics. 1963 Apr;48:617–620. doi: 10.1093/genetics/48.4.617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall D. H. Mutants of bacteriophage T4 unable to induce dihydrofolate reductase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Aug;58(2):584–591. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.2.584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall D. H., Tessman I. T4 mutants unable to induce deoxycytidylate deaminase activity. Virology. 1966 Jun;29(2):339–345. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(66)90041-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nester E W, Schafer M, Lederberg J. Gene Linkage in DNA Transfer: A Cluster of Genes Concerned with Aromatic Biosynthesis in Bacillus Subtilis. Genetics. 1963 Apr;48(4):529–551. doi: 10.1093/genetics/48.4.529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okubo S., Yanagida T. Isolation of a suppressor mutant in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1968 Mar;95(3):1187–1188. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.3.1187-1188.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid P., Berg P. T4 bacteriophage mutants suppressible by a missense suppressor which inserts glycine in place of arginine for the codon AGA. J Virol. 1968 Sep;2(9):905–914. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.9.905-914.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Revel H. R. Restriction of nonglucosylated T-even bacteriophage: properties of permissive mutants of Escherichia coli B and K12. Virology. 1967 Apr;31(4):688–701. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(67)90197-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roscoe D. H., Tucker R. G. The biosynthesis of 5-hydroxymethyldeoxyuridylic acid in bacteriophage-infected Bacillus subtilis. Virology. 1966 May;29(1):157–166. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(66)90205-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YANOFSKY C., HELINSKI D. R., MALING B. D. The effects of mutation on the composition and properties of the A protein of Escherichia coli tryptohan synthetase. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1961;26:11–24. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1961.026.01.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YOSHIKAWA H., SUEOKA N. Sequential replication of Bacillus subtilis chromosome. I. Comparison of marker frequencies in exponential and stationary growth phases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Apr;49:559–566. doi: 10.1073/pnas.49.4.559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


