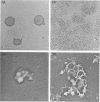
Abstract
Homologous pairs of virulent and attenuated or avirulent Mycoplasma pneumoniae strains were derived and compared in an effort to elucidate the mechanisms of virulence. These related strains were found to vary in growth, glycolysis, protein electrophoretic patterns, peroxide formation, morphology, and cytadsorption. Variations in the last two characteristics closely correlated with avirulence. This enables understanding of one stage in the pathogenic sequence and provides a convenient marker for avirulence. The derivation of infectious avirulent strains may make possible their use as live vaccines against M. pneumoniae disease.
Full text
PDF

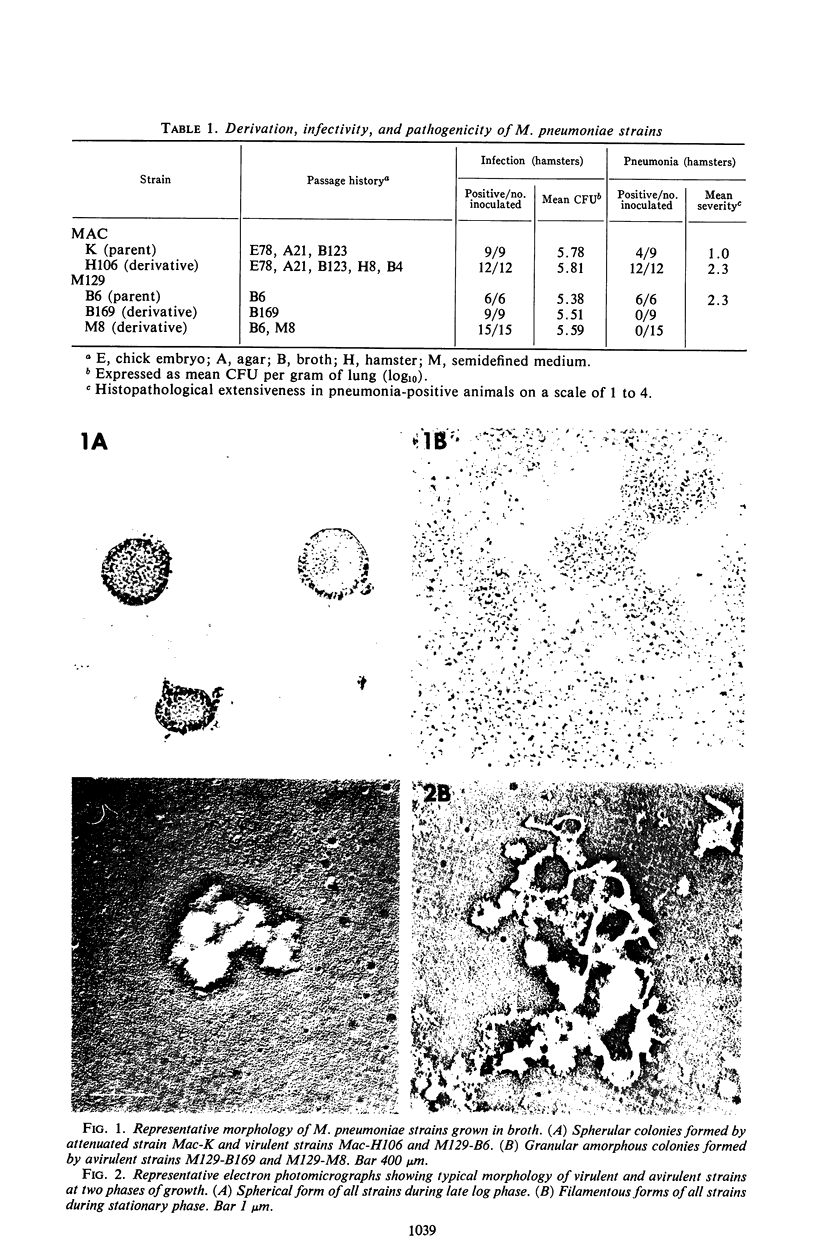


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARCHETTI I., HORSFALL F. L., Jr Persistent antigenic variation of influenza A viruses after incomplete neutralization in ovo with heterologous immune serum. J Exp Med. 1950 Nov 1;92(5):441–462. doi: 10.1084/jem.92.5.441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHANOCK R. M., HAYFLICK L., BARILE M. F. Growth on artificial medium of an agent associated with atypical pneumonia and its identification as a PPLO. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1962 Jan 15;48:41–49. doi: 10.1073/pnas.48.1.41. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLYDE W. A., Jr Hemolysis in identifying Eaton's pleuro-pneumonia-like organism. Science. 1963 Jan 4;139(3549):55–55. doi: 10.1126/science.139.3549.55. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLYDE W. A., Jr MYCOPLASMA SPECIES IDENTIFICATION BASED UPON GROWTH INHIBITION BY SPECIFIC ANTISERA. J Immunol. 1964 Jun;92:958–965. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COUCH R. B., CATE T. R., CHANOCK R. M. INFECTION WITH ARTIFICIALLY PROPAGATED EATON AGENT (MYCOPLASMA PNEUMONIAE). IMPLICATIONS FOR DEVELOPMENT OF ATTENUATED VACCINE FOR COLD AGGLUTININ-POSITIVE PNEUMONIA. JAMA. 1964 Feb 8;187:442–447. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chanock R. M. Mycoplasma infections of man. N Engl J Med. 1965 Dec 2;273(23):1257–concl. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196512022732307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clyde W. A., Jr Prevention of disease due to Mycoplasma pneumoniae. J Infect Dis. 1969 Aug;120(2):255–257. doi: 10.1093/infdis/120.2.255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAJANI A. S., CLYDE W. A., Jr, DENNY F. W. EXPERIMENTAL INFECTION WITH MYCOPLASMA PNEUMONIAE (EATON'S AGENT). J Exp Med. 1965 Jun 1;121:1071–1086. doi: 10.1084/jem.121.6.1071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EATON M. D., LIU C. Studies on sensitivity to streptomycin of the atypical pneumonia agent. J Bacteriol. 1957 Dec;74(6):784–787. doi: 10.1128/jb.74.6.784-787.1957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ENNY G. E., GRAYSTON J. T. EATON PLEUROPNEUMONIA-LIKE ORGANISM (MYCOPLASMA PNEUMONIAE) COMPLEMENT-FIXING ANTIGEN: EXTRACTION WITH ORGANIC SOLVENTS. J Immunol. 1965 Jul;95:19–25. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernald G. W., Clyde W. A., Jr, Denny F. W. Factors influencing growth inhibition of Mycoplasma pneumoniae by immune sera. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1967 Oct;126(1):161–166. doi: 10.3181/00379727-126-32391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernald G. W. Immunologic aspects of experimental Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection. J Infect Dis. 1969 Mar;119(3):255–266. doi: 10.1093/infdis/119.3.255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim K. S., Clyde W. A., Jr, Denny F. W. Physical properties of human Mycoplasma species. J Bacteriol. 1966 Jul;92(1):214–219. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.1.214-219.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipman R. P., Clyde W. A., Jr The interrelationship of virulence, cytadsorption, and peroxide formation in Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1969 Sep;131(4):1163–1167. doi: 10.3181/00379727-131-34061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mogabgab W. J. Protective effects of inactive Mycoplasma pneumoniae vaccine in military personnel, 1964-1966. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1968 Mar;97(3):359–365. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1968.97.3.359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razin S., Rottem S. Identification of Mycoplasma and other microorganisms by polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis of cell proteins. J Bacteriol. 1967 Dec;94(6):1807–1810. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.6.1807-1810.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEVER J. L. Application of a microtechnique to viral serological investigations. J Immunol. 1962 Mar;88:320–329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. B., Friedewald W. T., Chanock R. M. Inactivated Mycoplasma pneumoniae vaccine. Evaluation in volunteers. JAMA. 1967 Feb 6;199(6):353–358. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobeslavsky O., Prescott B., Chanock R. M. Adsorption of Mycoplasma pneumoniae to neuraminic acid receptors of various cells and possible role in virulence. J Bacteriol. 1968 Sep;96(3):695–705. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.3.695-705.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somerson N. L., Walls B. E., Chanock R. M. Hemolysin of Mycoplasma pneumoniae: tentative identification as a peroxide. Science. 1965 Oct 8;150(3693):226–228. doi: 10.1126/science.150.3693.226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanbridge E., Hayflick L. Growth inhibition test for identification of Mycoplasma species utilizing dried antiserum-impregnated paper discs. J Bacteriol. 1967 Apr;93(4):1392–1396. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.4.1392-1396.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg P., Horswood R. L., Chanock R. M. Temperature-sensitive mutants of Mycoplasma pneumoniae. I. In vitro biologic properties. J Infect Dis. 1969 Aug;120(2):217–224. doi: 10.1093/infdis/120.2.217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takayama K., MacLennan D. H., Tzagoloff A., Stoner C. D. Studies on the electron transfer system. LXVII. Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of the mitochondrial electron transfer complexes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1966 Apr;114(1):223–230. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(66)90324-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]