Abstract
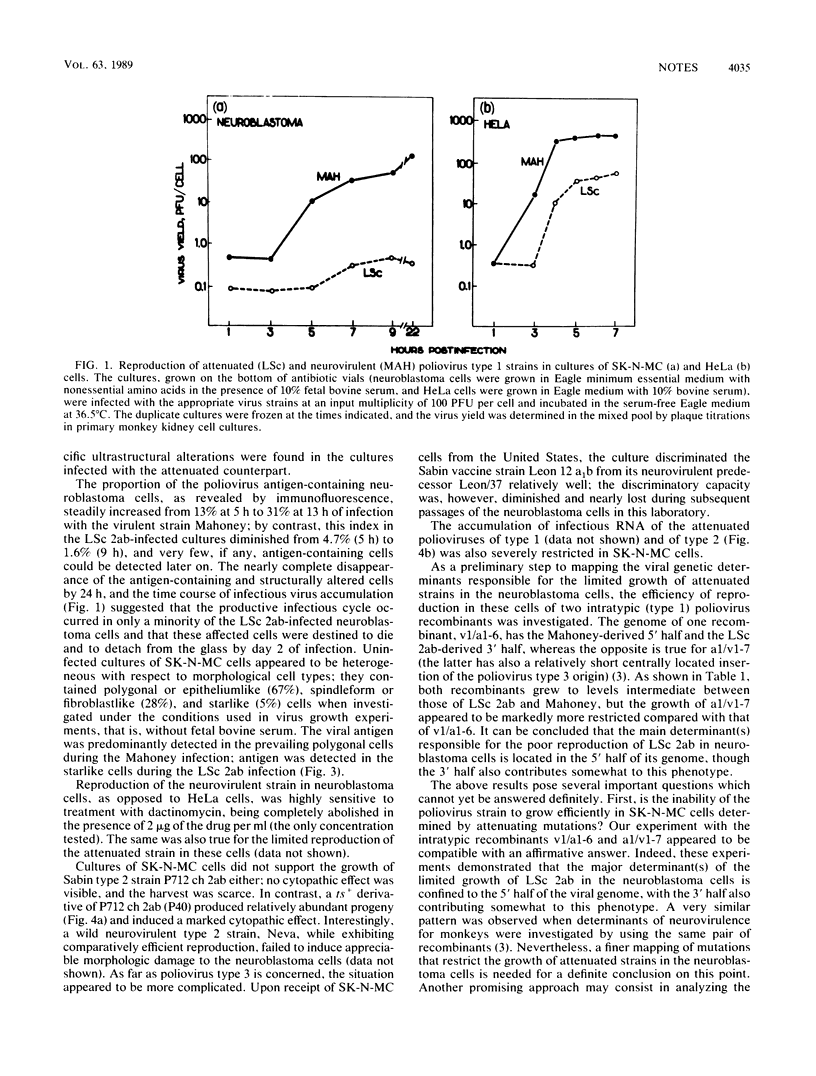
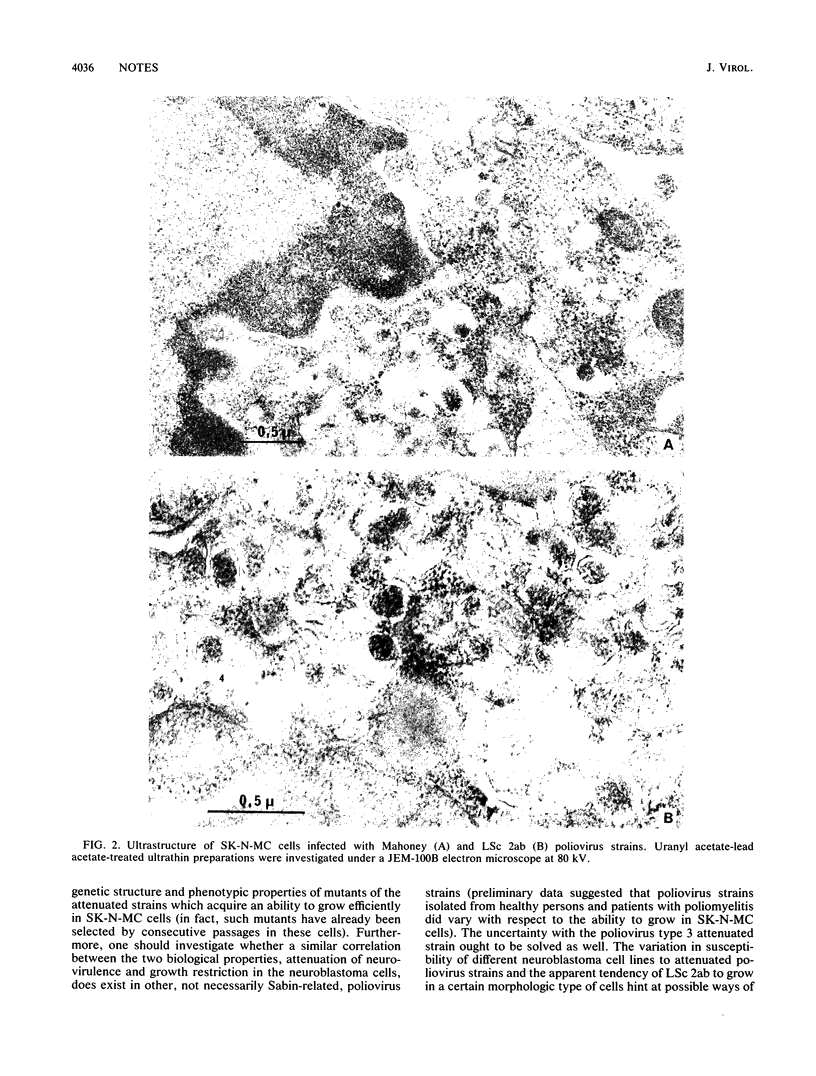
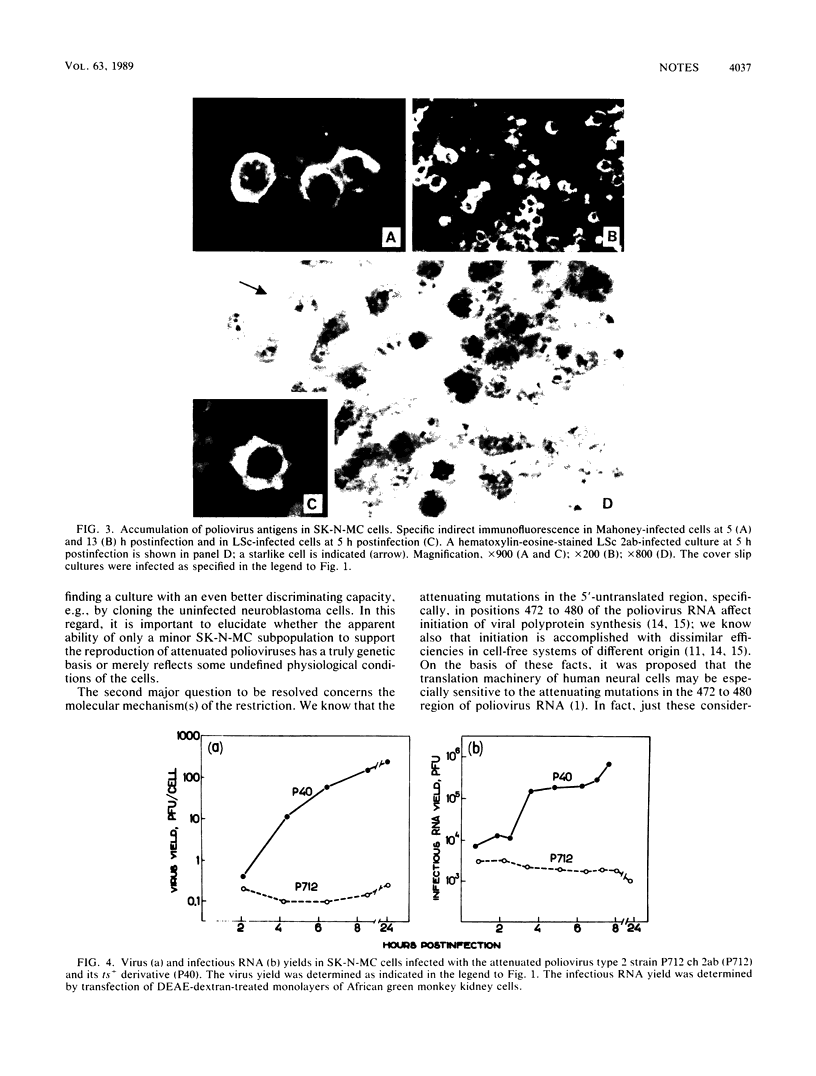
Cultured cells of a human neuroblastoma, SK-N-MC, were found to be highly resistant to Sabin attenuated poliovirus types 1 and 2 strains; no appreciable cytopathic effect was observed, and the total harvest was generally in the order of 1 PFU per cell or less. On the other hand, related neurovirulent strains of these antigenic types produced a relatively good (2 orders of magnitude higher) yield in a markedly protracted infectious cycle. The limited growth of the attenuated virus in the neuroblastoma cells appeared to be confined to a minor cell subpopulation. Experiments with intratypic (type 1) poliovirus recombinants suggested that the major genetic determinants limiting reproduction of the attenuated polioviruses in the neuroblastoma cells are located in the 5' half of the viral RNA, although the 3' half also appears to contribute somewhat to this phenotype. The possibility that neuroblastoma cells may represent an in vitro model for studying poliovirus neurovirulence is briefly discussed.
Full text
PDF
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AGOL V. I., CHUMAKOVA M. Ia. An agar polysaccharide and d marker of poliovirus. Virology. 1962 May;17:221–223. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(62)90111-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Agol V. I., Drozdov S. G., Grachev V. P., Kolesnikova M. S., Kozlov V. G., Ralph N. M., Romanova L. I., Tolskaya E. A., Tyufanov A. V., Viktorova E. G. Recombinants between attenuated and virulent strains of poliovirus type 1: derivation and characterization of recombinants with centrally located crossover points. Virology. 1985 Jun;143(2):467–477. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90386-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Almond J. W. The attenuation of poliovirus neurovirulence. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1987;41:153–180. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.41.100187.001101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KANDA Y., MELNICK J. L. In vitro differentiation of virulent and attenuated polioviruses by their growth characteristics on MS cells. J Exp Med. 1959 Jan 1;109(1):9–24. doi: 10.1084/jem.109.1.9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakano J. H., Hatch M. H., Thieme M. L., Nottay B. Parameters for differentiating vaccine-derived and wild poliovirus strains. Prog Med Virol. 1978;24:178–206. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Omata T., Kohara M., Kuge S., Komatsu T., Abe S., Semler B. L., Kameda A., Itoh H., Arita M., Wimmer E. Genetic analysis of the attenuation phenotype of poliovirus type 1. J Virol. 1986 May;58(2):348–358. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.2.348-358.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelletier J., Kaplan G., Racaniello V. R., Sonenberg N. Translational efficiency of poliovirus mRNA: mapping inhibitory cis-acting elements within the 5' noncoding region. J Virol. 1988 Jul;62(7):2219–2227. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.7.2219-2227.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Racaniello V. R. Poliovirus neurovirulence. Adv Virus Res. 1988;34:217–246. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60519-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabin A. B. Oral poliovirus vaccine: history of its development and use and current challenge to eliminate poliomyelitis from the world. J Infect Dis. 1985 Mar;151(3):420–436. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.3.420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svitkin Y. V., Maslova S. V., Agol V. I. The genomes of attenuated and virulent poliovirus strains differ in their in vitro translation efficiencies. Virology. 1985 Dec;147(2):243–252. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90127-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svitkin Y. V., Pestova T. V., Maslova S. V., Agol V. I. Point mutations modify the response of poliovirus RNA to a translation initiation factor: a comparison of neurovirulent and attenuated strains. Virology. 1988 Oct;166(2):394–404. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90510-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tershak D. R., Makkar R. Attachment, uncoating and blockage of cell protein synthesis by Sabin derivatives of poliovirus in HeLa and Vero cells. Intervirology. 1988;29(5):292–300. doi: 10.1159/000150058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]