Abstract
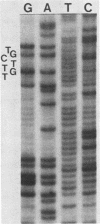
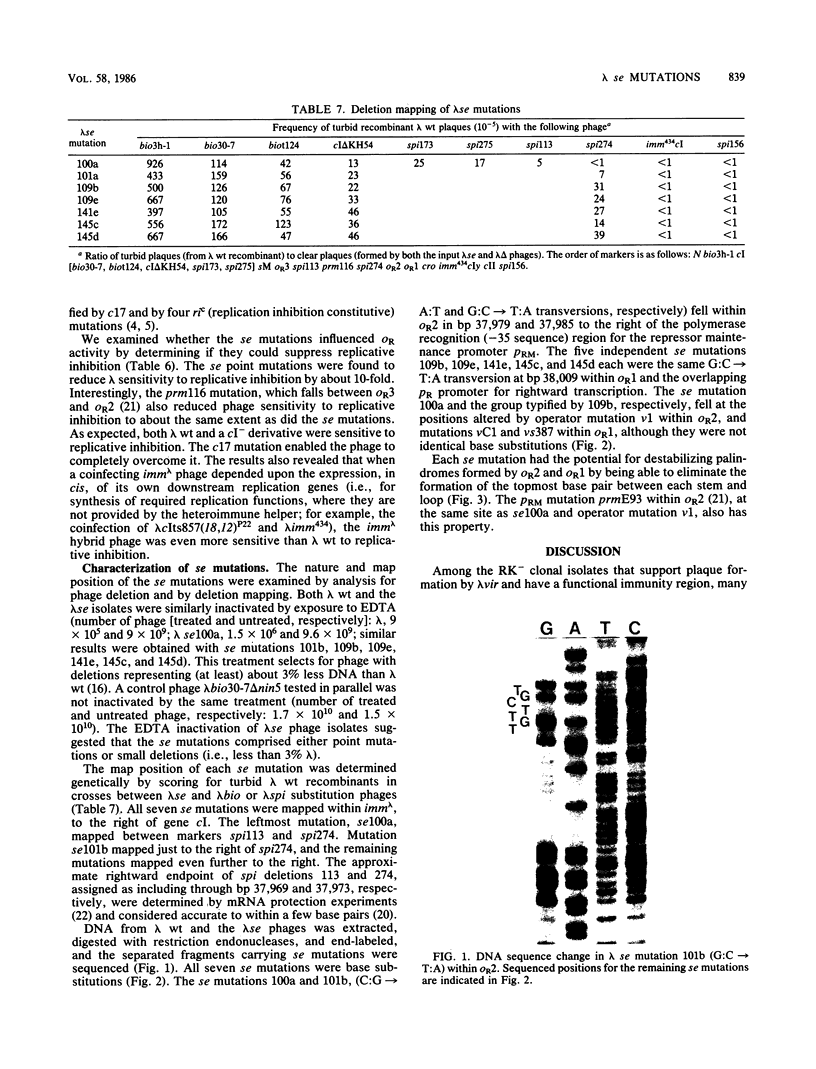
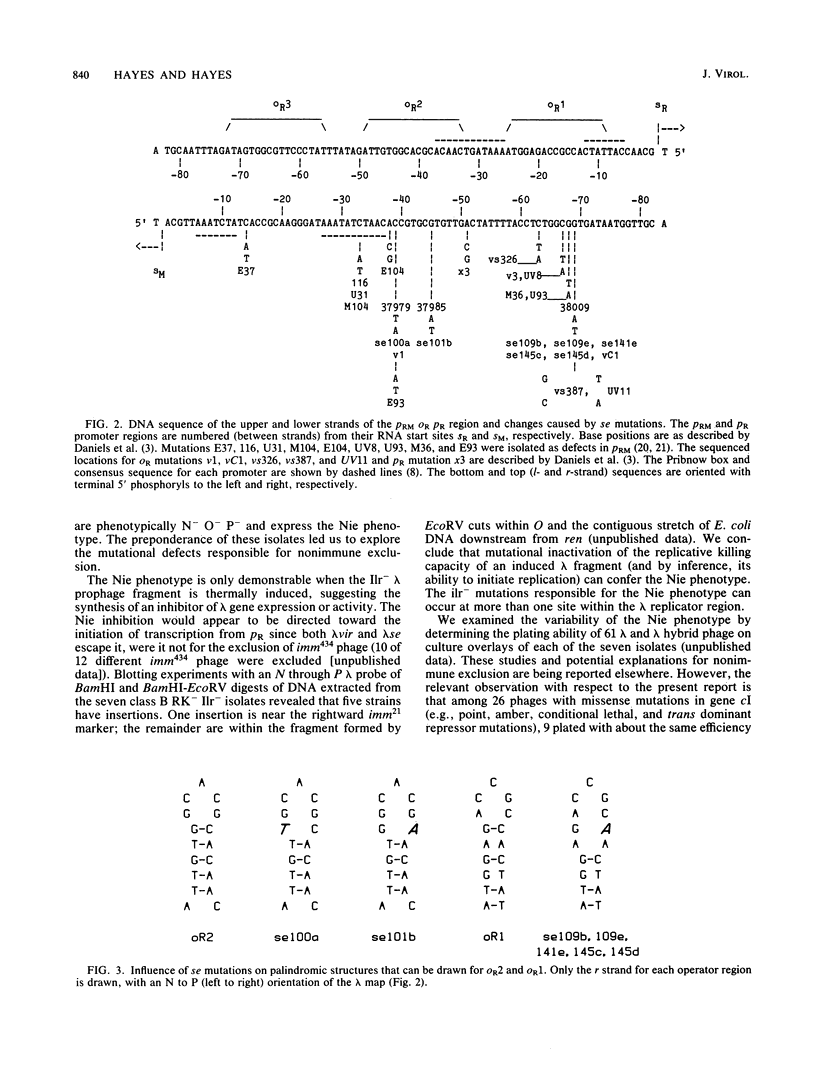
Survivor clones with defects in gene functions that participate in the replicative killing of thermally induced Escherichia coli constructs with integrated lambda N through P or cIII through P gene fragments were selected at a frequency of about 10(-6). Among the population of survivors, clones were identified that exhibited normal lambda immunity at 30 degrees C, as shown by their ability to prevent the plating of lambda wild type and to support the plating of a nearly identical heteroimmune bacteriophage lambda imm434. However, when placed at 42 degrees C to inactivate the cIts857 repressor, these survivor isolates excluded the plating of both lambda wild-type and lambda imm434 phages, a phenotype designated nonimmune exclusion (Nie). Spontaneous mutants of lambda wild type were isolated that overcame the Nie phenotype and would plaque at 42 degrees C on cell lawns of these isolates. The acquired lambda se mutations suppressed nonimmune exclusion, prevented lysogenization by interrupting repressor expression from PRM, and made the phage insensitive to replicative inhibition. The se mutations were genetically mapped and sequenced within the rightward lambda operator site.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Calef E., Neubauer Z. Active and inactive states of the CI gene in some lambda defective phages. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1968;33:765–767. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1968.033.01.087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisen H., Barrand P., Spiegelman W., Reichardt L. F., Heinemann S., Georgopoulos C. Mutants in the y region of bacteriophage lambda constitutive for repressor synthesis: their isolation and the characterization of the Hyp phenotype. Gene. 1982 Nov;20(1):71–81. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90088-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisen H., Pereira da Silva L., Jacob F. Sur la régulation précoce du bactériophage lambda. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1968 Mar 11;266(11):1176–1178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes S., Gordon A., Sadowski I., Hayes C. RK bacterial test for independently measuring chemical toxicity and mutagenicity: short-term forward selection assay. Mutat Res. 1984 Apr;130(2):97–106. doi: 10.1016/0165-1161(84)90109-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes S. Initiation of coliphage lambda replication, lit, oop RNA synthesis, and effect of gene dosage on transcription from promoters PL, PR, and PR. Virology. 1979 Sep;97(2):415–438. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90352-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson A. D., Poteete A. R., Lauer G., Sauer R. T., Ackers G. K., Ptashne M. lambda Repressor and cro--components of an efficient molecular switch. Nature. 1981 Nov 19;294(5838):217–223. doi: 10.1038/294217a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kröger M., Hobom G. A chain of interlinked genes in the ninR region of bacteriophage lambda. Gene. 1982 Nov;20(1):25–38. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90084-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer B. J., Ptashne M. Gene regulation at the right operator (OR) of bacteriophage lambda. III. lambda repressor directly activates gene transcription. J Mol Biol. 1980 May 15;139(2):195–205. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90304-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkinson J. S., Huskey R. J. Deletion mutants of bacteriophage lambda. I. Isolation and initial characterization. J Mol Biol. 1971 Mar 14;56(2):369–384. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90471-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pereira da Silva L., Eisen H., Jacob F. Sur la réplication du bactériophage lambda. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1968 Feb 26;266(9):926–928. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptashne M., Jeffrey A., Johnson A. D., Maurer R., Meyer B. J., Pabo C. O., Roberts T. M., Sauer R. T. How the lambda repressor and cro work. Cell. 1980 Jan;19(1):1–11. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90383-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rambach A. Replicator mutants of bacteriophage lambda: characterization of two subclasses. Virology. 1973 Jul;54(1):270–277. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90136-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen E. D., Gussin G. N. Clustering of Prm- mutations of bacteriophage lambda in the region between 33 and 40 nucleotides from the cL transcription start point. Virology. 1979 Oct 30;98(2):393–410. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90562-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen E. D., Hartley J. L., Matz K., Nichols B. P., Young K. M., Donelson J. E., Gussin G. N. DNA sequence analysis of prm-mutations of coliphage lambda. Gene. 1980 Nov;11(3-4):197–205. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90060-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. R., Eisen H., Reichardt L., Hedgepeth J. Deletions of lambda phage locating a prm mutation within the rightward operator. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Mar;73(3):712–716. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.3.712. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Susskind M. M., Botstein D. Superinfection exclusion by lambda prophage in lysogens of Salmonella typhimurium. Virology. 1980 Jan 15;100(1):212–216. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90571-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THOMAS R., BERTANI L. E. ON THE CONTROL OF THE REPLICATION OF TEMPERATE BACTERIOPHAGES SUPERINFECTING IMMUNE HOSTS. Virology. 1964 Nov;24:241–253. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(64)90163-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toothman P., Herskowitz I. Rex-dependent exclusion of lambdoid phages. I. Prophage requirements for exclusion. Virology. 1980 Apr 15;102(1):133–146. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90076-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]