Abstract
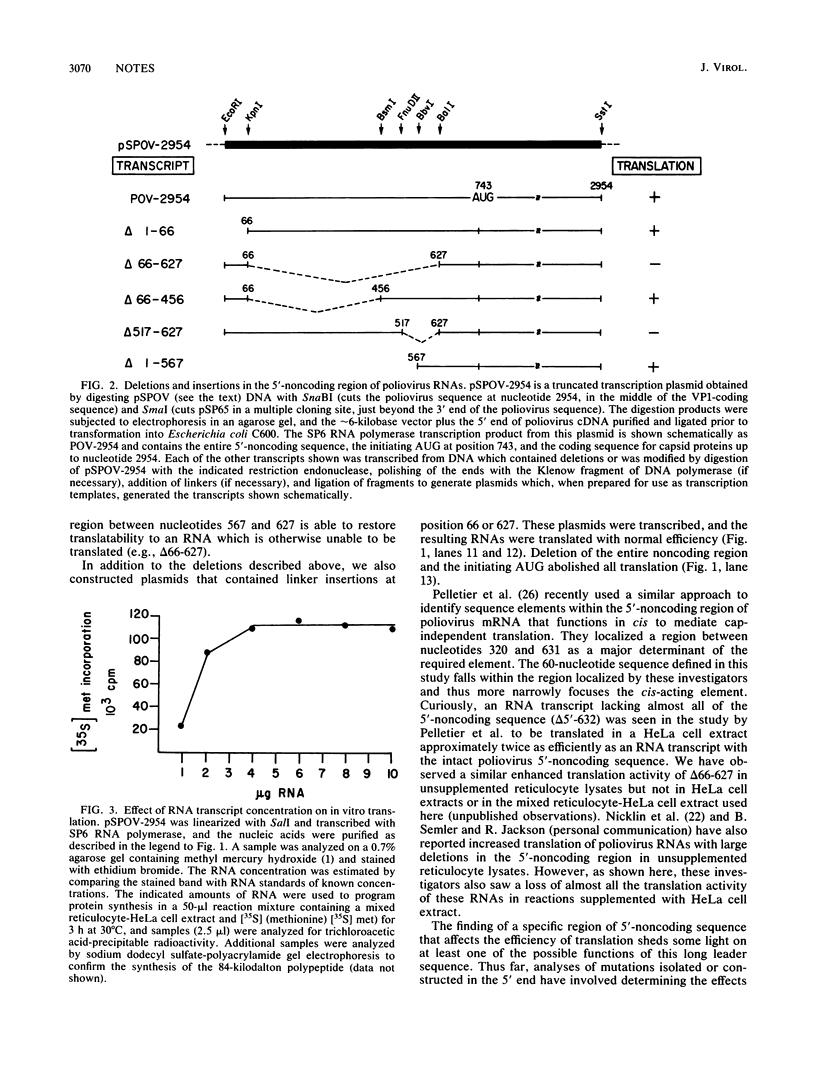
A truncated poliovirus RNA that contains the entire 5'-noncoding region as well as some capsid protein-coding sequences was produced from cloned cDNA inserted into an SP6 transcription vector and subsequently was translated in a mixed rabbit reticulocyte-HeLa cell lysate. Deletions or modifications of regions of the 5'-noncoding sequences had significant effects upon the efficiency of translation. The presence of a 60-nucleotide sequence located at positions 567 to 627 appeared to be essential for active ribosome binding and translation of this uncapped RNA.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bailey J. M., Davidson N. Methylmercury as a reversible denaturing agent for agarose gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1976 Jan;70(1):75–85. doi: 10.1016/s0003-2697(76)80049-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown B. A., Ehrenfeld E. Translation of poliovirus RNA in vitro: changes in cleavage pattern and initiation sites by ribosomal salt wash. Virology. 1979 Sep;97(2):396–405. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90350-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Currey K. M., Peterlin B. M., Maizel J. V., Jr Secondary structure of poliovirus RNA: correlation of computer-predicted with electron microscopically observed structure. Virology. 1986 Jan 15;148(1):33–46. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90401-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorner A. J., Dorner L. F., Larsen G. R., Wimmer E., Anderson C. W. Identification of the initiation site of poliovirus polyprotein synthesis. J Virol. 1982 Jun;42(3):1017–1028. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.3.1017-1028.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorner A. J., Semler B. L., Jackson R. J., Hanecak R., Duprey E., Wimmer E. In vitro translation of poliovirus RNA: utilization of internal initiation sites in reticulocyte lysate. J Virol. 1984 May;50(2):507–514. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.2.507-514.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. M., Dunn G., Minor P. D., Schild G. C., Cann A. J., Stanway G., Almond J. W., Currey K., Maizel J. V., Jr Increased neurovirulence associated with a single nucleotide change in a noncoding region of the Sabin type 3 poliovaccine genome. Nature. 1985 Apr 11;314(6011):548–550. doi: 10.1038/314548a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez-Munoz R., Darnell J. E. Structural difference between the 5' termini of viral and cellular mRNA in poliovirus-infected cells: possible basis for the inhibition of host protein synthesis. J Virol. 1976 May;18(2):719–726. doi: 10.1128/jvi.18.2.719-726.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagenbüchle O., Santer M., Steitz J. A., Mans R. J. Conservation of the primary structure at the 3' end of 18S rRNA from eucaryotic cells. Cell. 1978 Mar;13(3):551–563. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90328-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hassin D., Korn R., Horwitz M. S. A major internal initiation site for the in vitro translation of the adenovirus DNA polymerase. Virology. 1986 Nov;155(1):214–224. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90181-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herman R. C. Internal initiation of translation on the vesicular stomatitis virus phosphoprotein mRNA yields a second protein. J Virol. 1986 Jun;58(3):797–804. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.3.797-804.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewlett M. J., Rose J. K., Baltimore D. 5'-terminal structure of poliovirus polyribosomal RNA is pUp. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Feb;73(2):327–330. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.2.327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson V. H., Semler B. L. Defined recombinants of poliovirus and coxsackievirus: sequence-specific deletions and functional substitutions in the 5'-noncoding regions of viral RNAs. Virology. 1988 Jan;162(1):47–57. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90393-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamura N., Semler B. L., Rothberg P. G., Larsen G. R., Adler C. J., Dorner A. J., Emini E. A., Hanecak R., Lee J. J., van der Werf S. Primary structure, gene organization and polypeptide expression of poliovirus RNA. Nature. 1981 Jun 18;291(5816):547–553. doi: 10.1038/291547a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Bifunctional messenger RNAs in eukaryotes. Cell. 1986 Nov 21;47(4):481–483. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90609-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Comparison of initiation of protein synthesis in procaryotes, eucaryotes, and organelles. Microbiol Rev. 1983 Mar;47(1):1–45. doi: 10.1128/mr.47.1.1-45.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuge S., Nomoto A. Construction of viable deletion and insertion mutants of the Sabin strain of type 1 poliovirus: function of the 5' noncoding sequence in viral replication. J Virol. 1987 May;61(5):1478–1487. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.5.1478-1487.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- La Monica N., Meriam C., Racaniello V. R. Mapping of sequences required for mouse neurovirulence of poliovirus type 2 Lansing. J Virol. 1986 Feb;57(2):515–525. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.2.515-525.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen G. R., Semler B. L., Wimmer E. Stable hairpin structure within the 5'-terminal 85 nucleotides of poliovirus RNA. J Virol. 1981 Jan;37(1):328–335. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.1.328-335.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawson T. G., Ray B. K., Dodds J. T., Grifo J. A., Abramson R. D., Merrick W. C., Betsch D. F., Weith H. L., Thach R. E. Influence of 5' proximal secondary structure on the translational efficiency of eukaryotic mRNAs and on their interaction with initiation factors. J Biol Chem. 1986 Oct 25;261(30):13979–13989. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicklin M. J., Kräusslich H. G., Toyoda H., Dunn J. J., Wimmer E. Poliovirus polypeptide precursors: expression in vitro and processing by exogenous 3C and 2A proteinases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(12):4002–4006. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.12.4002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomoto A., Lee Y. F., Wimmer E. The 5' end of poliovirus mRNA is not capped with m7G(5')ppp(5')Np. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Feb;73(2):375–380. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.2.375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Omata T., Kohara M., Kuge S., Komatsu T., Abe S., Semler B. L., Kameda A., Itoh H., Arita M., Wimmer E. Genetic analysis of the attenuation phenotype of poliovirus type 1. J Virol. 1986 May;58(2):348–358. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.2.348-358.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peabody D. S., Berg P. Termination-reinitiation occurs in the translation of mammalian cell mRNAs. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;6(7):2695–2703. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.7.2695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelletier J., Kaplan G., Racaniello V. R., Sonenberg N. Cap-independent translation of poliovirus mRNA is conferred by sequence elements within the 5' noncoding region. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Mar;8(3):1103–1112. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.3.1103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips B. A., Emmert A. Modulation of the expression of poliovirus proteins in reticulocyte lysates. Virology. 1986 Jan 30;148(2):255–267. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90323-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Racaniello V. R., Baltimore D. Cloned poliovirus complementary DNA is infectious in mammalian cells. Science. 1981 Nov 20;214(4523):916–919. doi: 10.1126/science.6272391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Racaniello V. R., Baltimore D. Molecular cloning of poliovirus cDNA and determination of the complete nucleotide sequence of the viral genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):4887–4891. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.4887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Racaniello V. R., Meriam C. Poliovirus temperature-sensitive mutant containing a single nucleotide deletion in the 5'-noncoding region of the viral RNA. Virology. 1986 Dec;155(2):498–507. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90211-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray B. K., Lawson T. G., Kramer J. C., Cladaras M. H., Grifo J. A., Abramson R. D., Merrick W. C., Thach R. E. ATP-dependent unwinding of messenger RNA structure by eukaryotic initiation factors. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 25;260(12):7651–7658. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Semler B. L., Johnson V. H., Tracy S. A chimeric plasmid from cDNA clones of poliovirus and coxsackievirus produces a recombinant virus that is temperature-sensitive. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1777–1781. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shih D. S., Park I. W., Evans C. L., Jaynes J. M., Palmenberg A. C. Effects of cDNA hybridization on translation of encephalomyocarditis virus RNA. J Virol. 1987 Jun;61(6):2033–2037. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.6.2033-2037.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonenberg N., Guertin D., Lee K. A. Capped mRNAs with reduced secondary structure can function in extracts from poliovirus-infected cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Dec;2(12):1633–1638. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.12.1633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonenberg N. Regulation of translation by poliovirus. Adv Virus Res. 1987;33:175–204. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60318-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svitkin Y. V., Maslova S. V., Agol V. I. The genomes of attenuated and virulent poliovirus strains differ in their in vitro translation efficiencies. Virology. 1985 Dec;147(2):243–252. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90127-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toyoda H., Kohara M., Kataoka Y., Suganuma T., Omata T., Imura N., Nomoto A. Complete nucleotide sequences of all three poliovirus serotype genomes. Implication for genetic relationship, gene function and antigenic determinants. J Mol Biol. 1984 Apr 25;174(4):561–585. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90084-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ypma-Wong M. F., Semler B. L. In vitro molecular genetics as a tool for determining the differential cleavage specificities of the poliovirus 3C proteinase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Mar 11;15(5):2069–2088. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.5.2069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]