Abstract
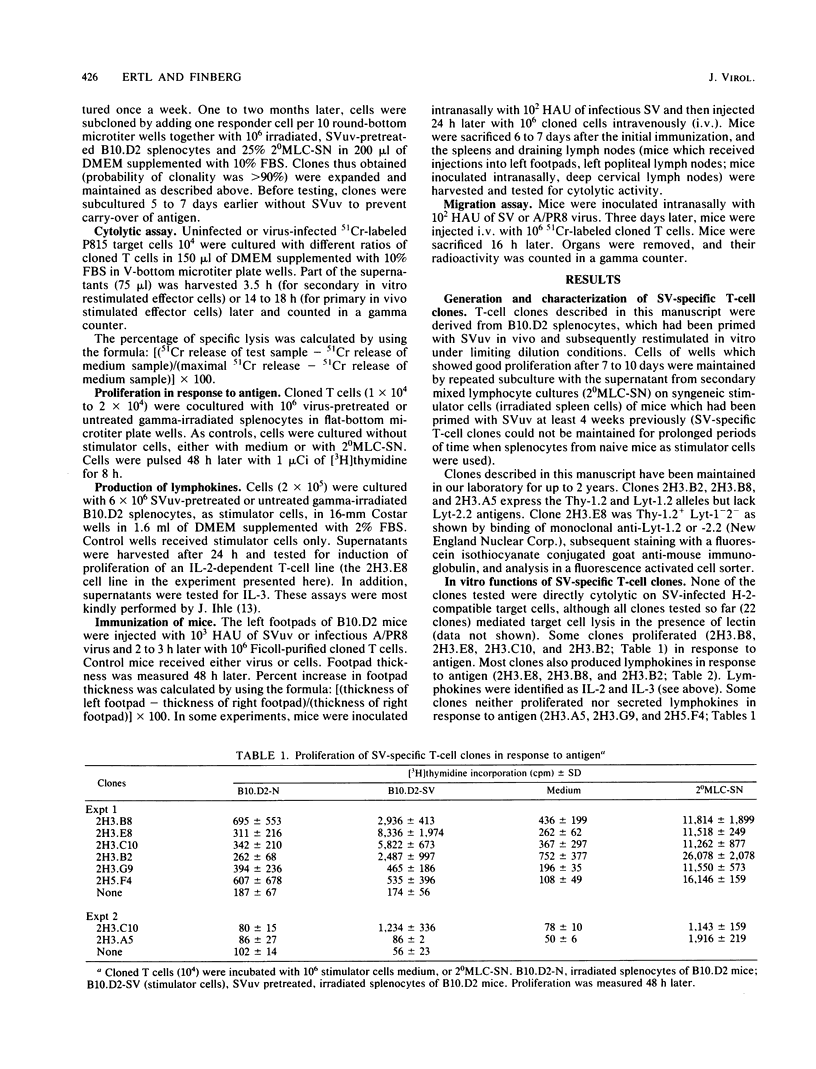
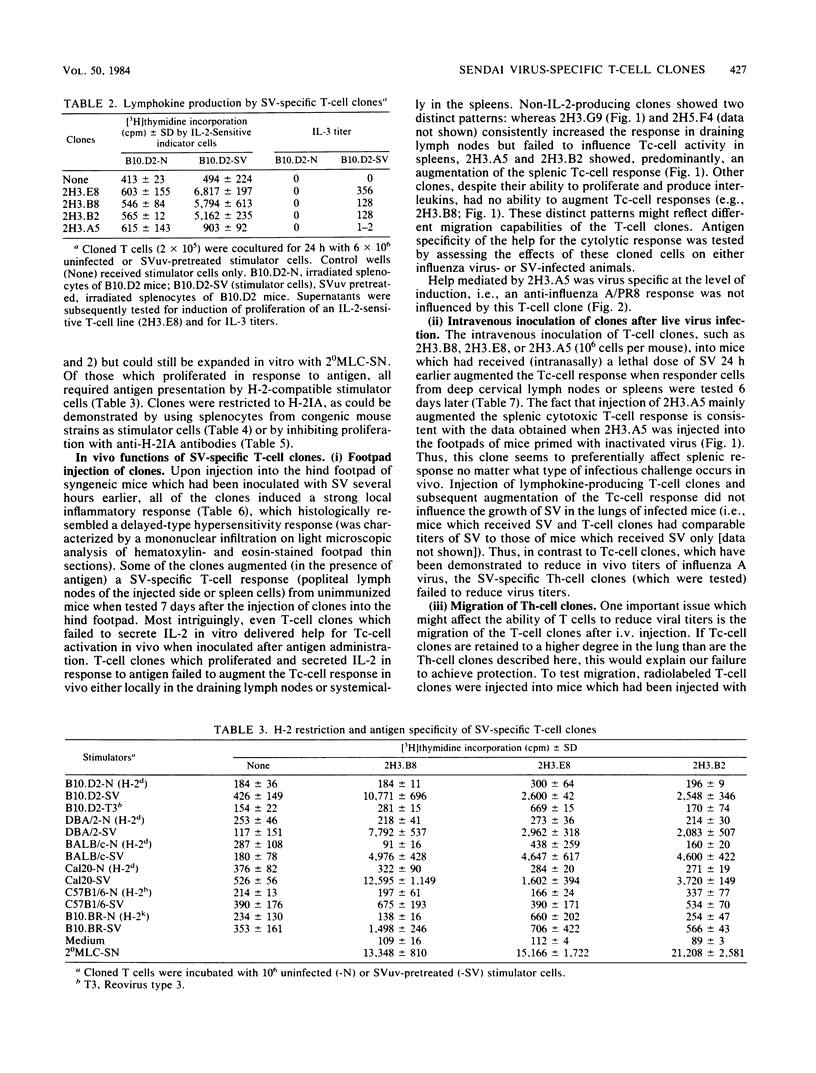
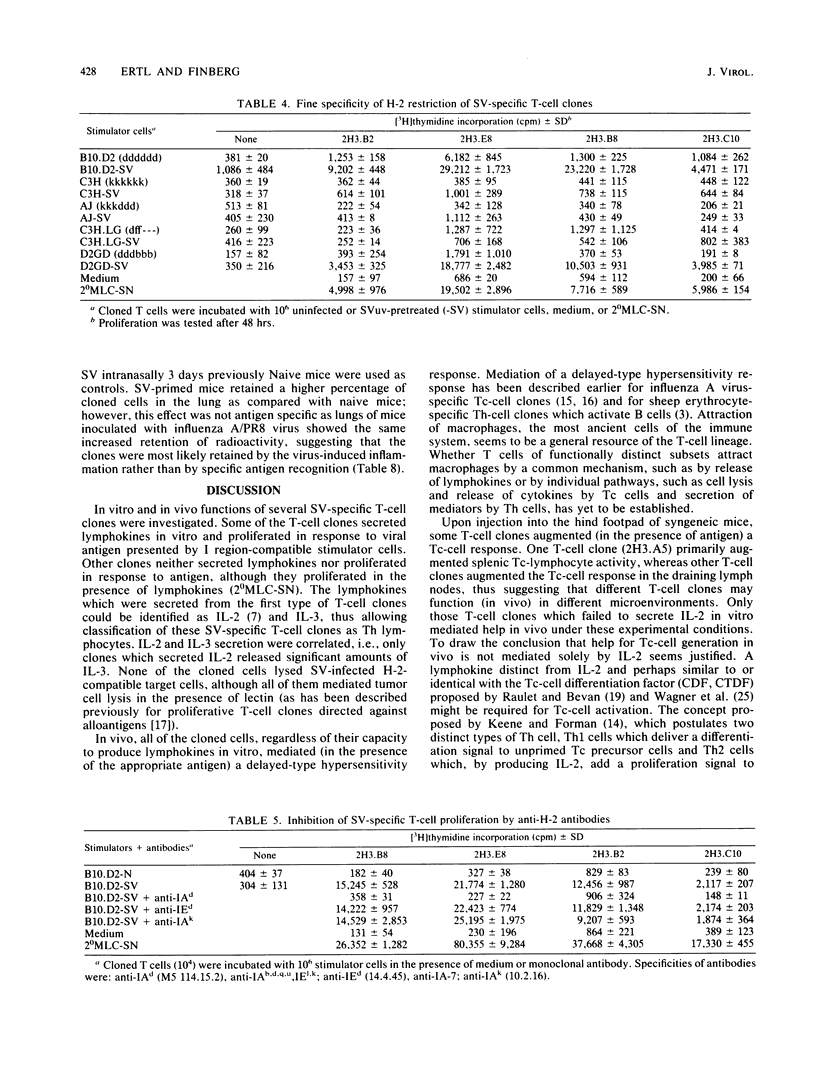
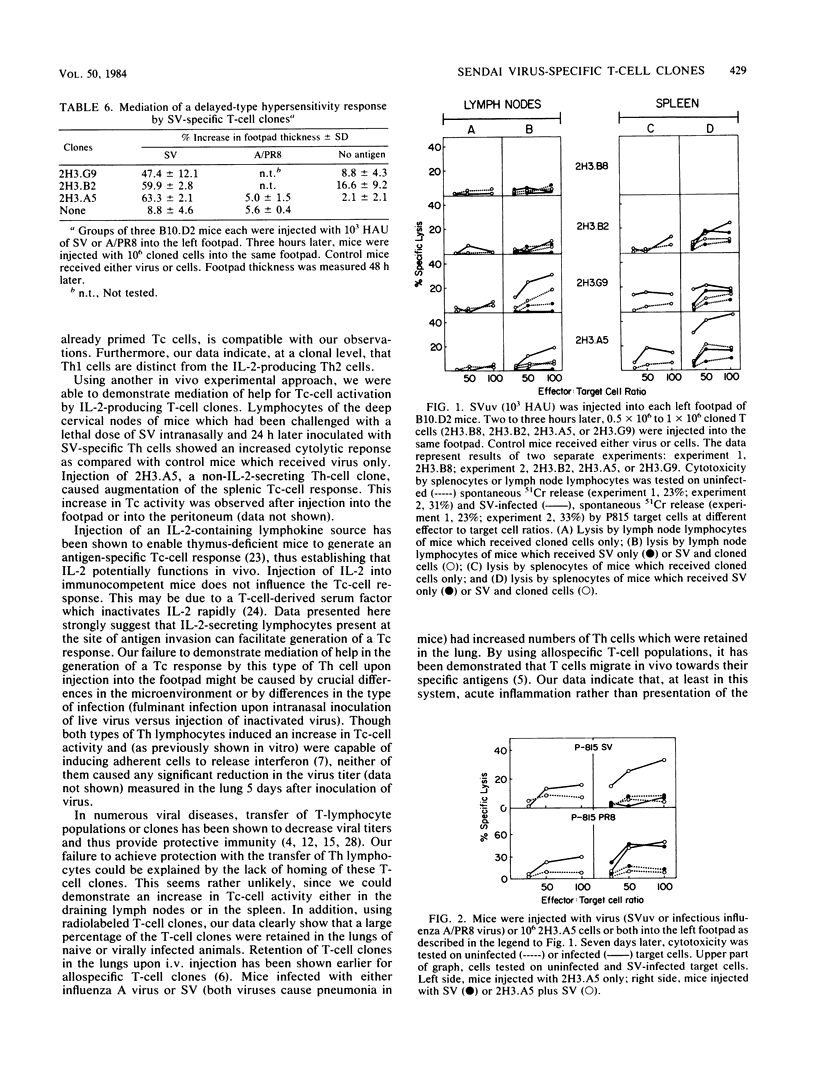
Several murine Sendai virus-specific T-cell clones were characterized in vitro and in vivo. All T-cell clones were phenotypically Thy-1.2+, and most clones were Lyt-1+,2-; one T-cell clone was Lyt-1-,2-. Some of the clones proliferated in response to antigen presented on I region-compatible stimulator cells. Proliferation could be inhibited by monoclonal antibodies directed against class II antigens. Clones which proliferated in response to antigen secreted lymphokines which could be identified as Interleukin 2 and Interleukin 3. All of the clones tested in vivo induced a delayed-type hypersensitivity response in syngeneic mice challenged with antigens. Depending on the experimental conditions chosen, Interleukin 2-producing clones as well as non-Interleukin 2-producing clones mediated help for stimulation of cytolytic T lymphocytes.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ada G. L., Leung K. N., Ertl H. An analysis of effector T cell generation and function in mice exposed to influenza A or Sendai viruses. Immunol Rev. 1981;58:5–24. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1981.tb00347.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altman A., Cohen I. R. Cell-free media of mixed lymphocyte cultures augmenting sensitization in vitro of mouse T lymphocytes against allogeneic fibroblasts. Eur J Immunol. 1976 Jul;5(7):437–444. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830050702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bianchi A. T., Hooijkaas H., Benner R., Tees R., Nordin A. A., Schreier M. H. Clones of helper T cells mediate antigen-specific, H-2-restricted DTH. Nature. 1981 Mar 5;290(5801):62–63. doi: 10.1038/290062a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanden R. V. T cell response to viral and bacterial infection. Transplant Rev. 1974;19(0):56–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1974.tb00128.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emeson E. E. Migratory behavior of lymphocytes with specific reactivity to alloantigens. II. Selective recruitment to lymphoid cell allografts and their draining lymph nodes. J Exp Med. 1978 Jan 1;147(1):13–24. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.1.13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ertl H. C., Brown E. G., Finberg R. W. Sendai virus-specific T cell clones II. Induction of interferon production by Sendai virus-specific T helper cell clones. Eur J Immunol. 1982 Dec;12(12):1051–1053. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830121212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ertl H. C., Gerlich W., Koszinowski U. H. Detection of antibodies to Sendai virus by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). J Immunol Methods. 1979;28(1-2):163–176. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(79)90338-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glasebrook A. L., Fitch F. W. Alloreactive cloned T cell lines. I. Interactions between cloned amplifier and cytolytic T cell lines. J Exp Med. 1980 Apr 1;151(4):876–895. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.4.876. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glasebrook A. L., Sarmiento M., Loken M. R., Dialynas D. P., Quintans J., Eisenberg L., Lutz C. T., Wilde D., Fitch F. W. Murine T lymphocyte clones with distinct immunological functions. Immunol Rev. 1981;54:225–266. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1981.tb00439.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas W., Mathur-Rochat J., Pohlit H., Nabholz M., von Boehmer H. Cytotoxic T cell responses to haptenated cells. III. Isolation and specificity analysis of continuously growing clones. Eur J Immunol. 1980 Nov;10(11):828–834. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830101106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howes E. L., Taylor W., Mitchison N. A., Simpson E. MHC matching shows that at least two T-cell subsets determine resistance to HSV. Nature. 1979 Jan 4;277(5691):66–68. doi: 10.1038/277067a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ihle J. N., Rebar L., Keller J., Lee J. C., Hapel A. J. Interleukin 3: possible roles in the regulation of lymphocyte differentiation and growth. Immunol Rev. 1982;63:5–32. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1982.tb00409.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keene J. A., Forman J. Helper activity is required for the in vivo generation of cytotoxic T lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1982 Mar 1;155(3):768–782. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.3.768. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin Y. L., Askonas B. A. Biological properties of an influenza A virus-specific killer T cell clone. Inhibition of virus replication in vivo and induction of delayed-type hypersensitivity reactions. J Exp Med. 1981 Aug 1;154(2):225–234. doi: 10.1084/jem.154.2.225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu L. Y., Askonas B. A. Cross-reactivity for different type A influenza viruses of a cloned T-killer cell line. Nature. 1980 Nov 13;288(5787):164–165. doi: 10.1038/288164a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plate J. M. Soluble factors substitute for T-T-cell collaboration in generation of T-killer lymphocytes. Nature. 1976 Mar 25;260(5549):329–331. doi: 10.1038/260329a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raulet D. H., Bevan M. J. A differentiation factor required for the expression of cytotoxic T-cell function. Nature. 1982 Apr 22;296(5859):754–757. doi: 10.1038/296754a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryser J. E., Cerottini J. C., Brunner K. T. Generation of cytolytic T lymphocytes in vitro. IX. induction of secondary CTL responses in primary long-term MLC by supernatants from secondary MLC. J Immunol. 1978 Feb;120(2):370–377. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreier M. H., Iscove N. N., Tees R., Aarden L., von Boehmer H. Clones of killer and helper T cells: growth requirements, specificity and retention of function in long-term culture. Immunol Rev. 1980;51:315–336. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1980.tb00326.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner H., Hardt C., Heeg K., Pfizenmaier K., Solbach W., Bartlett R., Stockinger H., Röllinghoff M. T-T cell interactions during cytotoxic T lymphocyte (CTL) responses: T cell derived helper factor (Interleukin 2) as a probe to analyze CTL responsiveness and thymic maturation of CTL progenitors. Immunol Rev. 1980;51:215–255. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1980.tb00323.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner H., Hardt C., Heeg K., Röllinghoff M., Pfizenmaier K. T-cell-derived helper factor allows in vivo induction of cytotoxic T cells in nu/nu mice. Nature. 1980 Mar 20;284(5753):278–278. doi: 10.1038/284278a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner H., Hardt C., Rouse B. T., Röllinghoff M., Scheurich P., Pfizenmaier K. Dissection of the proliferative and differentiative signals controlling murine cytotoxic T lymphocyte responses. J Exp Med. 1982 Jun 1;155(6):1876–1881. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.6.1876. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner H., Räollinghoff M., Pfizenmaier K., Hardt C., Johnscher G. T-T cell interactions during in vitro cytotoxic T lymphocyte (CTL) responses. II. Helper factor from activated Lyt 1+ T cells is rate limiting i) in T cell responses to nonimmunogenic alloantigen, ii) in thymocyte responses to allogeneic stimulator cells, and III) recruits allo- or H-2-restricted CTL precursors from the Lyt 123+ T subset. J Immunol. 1980 Mar;124(3):1058–1067. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widmer M. B., Bach F. H. Antigen-driven helper cell-independent cloned cytolytic T lymphocytes. Nature. 1981 Dec 24;294(5843):750–752. doi: 10.1038/294750a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yap K. L., Ada G. L., McKenzie I. F. Transfer of specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes protects mice inoculated with influenza virus. Nature. 1978 May 18;273(5659):238–239. doi: 10.1038/273238a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinkernagel R. M., Callahan G. N., Althage A., Cooper S., Klein P. A., Klein J. On the thymus in the differentiation of "H-2 self-recognition" by T cells: evidence for dual recognition? J Exp Med. 1978 Mar 1;147(3):882–896. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.3.882. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Boehmer H., Hengartner H., Nabholz M., Lernhardt W., Schreier M. H., Haas W. Fine specificity of a continuously growing killer cell clone specific for H-Y antigen. Eur J Immunol. 1979 Aug;9(8):592–597. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830090804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


