Abstract
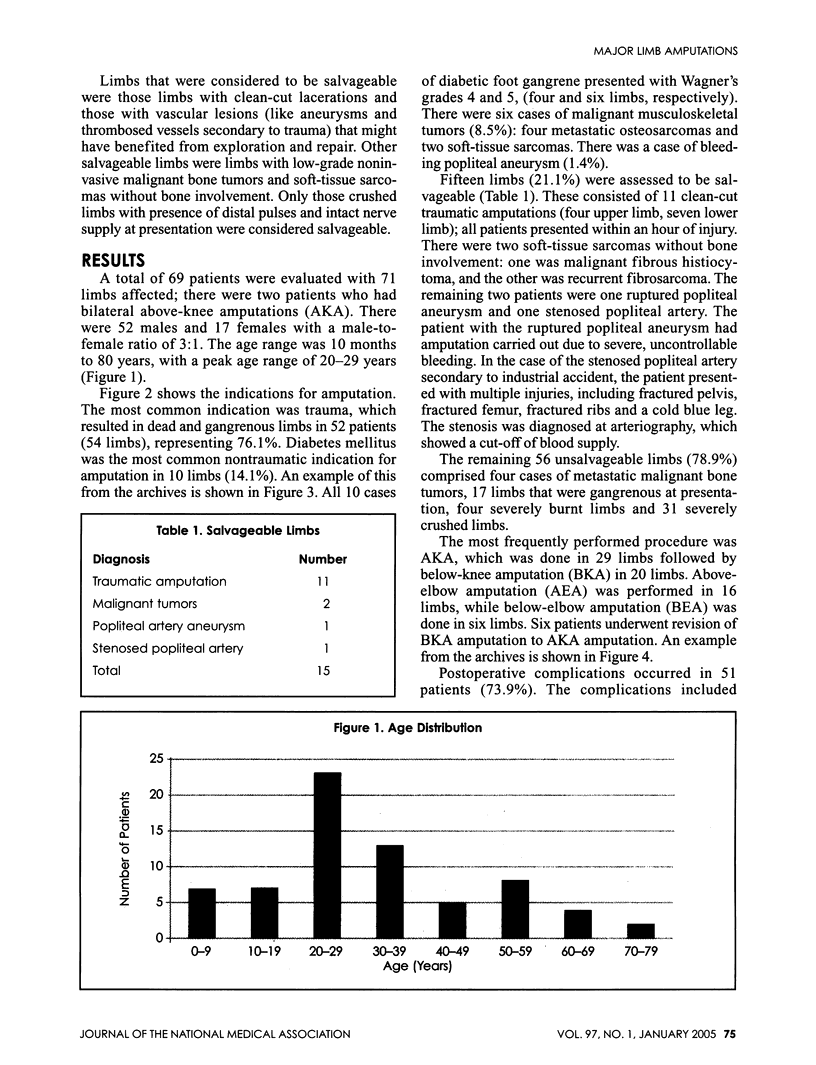
BACKGROUND: Advancements in vascular and microsurgery in developed countries have led to fewer major limb amputations. AIM: This audit of major limb amputations performed at the Olabisi Onabanjo University Teaching Hospital, Sagamu, Nigeria, between June 1998 and May 2003, was conducted to find out the indications for amputation and highlight those cases that could be salvageable. PATIENTS AND METHODS: This was a retrospective study. Case notes of all patients who had major limb amputations were examined for patients' age, sex, time of presentation, limb affected, indications for amputation, the severity of crush injury to limb, stage of musculoskeletal tumors and Wagner's grade of diabetic foot. RESULTS: A total of 71 limbs were amputated in 69 patients; 56 limbs (78.1%) were unsalvageable, while 15 limbs (21.1%) were salvageable. Trauma accounted for 76% followed by 22% performed due to gangrene secondary to diabetes mellitus. Out of the 56 unsalvageable limbs, 31 patients presented with severely crushed limbs. Out of the 15 salvageable limbs, there were 11 cases of clean-cut traumatic amputations, two of soft-tissue sarcoma and one each of ruptured popliteal aneurysm and stenosed popliteal artery. CONCLUSION: Trauma and diabetes mellitus were leading indications for amputation. Expertise in limb salvage procedures and availability of appropriate equipment may reduce the numbers of amputations performed.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abou-Zamzam Ahmed M., Jr, Teruya Theodore H., Killeen J. David, Ballard Jeffrey L. Major lower extremity amputation in an academic vascular center. Ann Vasc Surg. 2003 Jan 15;17(1):86–90. doi: 10.1007/s10016-001-0340-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aftabuddin M., Islam N., Jafar M. A., Haque I. The status of lower-limb amputation in Bangladesh: a 6-year review. Surg Today. 1997;27(2):130–134. doi: 10.1007/BF02385901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Axelrod T. S., Buchler U. Severe complex injuries to the upper extremity: revascularization and replantation. J Hand Surg Am. 1991 Jul;16(4):574–584. doi: 10.1016/0363-5023(91)90176-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowen C. V., Beveridge J., Milliken R. G., Johnston G. H. Rotating shaft avulsion amputations of the thumb. J Hand Surg Am. 1991 Jan;16(1):117–121. doi: 10.1016/s0363-5023(10)80024-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregory-Dean A. Amputations: statistics and trends. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 1991 May;73(3):137–142. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregory R. T., Gould R. J., Peclet M., Wagner J. S., Gilbert D. A., Wheeler J. R., Snyder S. O., Gayle R. G., Schwab C. W. The mangled extremity syndrome (M.E.S.): a severity grading system for multisystem injury of the extremity. J Trauma. 1985 Dec;25(12):1147–1150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helfet D. L., Howey T., Sanders R., Johansen K. Limb salvage versus amputation. Preliminary results of the Mangled Extremity Severity Score. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1990 Jul;(256):80–86. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korn P., Hoenig S. J., Skillman J. J., Kent K. C. Is lower extremity revascularization worthwhile in patients with end-stage renal disease? Surgery. 2000 Sep;128(3):472–479. doi: 10.1067/msy.2000.108049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kutz J. E., Jupiter J. B., Tsai T. M. Lower limb replantation. A report of nine cases. Foot Ankle. 1983 Jan-Feb;3(4):197–202. doi: 10.1177/107110078300300403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muyembe V. M., Muhinga M. N. Major limb amputation at a provincial general hospital in Kenya. East Afr Med J. 1999 Mar;76(3):163–166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogunlade S. O., Alonge T. O., Omololu A. B. O., Gana J. Y., Salawu S. A. Major limb amputation in Ibadan. Afr J Med Med Sci. 2002 Dec;31(4):333–336. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onuminya J. E., Obekpa P. O., Ihezue H. C., Ukegbu N. D., Onabowale B. O. Major amputations in Nigeria: a plea to educate traditional bone setters. Trop Doct. 2000 Jul;30(3):133–135. doi: 10.1177/004947550003000306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sillesen H. Conservative treatment, amputation or revascularisation for critical limb ischaemia. Ann Chir Gynaecol. 1998;87(2):159–161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soucacos P. N., Dailiana Z. H., Beris A. E., Xenakis T. H., Malizos K. N., Chrisovitsinos J. Major ablative procedures in orthopaedic surgery. Bull Hosp Jt Dis. 1996;55(1):46–52. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stojadinovic A., Jaques D. P., Leung D. H., Healey J. H., Brennan M. F. Amputation for recurrent soft tissue sarcoma of the extremity: indications and outcome. Ann Surg Oncol. 2001 Jul;8(6):509–518. doi: 10.1007/s10434-001-0509-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan M. H., Gwee H. M., Yeo P. P., Lim P., Bose K. Diabetic amputees in Singapore. Tohoku J Exp Med. 1983 Dec;141 (Suppl):575–582. doi: 10.1620/tjem.141.suppl_575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tefera Girma, Turnipseed William, Tanke Timothy. Limb salvage angioplasty in poor surgical candidates. Vasc Endovascular Surg. 2003 Mar-Apr;37(2):99–104. doi: 10.1177/153857440303700203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomaino M. M. Lower limb salvage: microvascular reconstruction of post-traumatic soft tissue and skeletal defects. Orthopedics. 1995 Jul;18(7):665–672. doi: 10.3928/0147-7447-19950701-15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomaino M., Bowen V. Reconstructive surgery for lower limb salvage. Can J Surg. 1995 Jun;38(3):221–228. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williard W. C., Collin C., Casper E. S., Hajdu S. I., Brennan M. F. The changing role of amputation for soft tissue sarcoma of the extremity in adults. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1992 Nov;175(5):389–396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




