Abstract
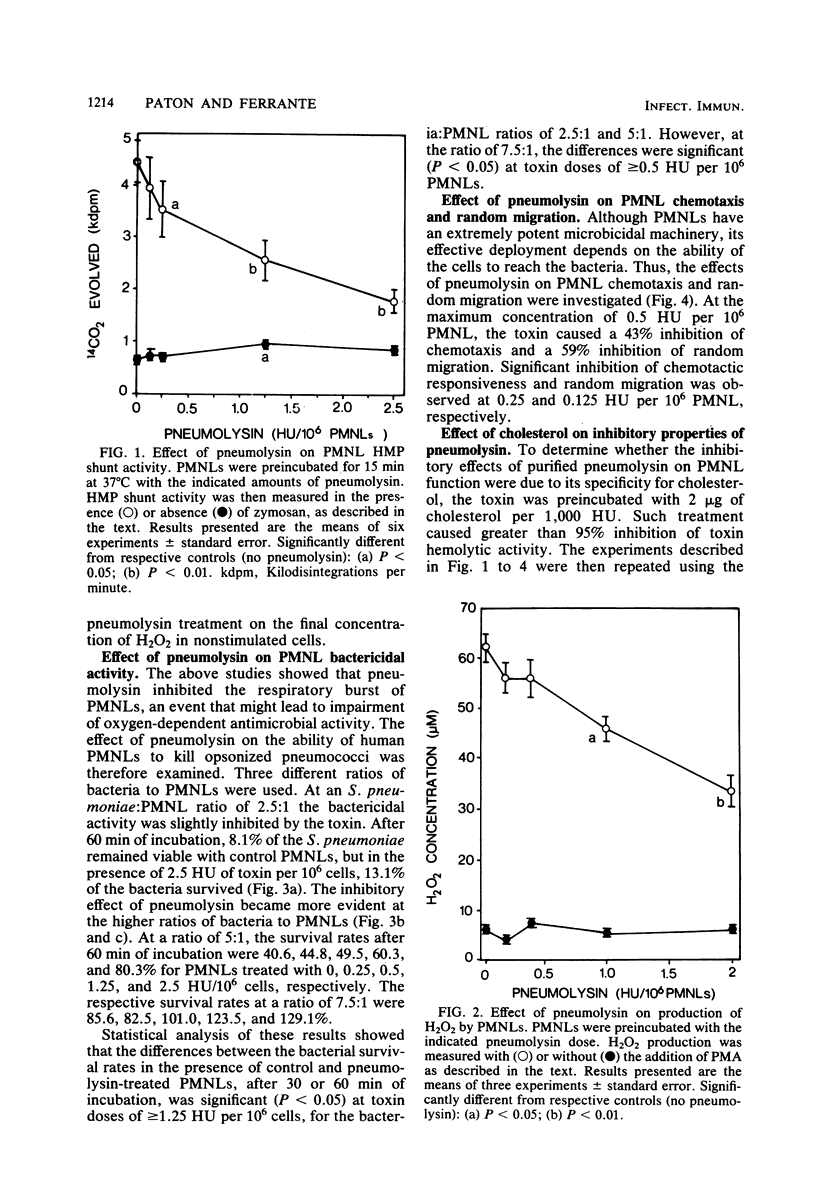
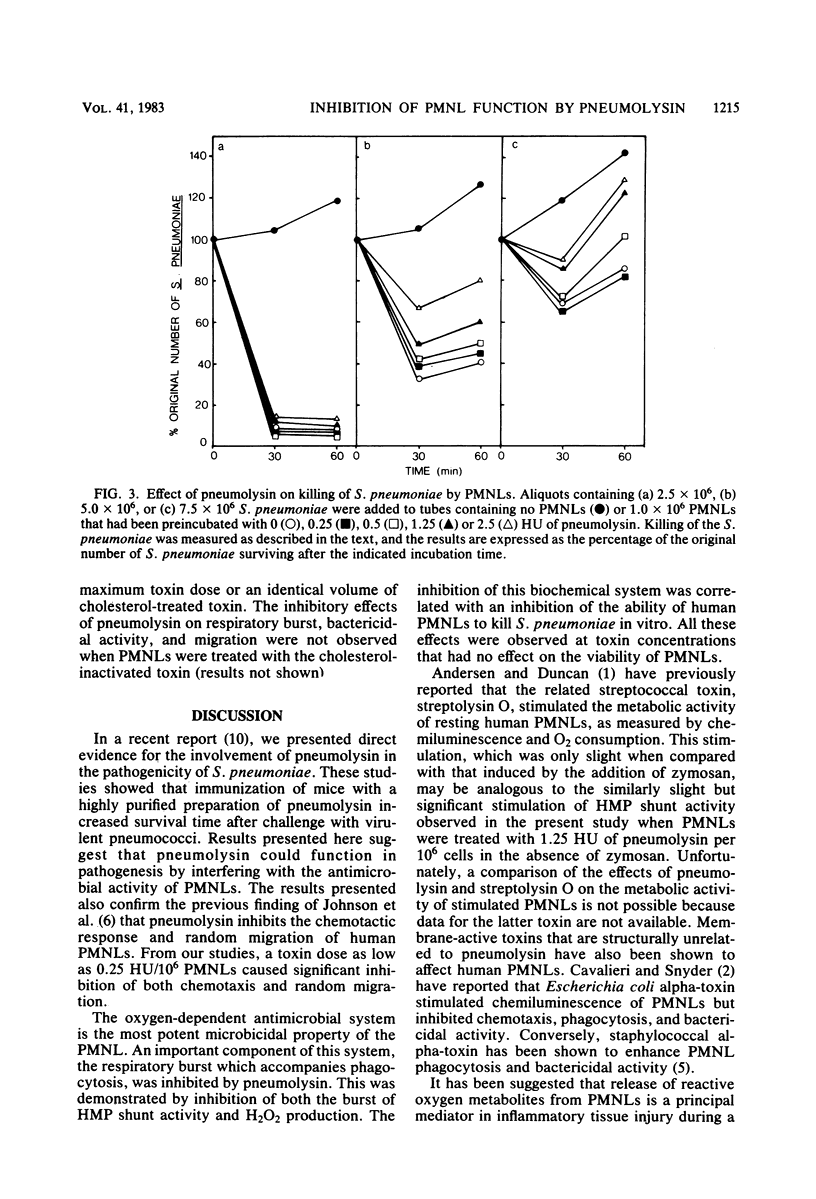
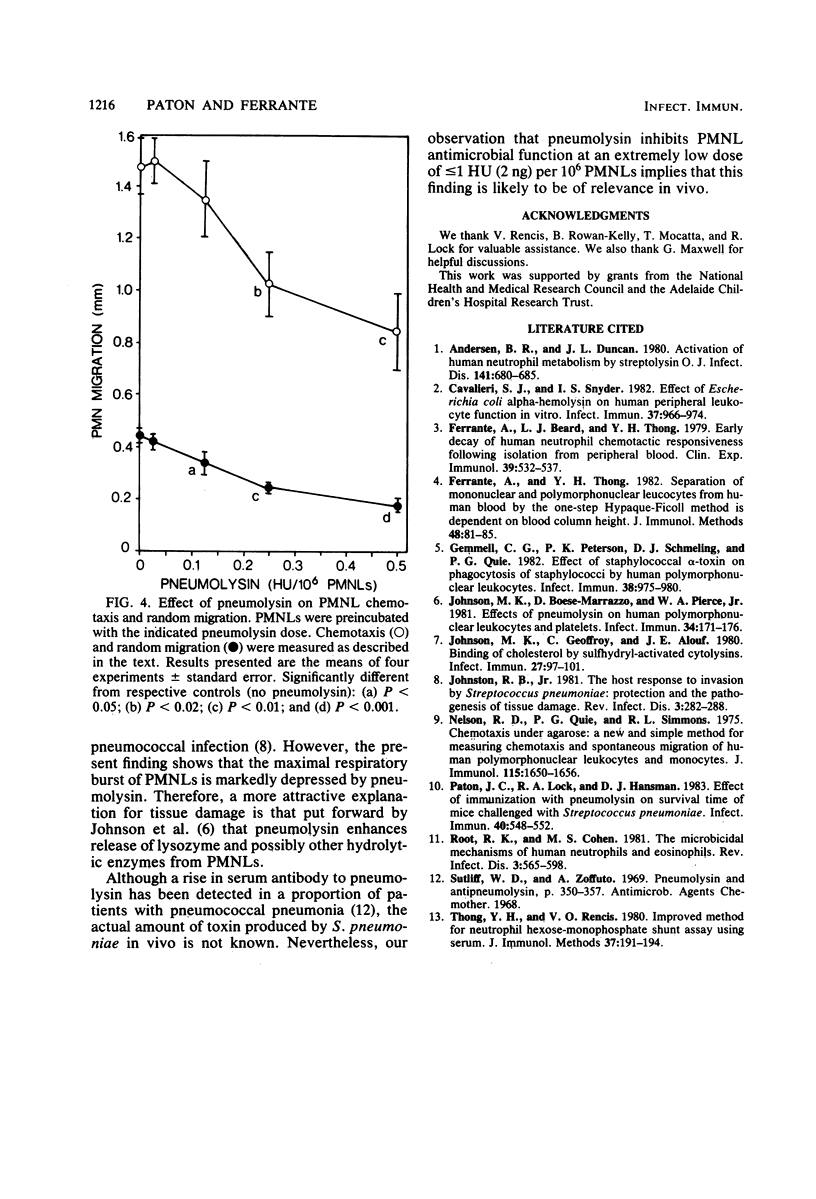
The in vitro effects of pneumolysin, a sulfhydryl-activated toxin produced by Streptococcus pneumoniae, on various functions of human polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMNLs) was investigated. Treatment of PMNLs with highly purified toxin significantly inhibited respiratory burst (in response to stimulation), ability to kill opsonized pneumococci, chemotaxis, and random migration. These inhibitions were observed at very low toxin doses (less than or equal to 1 hemolytic unit (2 ng) per 10(6) PMNLs), which had no effect on PMNL viability. These results suggest that pneumolysin could function in pathogenicity by interfering with the ability of PMNLs to migrate toward and kill pneumococci.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersen B. R., Duncan J. L. Activation of human neutrophil metabolism by streptolysin O. J Infect Dis. 1980 May;141(5):680–685. doi: 10.1093/infdis/141.5.680. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavalieri S. J., Snyder I. S. Effect of Escherichia coli alpha-hemolysin on human peripheral leukocyte function in vitro. Infect Immun. 1982 Sep;37(3):966–974. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.3.966-974.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrante A., Beard L. J., Thong Y. H. Early decay of human neutrophil chemotactic responsiveness following isolation from peripheral blood. Clin Exp Immunol. 1980 Feb;39(2):532–537. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrante A., Thong Y. H. Separation of mononuclear and polymorphonuclear leucocytes from human blood by the one-step Hypaque-Ficoll method is dependent on blood column height. J Immunol Methods. 1982;48(1):81–85. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(82)90212-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gemmell C. G., Peterson P. K., Schmeling D. J., Quie P. G. Effect of staphylococcal alpha-toxin on phagocytosis of staphylococci by human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Infect Immun. 1982 Dec;38(3):975–980. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.3.975-980.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson M. K., Boese-Marrazzo D., Pierce W. A., Jr Effects of pneumolysin on human polymorphonuclear leukocytes and platelets. Infect Immun. 1981 Oct;34(1):171–176. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.1.171-176.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson M. K., Geoffroy C., Alouf J. E. Binding of cholesterol by sulfhydryl-activated cytolysins. Infect Immun. 1980 Jan;27(1):97–101. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.1.97-101.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston R. B., Jr The host response to invasion by Streptococcus pneumoniae: protection and the pathogenesis to tissue damage. Rev Infect Dis. 1981 Mar-Apr;3(2):282–288. doi: 10.1093/clinids/3.2.282. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson R. D., Quie P. G., Simmons R. L. Chemotaxis under agarose: a new and simple method for measuring chemotaxis and spontaneous migration of human polymorphonuclear leukocytes and monocytes. J Immunol. 1975 Dec;115(6):1650–1656. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paton J. C., Lock R. A., Hansman D. J. Effect of immunization with pneumolysin on survival time of mice challenged with Streptococcus pneumoniae. Infect Immun. 1983 May;40(2):548–552. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.2.548-552.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Root R. K., Cohen M. S. The microbicidal mechanisms of human neutrophils and eosinophils. Rev Infect Dis. 1981 May-Jun;3(3):565–598. doi: 10.1093/clinids/3.3.565. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thong Y. H., Rencis V. O. Improved method for neutrophil hexose-monophosphate shunt assay using serum. J Immunol Methods. 1980;37(2):191–194. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(80)90204-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


