Abstract
The clinical course of a patient with bronchitis caused by Bordetella bronchiseptica is described. The organism was recovered on one occasion from a protected catheter brush specimen obtained at bronchoscopy and on two occasions from expectorated sputum specimens. The infection was eradicated with antimicrobial therapy.
Full text
PDF
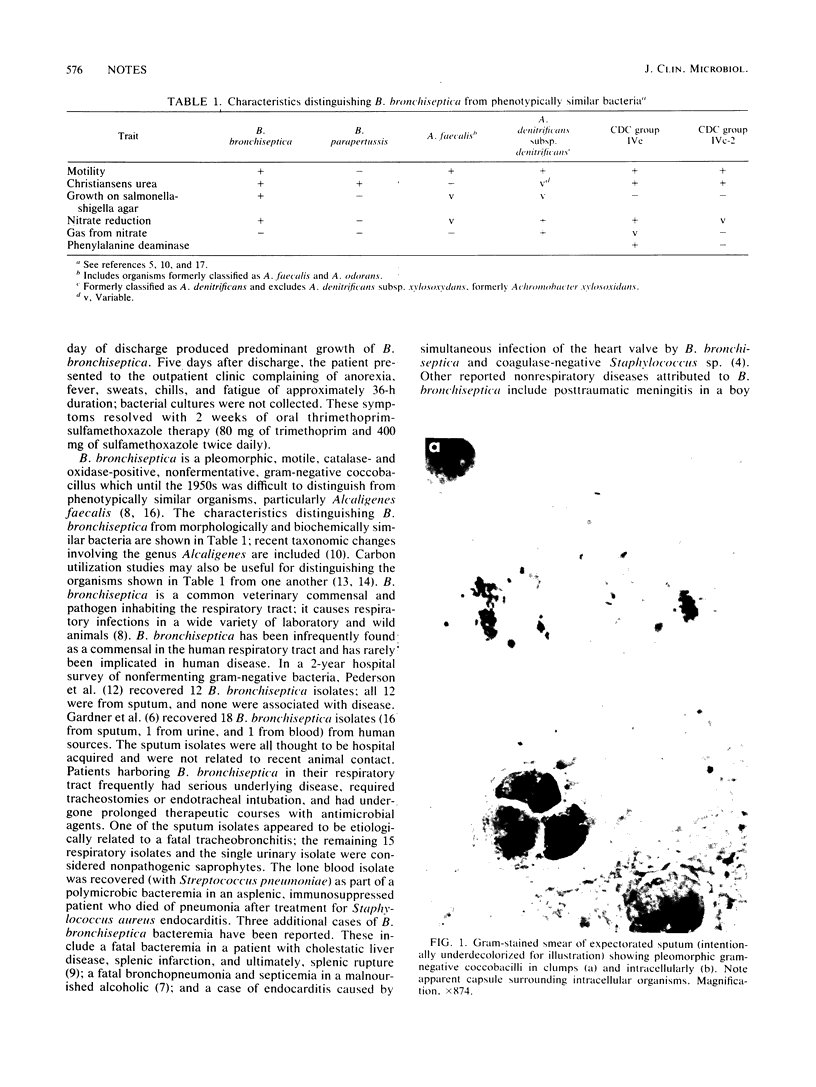

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Byrd L. H., Anama L., Gutkin M., Chmel H. Bordetella bronchiseptica peritonitis associated with continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Aug;14(2):232–233. doi: 10.1128/jcm.14.2.232-233.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang K. C., Zakhein R. M., Cho C. T., Montgomery J. C. Letter: Posttraumatic purulent meningitis due to Bordetella bronchiseptica. J Pediatr. 1975 Apr;86(4):639–640. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(75)80178-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner P., Griffin W. B., Swartz M. N., Kunz L. J. Nonfermentative gram-negative bacilli of nosocomial interest. Am J Med. 1970 Jun;48(6):735–749. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9343(70)80009-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh H. K., Tranter J. Bordetella bronchicanis (bronchiseptica) infection in man: review and a case report. J Clin Pathol. 1979 Jun;32(6):546–548. doi: 10.1136/jcp.32.6.546. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodnow R. A. Biology of Bordetella bronchiseptica. Microbiol Rev. 1980 Dec;44(4):722–738. doi: 10.1128/mr.44.4.722-738.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRISTENSEN K. H., LAUTROP H. [A family epidemic caused by the whooping-cough bacterium Bordetella bronchiseptica]. Ugeskr Laeger. 1962 Mar 9;124:303–308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katzenstein D. A., Ciofalo L., Jordan M. C. Bordetella bronchiseptica bacteremia. West J Med. 1984 Jan;140(1):96–98. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen M. M., Marso E., Pickett M. J. Nonfermentative bacilli associated with man. 3. Pathogenicity and antibiotic susceptibility. Am J Clin Pathol. 1970 Aug;54(2):178–192. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/54.2.178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickett M. J., Greenwood J. R. Identification of oxidase-positive, glucose-negative, motile species of nonfermentative bacilli. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 May;23(5):920–923. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.5.920-923.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rarick H. R., Riley P. S., Martin R. Carbon substrate utilization studies of some cultures of Alcaligenes denitrificans, Alcaligenes faecalis, and Alcaligenes odorans isolated from clinical specimens. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Sep;8(3):313–319. doi: 10.1128/jcm.8.3.313-319.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoll D. B., Murphey S. A., Ballas S. K. Bordetella bronchiseptica infection in stage IV Hodgkin's disease. Postgrad Med J. 1981 Nov;57(673):723–724. doi: 10.1136/pgmj.57.673.723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ULRICH J. A., NEEDHAM G. M. Differentiation of Alcaligenes faecalis from Brucella bronchisepticus by biochemical and nutritional methods. J Bacteriol. 1953 Feb;65(2):210–215. doi: 10.1128/jb.65.2.210-215.1953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]