Abstract
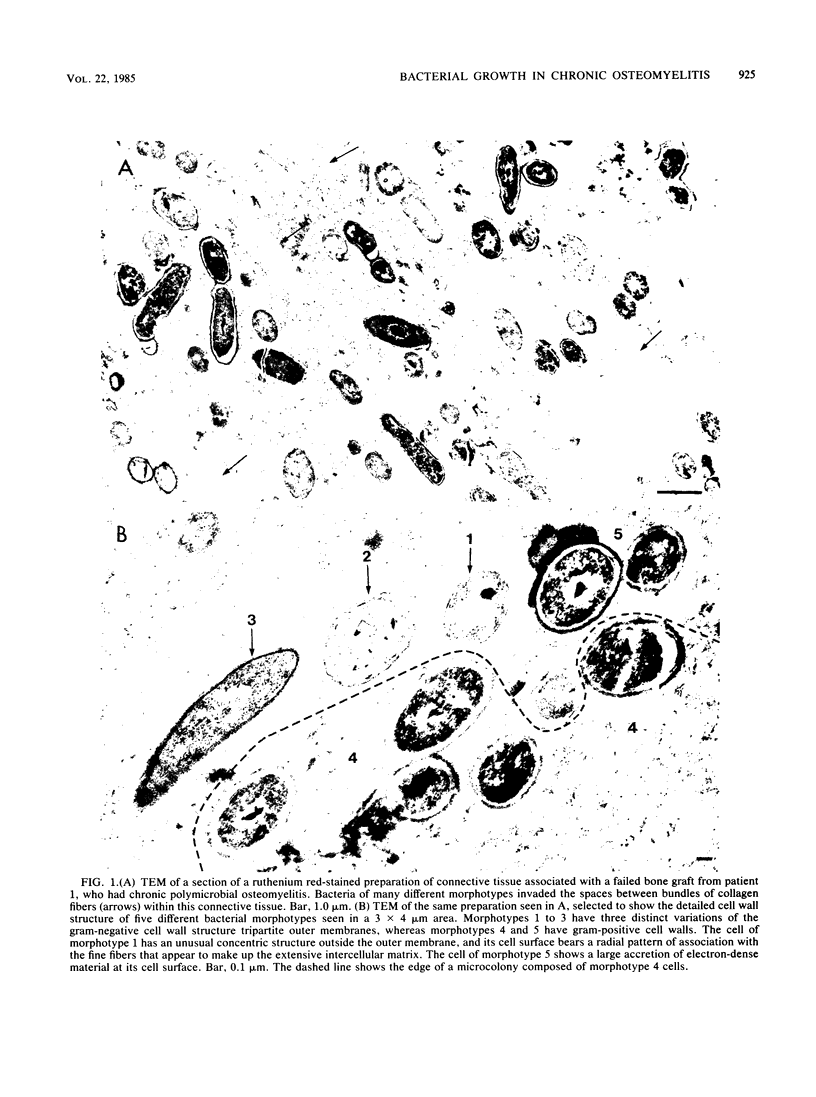
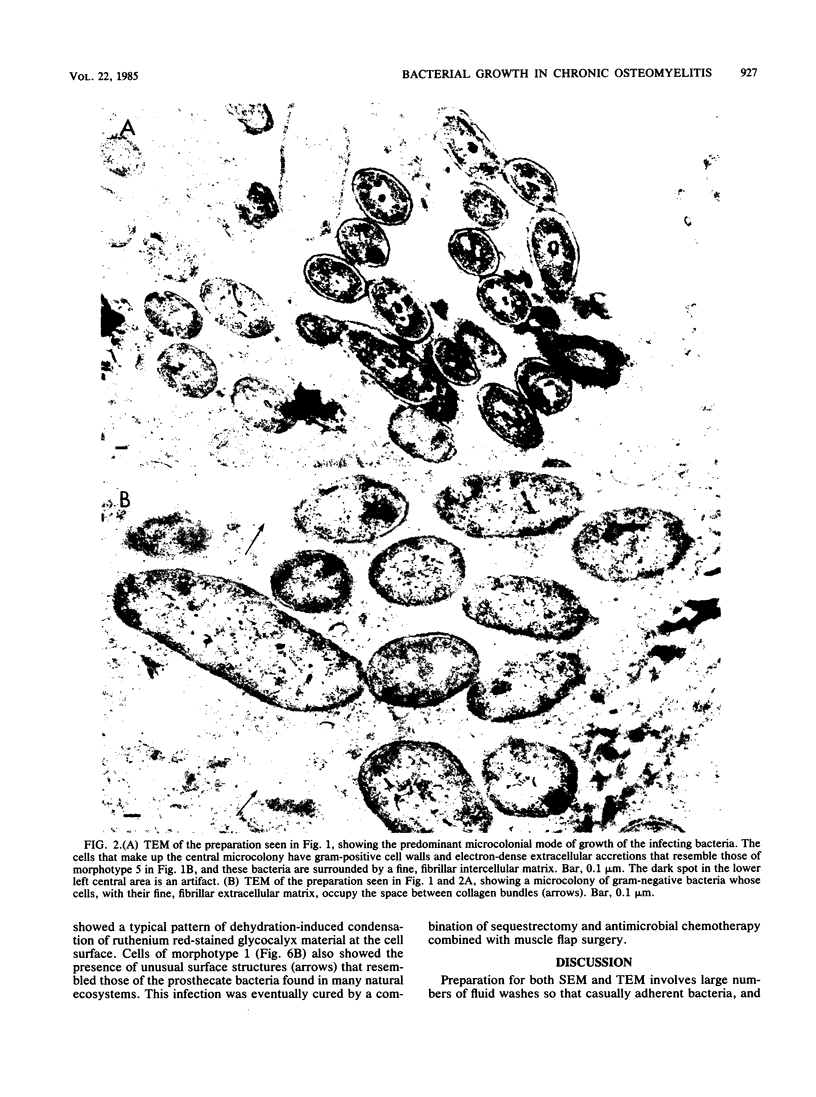
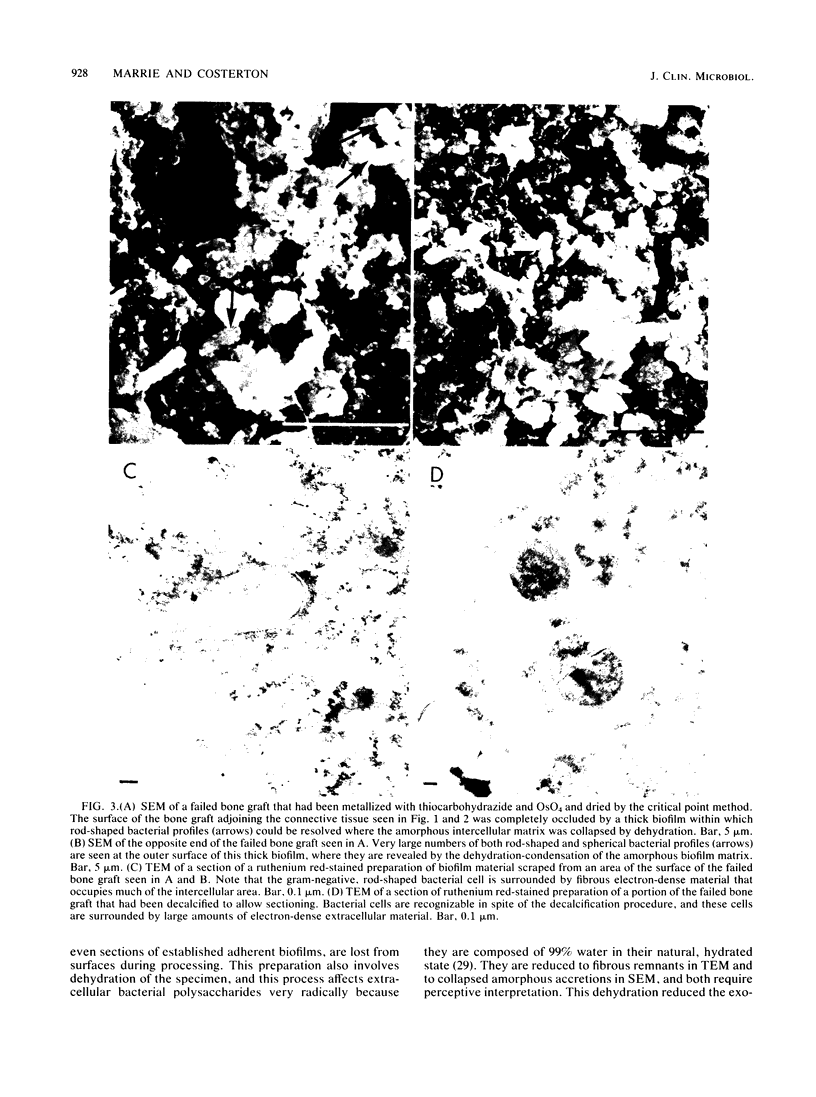
Direct examination of material from two cases of persistent (2 and 60 years) osteomyelitis by morphological and culture techniques showed that the pathogens comprised several bacterial species whose cells grew predominantly in discrete exopolysaccharide-enclosed microcolonies made up of a single bacterial morphotype. Bacterial microcolonies were seen between tissue elements in infected connective tissue, and the microcolonies adherent to bone surfaces coalesced to form extensive biofilms that occluded the surfaces of dead bone in sequestrae. Decalcification techniques were required to examine the interior of infected bone, but recognizable remnants were associated with very large amounts of fibrous, ruthenium red-stained material. All bacterial growth in these persistent infections occurred within an intercellular matrix, and some elements of this matrix, which was fibrous in transmission electron microscopy and amorphous in scanning electron microscopy, were associated with the surfaces of bacterial cells in a manner that suggested their production by these organisms. All of the implications of this microcolony mode of bacterial growth in osteomyelitis, and in other chronic bacterial diseases, have yet to be determined.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baltimore R. S., Mitchell M. Immunologic investigations of mucoid strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: comparison of susceptibility to opsonic antibody in mucoid and nonmucoid strains. J Infect Dis. 1980 Feb;141(2):238–247. doi: 10.1093/infdis/141.2.238. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng K. J., Irvin R. T., Costerton J. W. Autochthonous and pathogenic colonization of animal tissues by bacteria. Can J Microbiol. 1981 May;27(5):461–490. doi: 10.1139/m81-071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen G. D., Simpson W. A., Bisno A. L., Beachey E. H. Adherence of slime-producing strains of Staphylococcus epidermidis to smooth surfaces. Infect Immun. 1982 Jul;37(1):318–326. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.1.318-326.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costerton J. W., Irvin R. T., Cheng K. J. The role of bacterial surface structures in pathogenesis. Crit Rev Microbiol. 1981;8(4):303–338. doi: 10.3109/10408418109085082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costerton J. W. The etiology and persistence of cryptic bacterial infections: a hypothesis. Rev Infect Dis. 1984 Sep-Oct;6 (Suppl 3):S608–S616. doi: 10.1093/clinids/6.supplement_3.s608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Govan J. R. Mucoid strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: the influence of culture medium on the stability of mucus production. J Med Microbiol. 1975 Nov;8(4):513–522. doi: 10.1099/00222615-8-4-513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gristina A. G., Costerton J. W. Bacterial adherence and the glycocalyx and their role in musculoskeletal infection. Orthop Clin North Am. 1984 Jul;15(3):517–535. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lam J., Chan R., Lam K., Costerton J. W. Production of mucoid microcolonies by Pseudomonas aeruginosa within infected lungs in cystic fibrosis. Infect Immun. 1980 May;28(2):546–556. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.2.546-556.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Locci R., Peters G., Pulverer G. Microbial colonization of prosthetic devices. III. Adhesion of staphylococci to lumina of intravenous catheters perfused with bacterial suspensions. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg B. 1981;173(5):300–307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marrie T. J., Cooper J. H., Costerton J. W. Ultrastructure of Candida parapsilosis endocarditis. Infect Immun. 1984 Aug;45(2):390–398. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.2.390-398.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marrie T. J., Noble M. A., Costerton J. W. Examination of the morphology of bacteria adhering to peritoneal dialysis catheters by scanning and transmission electron microscopy. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Dec;18(6):1388–1398. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.6.1388-1398.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayberry-Carson K. J., Tober-Meyer B., Smith J. K., Lambe D. W., Jr, Costerton J. W. Bacterial adherence and glycocalyx formation in osteomyelitis experimentally induced with Staphylococcus aureus. Infect Immun. 1984 Mar;43(3):825–833. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.3.825-833.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McInerney M. J., Bryant M. P., Hespell R. B., Costerton J. W. Syntrophomonas wolfei gen. nov. sp. nov., an Anaerobic, Syntrophic, Fatty Acid-Oxidizing Bacterium. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Apr;41(4):1029–1039. doi: 10.1128/aem.41.4.1029-1039.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills J., Pulliam L., Dall L., Marzouk J., Wilson W., Costerton J. W. Exopolysaccharide production by viridans streptococci in experimental endocarditis. Infect Immun. 1984 Jan;43(1):359–367. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.1.359-367.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nickel J. C., Ruseska I., Wright J. B., Costerton J. W. Tobramycin resistance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa cells growing as a biofilm on urinary catheter material. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Apr;27(4):619–624. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.4.619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nickel J. C., Wright J. B., Ruseska I., Marrie T. J., Whitfield C., Costerton J. W. Antibiotic resistance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa colonizing a urinary catheter in vitro. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Apr;4(2):213–218. doi: 10.1007/BF02013600. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters G., Locci R., Pulverer G. Microbial colonization of prosthetic devices. II. Scanning electron microscopy of naturally infected intravenous catheters. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg B. 1981;173(5):293–299. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarzmann S., Boring J. R. Antiphagocytic Effect of Slime from a Mucoid Strain of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1971 Jun;3(6):762–767. doi: 10.1128/iai.3.6.762-767.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]