Abstract
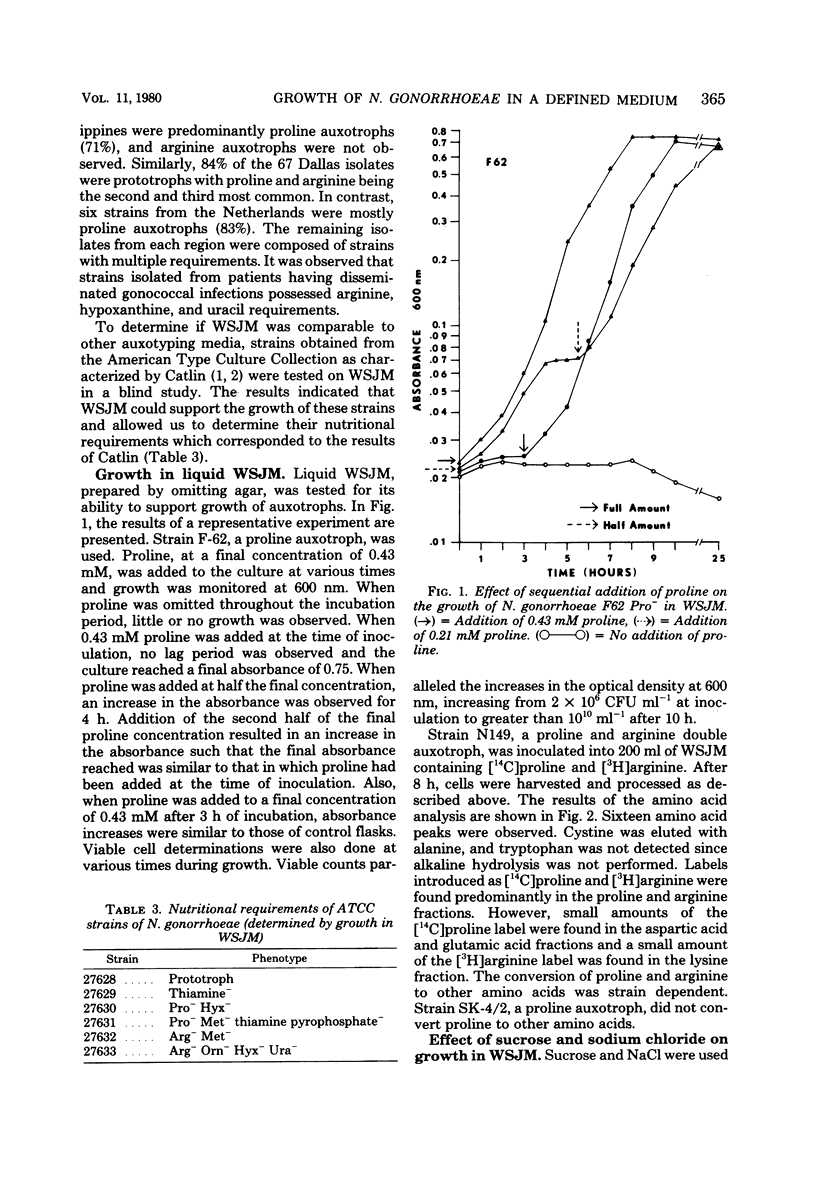
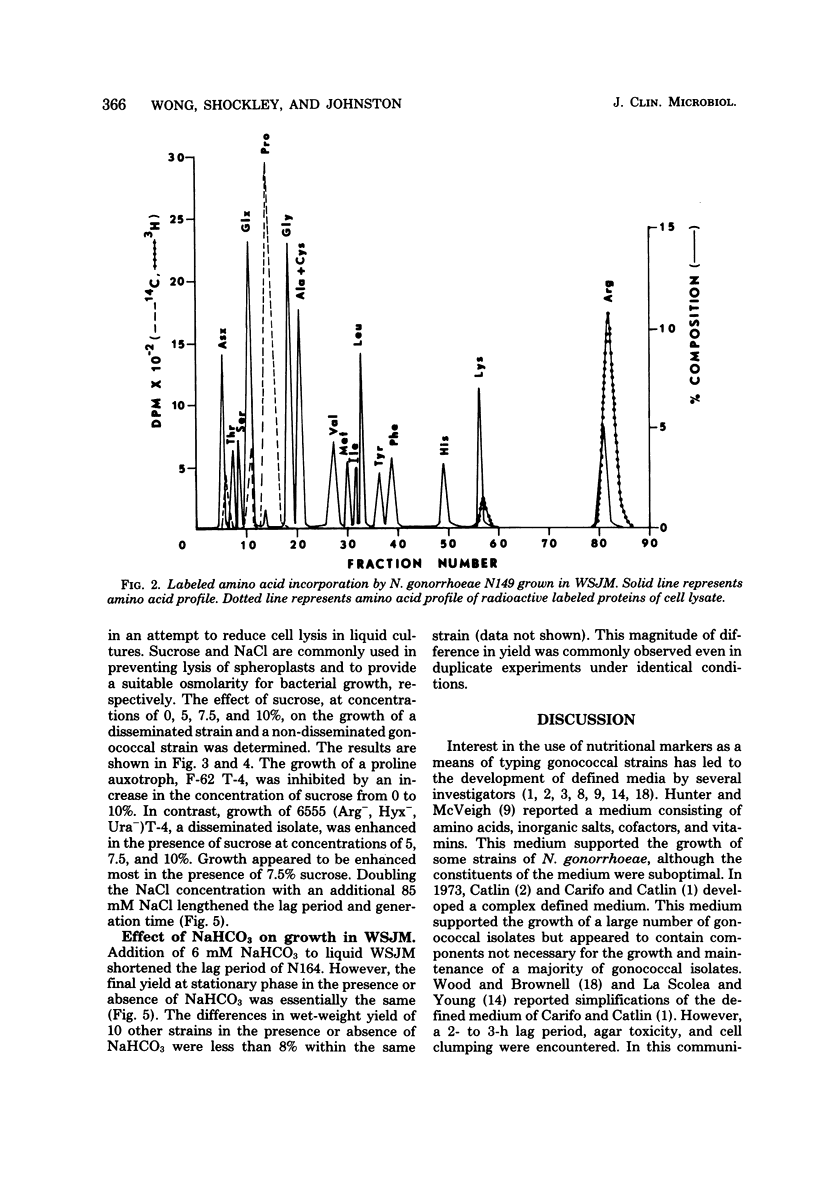
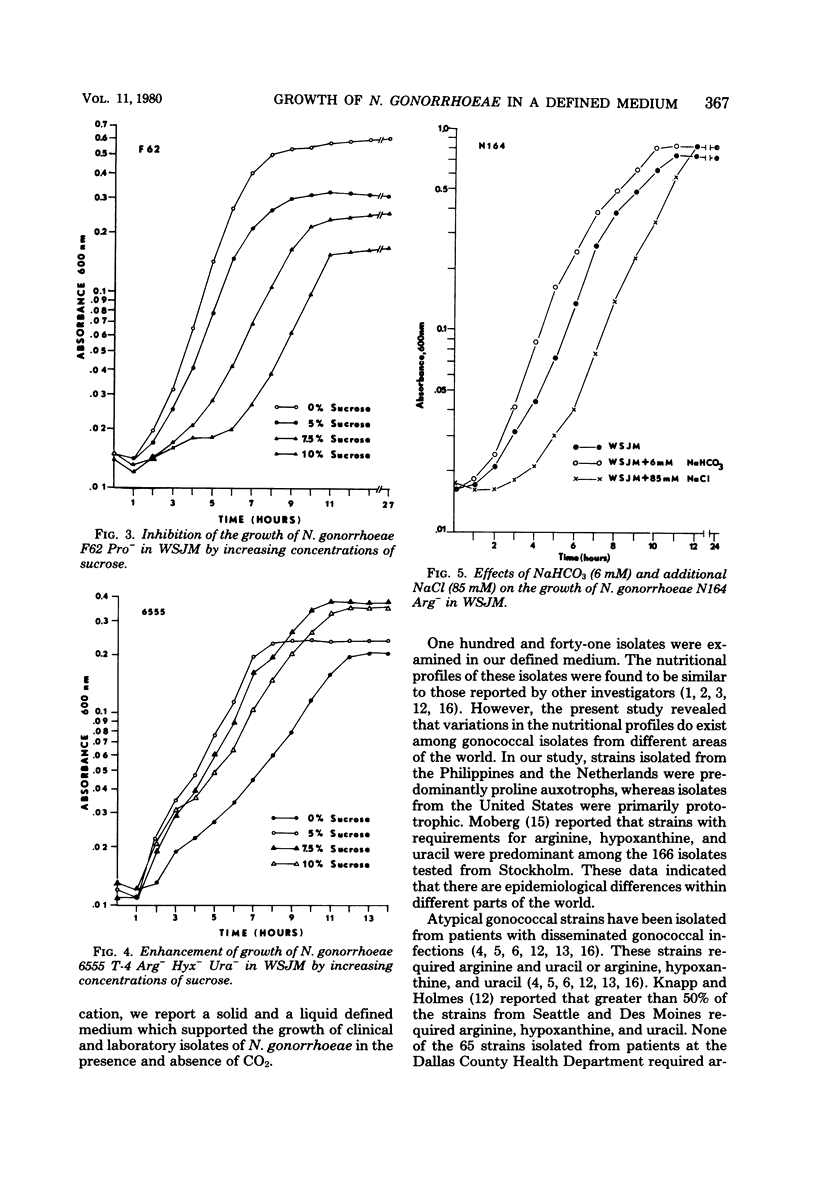
The growth requirements of 135 clinical isolates of Neisseria gonorrhoeae and six American Type Culture Collection reference strains were examined by using a simple chemically defined medium known as Wong-Shockley-Johnston medium, WSJM. The simple liquid medium supported growth of gonococci from an inoculum of 2 X 10(6) colony-forming units ml-1 and yielded 10(10) colony-forming units ml-1 in 10 h in the absence of CO2. Scale-up experiments with the complete medium yielded 5 to 10 g, wet weight, of cells per liter. The complete medium was stable upon storage at 5 degrees C and after lyophilization.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Carifo K., Catlin B. W. Neisseria gonorrhoeae auxotyping: differentiation of clinical isolates based on growth responses on chemically defined media. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Sep;26(3):223–230. doi: 10.1128/am.26.3.223-230.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catlin B. W. Nutritional profiles of Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Neisseria meningitidis, and Neisseria lactamica in chemically defined media and the use of growth requirements for gonococcal typing. J Infect Dis. 1973 Aug;128(2):178–194. doi: 10.1093/infdis/128.2.178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catlin B. W., Pace P. J. Auxotypes and penicillin susceptibilities of Neisseria gonorrhoeae isolated from patients with gonorrhea involving two or more sites. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Aug;12(2):147–156. doi: 10.1128/aac.12.2.147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catlin B. W., Pace P. J. Nutritional requirements and penicillin susceptibilities of gonococci from pharyngeal and anogenital sites. Br J Vener Dis. 1977 Oct;53(5):299–303. doi: 10.1136/sti.53.5.299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford C., Knapp J. S., Hale J., Holmes K. K. Asymptomatic gonorrhea in men: caused by gonococci with unique nutritional requirements. Science. 1977 Jun 17;196(4296):1352–1353. doi: 10.1126/science.405742. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elmros T., Sandström G., Burman L. Autolysis of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Relation between mechanical stability and viability. Br J Vener Dis. 1976 Aug;52(4):246–249. doi: 10.1136/sti.52.4.246. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendry A. T., Stewart I. O. Auxanographic grouping and typing of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Can J Microbiol. 1979 Apr;25(4):512–521. doi: 10.1139/m79-075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter K. M., McVeigh I. Development of a chemically defined medium for growth of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1970;36(2):305–316. doi: 10.1007/BF02069032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones R. T., Talley R. S. Effects of Gaseous CO2 and bicarbonate on the growth of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Apr;5(4):427–432. doi: 10.1128/jcm.5.4.427-432.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELLOGG D. S., Jr, PEACOCK W. L., Jr, DEACON W. E., BROWN L., PIRKLE D. I. NEISSERIA GONORRHOEAE. I. VIRULENCE GENETICALLY LINKED TO CLONAL VARIATION. J Bacteriol. 1963 Jun;85:1274–1279. doi: 10.1128/jb.85.6.1274-1279.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knapp J. S., Holmes K. K. Disseminated gonococcal infections caused by Neisseria gonorrhoeae with unique nutritional requirements. J Infect Dis. 1975 Aug;132(2):204–208. doi: 10.1093/infdis/132.2.204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- La Scolea L. J., Jr, Young F. E. Development of a defined minimal medium for the growth of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Jul;28(1):70–76. doi: 10.1128/am.28.1.70-76.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morello J. A., Lerner S. A., Bohnhoff M. Characteristics of atypical Neisseria gonorrhoeae from disseminated and localized infections. Infect Immun. 1976 May;13(5):1510–1516. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.5.1510-1516.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Short H. B., Ploscowe V. B., Weiss J. A., Young F. E. Rapid method for auxotyping multiple strains of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Sep;6(3):244–248. doi: 10.1128/jcm.6.3.244-248.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood D. O., Brownell G. H. Transformation of leucine and rifampin traits in Neisseria gonorrhoeae with deoxyribonucleic acid from homologous and heterologous origins. J Bacteriol. 1975 Feb;121(2):471–474. doi: 10.1128/jb.121.2.471-474.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


