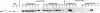Abstract
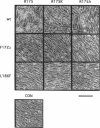
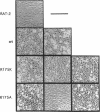
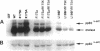
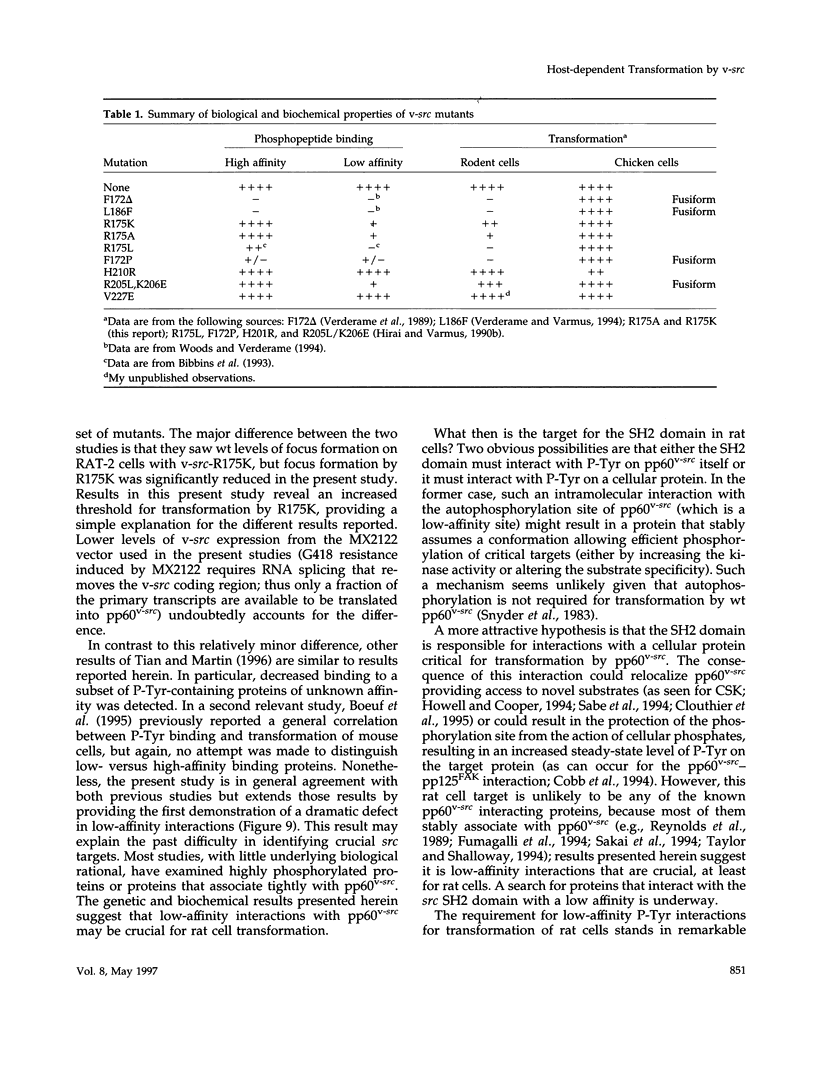
Substrates critical for transformation by pp60v-src remain unknown, as does the precise role of the src homology 2 (SH2) domain in this process. To continue exploring the role of the SH2 domain in pp60v-src-mediated transformation, site-directed mutagenesis was used to create mutant v-src alleles predicted to encode proteins with overall structural integrity intact but with reduced ability to bind phosphotyrosine-containing peptides. Arginine-175, which makes critical contacts in the phosphotyrosine-binding pocket, was mutated to lysine or alanine. Unexpectedly, both mutations created v-src alleles that transform chicken cells with wild-type (wt) efficiency and are reduced for transformation of rat cells; these alleles are host dependent for transformation. Additionally, these alleles resulted in a round morphological transformation of chicken cells, unlike 12 of the 13 known host-dependent src SH2 mutations that result in a fusiform morphology. Analysis of phosphopeptide binding by the mutant SH2 domains reveal that the in vitro ability to bind phosphopeptides known to have a high affinity for wt src SH2 correlates with wt (round) morphological transformation in chicken cells and in vitro ability to bind phosphopeptides known to have a low affinity for wt src SH2 correlates with rat cell transformation. These results suggest that the search for critical substrates in rat cells should be among proteins that interact with pp60v-src with low affinity.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bibbins K. B., Boeuf H., Varmus H. E. Binding of the Src SH2 domain to phosphopeptides is determined by residues in both the SH2 domain and the phosphopeptides. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Dec;13(12):7278–7287. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.12.7278. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boeuf H., Murphy J., Bibbins K. B., Varmus H. E. Binding in vitro of phosphotyrosine-containing proteins to pp60c-src SH2 domain does not correlate with CEF transformation. Oncogene. 1995 Feb 2;10(3):433–438. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolen J. B., Veillette A., Schwartz A. M., DeSeau V., Rosen N. Activation of pp60c-src protein kinase activity in human colon carcinoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2251–2255. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buss J. E., Kamps M. P., Gould K., Sefton B. M. The absence of myristic acid decreases membrane binding of p60src but does not affect tyrosine protein kinase activity. J Virol. 1986 May;58(2):468–474. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.2.468-474.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cartwright C. A., Eckhart W., Simon S., Kaplan P. L. Cell transformation by pp60c-src mutated in the carboxy-terminal regulatory domain. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):83–91. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90758-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cartwright C. A., Kamps M. P., Meisler A. I., Pipas J. M., Eckhart W. pp60c-src activation in human colon carcinoma. J Clin Invest. 1989 Jun;83(6):2025–2033. doi: 10.1172/JCI114113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cartwright C. A., Meisler A. I., Eckhart W. Activation of the pp60c-src protein kinase is an early event in colonic carcinogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(2):558–562. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.2.558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cloutier J. F., Chow L. M., Veillette A. Requirement of the SH3 and SH2 domains for the inhibitory function of tyrosine protein kinase p50csk in T lymphocytes. Mol Cell Biol. 1995 Nov;15(11):5937–5944. doi: 10.1128/mcb.15.11.5937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cobb B. S., Schaller M. D., Leu T. H., Parsons J. T. Stable association of pp60src and pp59fyn with the focal adhesion-associated protein tyrosine kinase, pp125FAK. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Jan;14(1):147–155. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.1.147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Howell B. The when and how of Src regulation. Cell. 1993 Jun 18;73(6):1051–1054. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90634-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeClue J. E., Martin G. S. Linker insertion-deletion mutagenesis of the v-src gene: isolation of host- and temperature-dependent mutants. J Virol. 1989 Feb;63(2):542–554. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.2.542-554.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eck M. J., Shoelson S. E., Harrison S. C. Recognition of a high-affinity phosphotyrosyl peptide by the Src homology-2 domain of p56lck. Nature. 1993 Mar 4;362(6415):87–91. doi: 10.1038/362087a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster R., Martin G. S. A mutation in the catalytic domain of pp60v-src is responsible for the host- and temperature-dependent phenotype of the Rous sarcoma virus mutant tsLA33-1. Virology. 1992 Mar;187(1):145–155. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90303-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fumagalli S., Totty N. F., Hsuan J. J., Courtneidge S. A. A target for Src in mitosis. Nature. 1994 Apr 28;368(6474):871–874. doi: 10.1038/368871a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia R., Parikh N. U., Saya H., Gallick G. E. Effect of herbimycin A on growth and pp60c-src activity in human colon tumor cell lines. Oncogene. 1991 Nov;6(11):1983–1989. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirai H., Varmus H. E. Mutations in src homology regions 2 and 3 of activated chicken c-src that result in preferential transformation of mouse or chicken cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(21):8592–8596. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.21.8592. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirai H., Varmus H. E. Site-directed mutagenesis of the SH2- and SH3-coding domains of c-src produces varied phenotypes, including oncogenic activation of p60c-src. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;10(4):1307–1318. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.4.1307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howell B. W., Cooper J. A. Csk suppression of Src involves movement of Csk to sites of Src activity. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Aug;14(8):5402–5411. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.8.5402. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes S. H., Greenhouse J. J., Petropoulos C. J., Sutrave P. Adaptor plasmids simplify the insertion of foreign DNA into helper-independent retroviral vectors. J Virol. 1987 Oct;61(10):3004–3012. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.10.3004-3012.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwashita S., Kitamura N., Yoshida M. Molecular events leading to fusiform morphological transformation by partial src deletion mutant of Rous sarcoma virus. Virology. 1983 Mar;125(2):419–431. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90213-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamps M. P., Buss J. E., Sefton B. M. Mutation of NH2-terminal glycine of p60src prevents both myristoylation and morphological transformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(14):4625–4628. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.14.4625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamps M. P., Buss J. E., Sefton B. M. Rous sarcoma virus transforming protein lacking myristic acid phosphorylates known polypeptide substrates without inducing transformation. Cell. 1986 Apr 11;45(1):105–112. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90542-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan K. B., Bibbins K. B., Swedlow J. R., Arnaud M., Morgan D. O., Varmus H. E. Association of the amino-terminal half of c-Src with focal adhesions alters their properties and is regulated by phosphorylation of tyrosine 527. EMBO J. 1994 Oct 17;13(20):4745–4756. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06800.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kmiecik T. E., Shalloway D. Activation and suppression of pp60c-src transforming ability by mutation of its primary sites of tyrosine phosphorylation. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):65–73. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90756-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch C. A., Moran M. F., Anderson D., Liu X. Q., Mbamalu G., Pawson T. Multiple SH2-mediated interactions in v-src-transformed cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Mar;12(3):1366–1374. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.3.1366. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):488–492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ladbury J. E., Lemmon M. A., Zhou M., Green J., Botfield M. C., Schlessinger J. Measurement of the binding of tyrosyl phosphopeptides to SH2 domains: a reappraisal. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Apr 11;92(8):3199–3203. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.8.3199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu X., Brodeur S. R., Gish G., Songyang Z., Cantley L. C., Laudano A. P., Pawson T. Regulation of c-Src tyrosine kinase activity by the Src SH2 domain. Oncogene. 1993 May;8(5):1119–1126. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu X., Marengere L. E., Koch C. A., Pawson T. The v-Src SH3 domain binds phosphatidylinositol 3'-kinase. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Sep;13(9):5225–5232. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.9.5225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marengere L. E., Pawson T. Identification of residues in GTPase-activating protein Src homology 2 domains that control binding to tyrosine phosphorylated growth factor receptors and p62. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 15;267(32):22779–22786. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marengere L. E., Pawson T. Structure and function of SH2 domains. J Cell Sci Suppl. 1994;18:97–104. doi: 10.1242/jcs.1994.supplement_18.14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer B. J., Jackson P. K., Van Etten R. A., Baltimore D. Point mutations in the abl SH2 domain coordinately impair phosphotyrosine binding in vitro and transforming activity in vivo. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Feb;12(2):609–618. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.2.609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGlade J., Cheng A., Pelicci G., Pelicci P. G., Pawson T. Shc proteins are phosphorylated and regulated by the v-Src and v-Fps protein-tyrosine kinases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 1;89(19):8869–8873. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.19.8869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy S. M., Bergman M., Morgan D. O. Suppression of c-Src activity by C-terminal Src kinase involves the c-Src SH2 and SH3 domains: analysis with Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Sep;13(9):5290–5300. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.9.5290. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nemeth S. P., Fox L. G., DeMarco M., Brugge J. S. Deletions within the amino-terminal half of the c-src gene product that alter the functional activity of the protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Mar;9(3):1109–1119. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.3.1109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novotny-Smith C. L., Gallick G. E. Growth inhibition of human colorectal carcinoma cell lines by tumor necrosis factor-alpha correlates with reduced activity of pp60c-src. J Immunother (1991) 1992 Apr;11(3):159–168. doi: 10.1097/00002371-199204000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien M. C., Fukui Y., Hanafusa H. Activation of the proto-oncogene p60c-src by point mutations in the SH2 domain. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):2855–2862. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.2855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada M., Howell B. W., Broome M. A., Cooper J. A. Deletion of the SH3 domain of Src interferes with regulation by the phosphorylated carboxyl-terminal tyrosine. J Biol Chem. 1993 Aug 25;268(24):18070–18075. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamura H., Resh M. D. Differential binding of pp60c-src and pp60v-src to cytoskeleton is mediated by SH2 and catalytic domains. Oncogene. 1994 Aug;9(8):2293–2303. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panchamoorthy G., Fukazawa T., Stolz L., Payne G., Reedquist K., Shoelson S., Songyang Z., Cantley L., Walsh C., Band H. Physical and functional interactions between SH2 and SH3 domains of the Src family protein tyrosine kinase p59fyn. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Sep;14(9):6372–6385. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.9.6372. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker R. C., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M. Expression of v-src and chicken c-src in rat cells demonstrates qualitative differences between pp60v-src and pp60c-src. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):131–139. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90308-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsons J. T., Weber M. J. Genetics of src: structure and functional organization of a protein tyrosine kinase. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1989;147:79–127. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-74697-0_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piwnica-Worms H., Saunders K. B., Roberts T. M., Smith A. E., Cheng S. H. Tyrosine phosphorylation regulates the biochemical and biological properties of pp60c-src. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):75–82. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90757-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resh M. D. Interaction of tyrosine kinase oncoproteins with cellular membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993 Dec 23;1155(3):307–322. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(93)90012-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds A. B., Kanner S. B., Wang H. C., Parsons J. T. Stable association of activated pp60src with two tyrosine-phosphorylated cellular proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Sep;9(9):3951–3958. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.9.3951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabe H., Hata A., Okada M., Nakagawa H., Hanafusa H. Analysis of the binding of the Src homology 2 domain of Csk to tyrosine-phosphorylated proteins in the suppression and mitotic activation of c-Src. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Apr 26;91(9):3984–3988. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.9.3984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakai R., Iwamatsu A., Hirano N., Ogawa S., Tanaka T., Mano H., Yazaki Y., Hirai H. A novel signaling molecule, p130, forms stable complexes in vivo with v-Crk and v-Src in a tyrosine phosphorylation-dependent manner. EMBO J. 1994 Aug 15;13(16):3748–3756. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06684.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffhausen B. SH2 domain structure and function. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1995 Jul 28;1242(1):61–75. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(95)00004-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sefton B. M., Hunter T. From c-src to v-src, or the case of the missing C terminus. Cancer Surv. 1986;5(2):159–172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidel-Dugan C., Meyer B. E., Thomas S. M., Brugge J. S. Effects of SH2 and SH3 deletions on the functional activities of wild-type and transforming variants of c-Src. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Apr;12(4):1835–1845. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.4.1835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverman L., Resh M. D. Lysine residues form an integral component of a novel NH2-terminal membrane targeting motif for myristylated pp60v-src. J Cell Biol. 1992 Oct;119(2):415–425. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.2.415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. R., DeGudicibus S. J., Stacey D. W. Requirement for c-ras proteins during viral oncogene transformation. Nature. 1986 Apr 10;320(6062):540–543. doi: 10.1038/320540a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder M. A., Bishop J. M., Colby W. W., Levinson A. D. Phosphorylation of tyrosine-416 is not required for the transforming properties and kinase activity of pp60v-src. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):891–901. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90074-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Songyang Z., Shoelson S. E., Chaudhuri M., Gish G., Pawson T., Haser W. G., King F., Roberts T., Ratnofsky S., Lechleider R. J. SH2 domains recognize specific phosphopeptide sequences. Cell. 1993 Mar 12;72(5):767–778. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90404-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stacey D. W., Roudebush M., Day R., Mosser S. D., Gibbs J. B., Feig L. A. Dominant inhibitory Ras mutants demonstrate the requirement for Ras activity in the action of tyrosine kinase oncogenes. Oncogene. 1991 Dec;6(12):2297–2304. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Superti-Furga G., Fumagalli S., Koegl M., Courtneidge S. A., Draetta G. Csk inhibition of c-Src activity requires both the SH2 and SH3 domains of Src. EMBO J. 1993 Jul;12(7):2625–2634. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05923.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor S. J., Shalloway D. An RNA-binding protein associated with Src through its SH2 and SH3 domains in mitosis. Nature. 1994 Apr 28;368(6474):867–871. doi: 10.1038/368867a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tian M., Martin G. S. Reduced phosphotyrosine binding by the v-Src SH2 domain is compatible with wild-type transformation. Oncogene. 1996 Feb 15;12(4):727–734. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verderame M. F., Guan J. L., Woods Ignatoski K. M. Transformation and pp60v-src autophosphorylation correlate with SHC-GRB2 complex formation in rat and chicken cells expressing host-range and kinase-active, transformation-defective alleles of v-src. Mol Biol Cell. 1995 Aug;6(8):953–966. doi: 10.1091/mbc.6.8.953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verderame M. F., Kaplan J. M., Varmus H. E. A mutation in v-src that removes a single conserved residue in the SH-2 domain of pp60v-src restricts transformation in a host-dependent manner. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):338–348. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.338-348.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verderame M. F., Varmus H. E. Highly conserved amino acids in the SH2 and catalytic domains of v-src are altered in naturally occurring, transformation-defective alleles. Oncogene. 1994 Jan;9(1):175–182. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waksman G., Kominos D., Robertson S. C., Pant N., Baltimore D., Birge R. B., Cowburn D., Hanafusa H., Mayer B. J., Overduin M. Crystal structure of the phosphotyrosine recognition domain SH2 of v-src complexed with tyrosine-phosphorylated peptides. Nature. 1992 Aug 20;358(6388):646–653. doi: 10.1038/358646a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waksman G., Shoelson S. E., Pant N., Cowburn D., Kuriyan J. Binding of a high affinity phosphotyrosyl peptide to the Src SH2 domain: crystal structures of the complexed and peptide-free forms. Cell. 1993 Mar 12;72(5):779–790. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90405-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods K. M., Verderame M. F. Autophosphorylation is required for high kinase activity and efficient transformation ability of proteins encoded by host range alleles of v-src. J Virol. 1994 Nov;68(11):7267–7274. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.11.7267-7274.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyke J. A., Stoker A. W. Genetic analysis of the form and function of the viral src oncogene product. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Apr 20;907(1):47–69. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(87)90018-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]