Abstract
Formal, Samuel B., (Walter Reed Army Institute of Research, Washington, D.C.), E. H. LaBrec, T. H. Kent, and S. Falkow. Abortive intestinal infection with an Escherichia coli-Shigella flexneri hybrid strain. J. Bacteriol. 89:1374–1382. 1965.—The mechanism of the apparent loss of virulence of an Escherichia coli-Shigella flexneri hybrid strain was studied. The parent Shigella strain caused a fatal enteric infection when fed to starved guinea pigs, and signs of dysentery followed its oral administration to monkeys. The hybrid strain failed to produce any apparent symptoms when fed to either of these species. The parent strain was shown to invade the intestinal mucosa of starved guinea pigs. This caused a severe inflammatory reaction in the lamina propria, which progressed to ulceration of the intestinal epithelium and resulted in death of the animal. The hybrid strain also invaded the intestinal mucosa and produced an inflammatory reaction. In this case, the inflammatory reaction subsided, the intestine returned to normal within 4 days after challenge, and the animal survived. Both fluorescent-antibody techniques and in vivo growth studies have shown that the hybrid strain can not maintain itself in the intestinal mucosa. Preliminary studies have indicated that a similar situation also exists in the monkey. It is concluded that the virulence of dysentery bacilli rests not only in the capacity to reach the lamina propria, but also in the ability to multiply in this region.
Full text
PDF


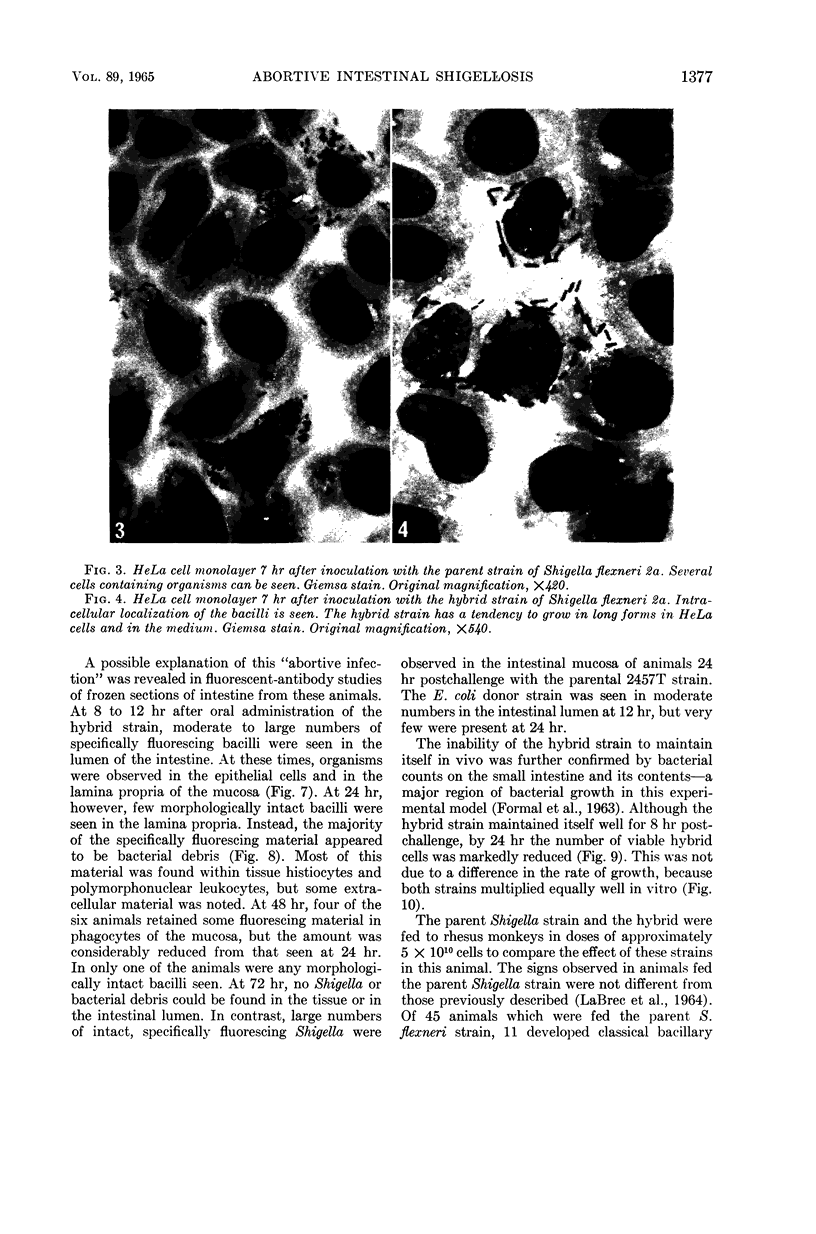





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- FORMAL S. B., ABRAMS G. D., SCHNEIDER H., SPRINZ H. Experimental Shigella infections. VI. Role of the small intestine in an experimental infection in guinea pigs. J Bacteriol. 1963 Jan;85:119–125. doi: 10.1128/jb.85.1.119-125.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FORMAL S. B., DAMMIN G. J., LABREC E. H., SCHNEIDER H. Experimental Shigella infections: characteristics of a fatal infection produced in guinea pigs. J Bacteriol. 1958 May;75(5):604–610. doi: 10.1128/jb.75.5.604-610.1958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LABREC E. H., FORMAL S. B. Experimental Shigella infections. IV. Fluorescent antibody studies of an infection in guinea pigs. J Immunol. 1961 Nov;87:562–572. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]