Abstract
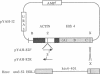
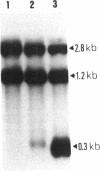
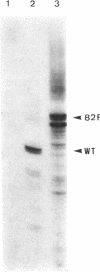
We have cloned an 82-base-pair region spanning the site of normal 3' end formation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae CYC1 mRNA into an integrative vector carrying the 5' end of the actin gene (including its intron) fused in frame to HIS4ABC sequences. This vector can confer the ability to grow on histidinol if HIS4C (encoding histidinol dehydrogenase) is sufficiently expressed. With the CYC1 fragment cloned in its wild-type (forward) orientation within the actin intron, transformants cannot grow on histidinol, whereas cells transformed with the vector carrying the reverse orientation of this fragment are able to grow well. RNA transfers demonstrate that transformants containing the forward orientation accumulate less than 40% of the control level of full-length mRNA and reveal the presence of a short, stable (approximately equal to 300 nucleotides) poly(A) RNA that represents 60-70% of the transcripts originating from the same promoter. The reverse orientation of the insert allows near-normal levels of full-length mRNA. Mapping of the 3' end of the truncated RNA indicates that poly(A) addition is variable in length but occurs at the same location as in the normal CYC1 transcript. Dominant and recessive suppressor mutations permit growth on histidinol despite the inserted fragment. Genetic analyses indicate that most of the dominant mutants are cis-acting and that the recessive mutants define a minimum of three complementation groups, indicating that defects in several different genes can restore higher levels of HIS4C expression.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Birnstiel M. L., Busslinger M., Strub K. Transcription termination and 3' processing: the end is in site! Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):349–359. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80007-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brady H. A., Wold W. S. Identification of a novel sequence that governs both polyadenylation and alternative splicing in region E3 of adenovirus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Nov 25;15(22):9397–9416. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.22.9397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Domdey H., Apostol B., Lin R. J., Newman A., Brody E., Abelson J. Lariat structures are in vivo intermediates in yeast pre-mRNA splicing. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):611–621. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90468-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falck-Pedersen E., Logan J., Shenk T., Darnell J. E., Jr Transcription termination within the E1A gene of adenovirus induced by insertion of the mouse beta-major globin terminator element. Cell. 1985 Apr;40(4):897–905. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90349-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frayne E. G., Kellems R. E. Structural features of the murine dihydrofolate reductase transcription termination region: identification of a conserved DNA sequence element. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 May 27;14(10):4113–4125. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.10.4113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S., Cohen E. H. Sequences responsible for transcription termination on a gene segment in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Aug;4(8):1515–1520. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.8.1515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinnen A., Hicks J. B., Fink G. R. Transformation of yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Apr;75(4):1929–1933. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.4.1929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen R., Sprague G. F., Jr, Herskowitz I. Regulation of yeast mating-type interconversion: feedback control of HO gene expression by the mating-type locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(10):3035–3039. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.10.3035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson M. R., Norman C., Reeve M. A., Scully J., Proudfoot N. J. Tripartite sequences within and 3' to the sea urchin H2A histone gene display properties associated with a transcriptional termination process. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;6(11):4008–4018. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.11.4008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klinz F. J., Gallwitz D. Size and position of intervening sequences are critical for the splicing efficiency of pre-mRNA in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jun 11;13(11):3791–3804. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.11.3791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotval J., Zaret K. S., Consaul S., Sherman F. Revertants of a transcription termination mutant of yeast contain diverse genetic alterations. Genetics. 1983 Mar;103(3):367–388. doi: 10.1093/genetics/103.3.367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Logan J., Falck-Pedersen E., Darnell J. E., Jr, Shenk T. A poly(A) addition site and a downstream termination region are required for efficient cessation of transcription by RNA polymerase II in the mouse beta maj-globin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8306–8310. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mott J. E., Galloway J. L., Platt T. Maturation of Escherichia coli tryptophan operon mRNA: evidence for 3' exonucleolytic processing after rho-dependent termination. EMBO J. 1985 Jul;4(7):1887–1891. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03865.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborne B. I., Guarente L. Transcription by RNA polymerase II induces changes of DNA topology in yeast. Genes Dev. 1988 Jun;2(6):766–772. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.6.766. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osheim Y. N., Miller O. L., Jr, Beyer A. L. Two Drosophila chorion genes terminate transcription in discrete regions near their poly(A) sites. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 20;5(13):3591–3596. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04687.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker R., Guthrie C. A point mutation in the conserved hexanucleotide at a yeast 5' splice junction uncouples recognition, cleavage, and ligation. Cell. 1985 May;41(1):107–118. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90065-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Platt T. Transcription termination and the regulation of gene expression. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:339–372. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.002011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stauber C., Lüscher B., Eckner R., Lötscher E., Schümperli D. A signal regulating mouse histone H4 mRNA levels in a mammalian cell cycle mutant and sequences controlling RNA 3' processing are both contained within the same 80-bp fragment. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 1;5(12):3297–3303. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04643.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitelaw E., Proudfoot N. Alpha-thalassaemia caused by a poly(A) site mutation reveals that transcriptional termination is linked to 3' end processing in the human alpha 2 globin gene. EMBO J. 1986 Nov;5(11):2915–2922. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04587.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarger J. G., Armilei G., Gorman M. C. Transcription terminator-like element within a Saccharomyces cerevisiae promoter region. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Apr;6(4):1095–1101. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.4.1095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaret K. S., Sherman F. DNA sequence required for efficient transcription termination in yeast. Cell. 1982 Mar;28(3):563–573. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90211-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaret K. S., Sherman F. Mutationally altered 3' ends of yeast CYC1 mRNA affect transcript stability and translational efficiency. J Mol Biol. 1984 Jul 25;177(1):107–135. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90060-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]