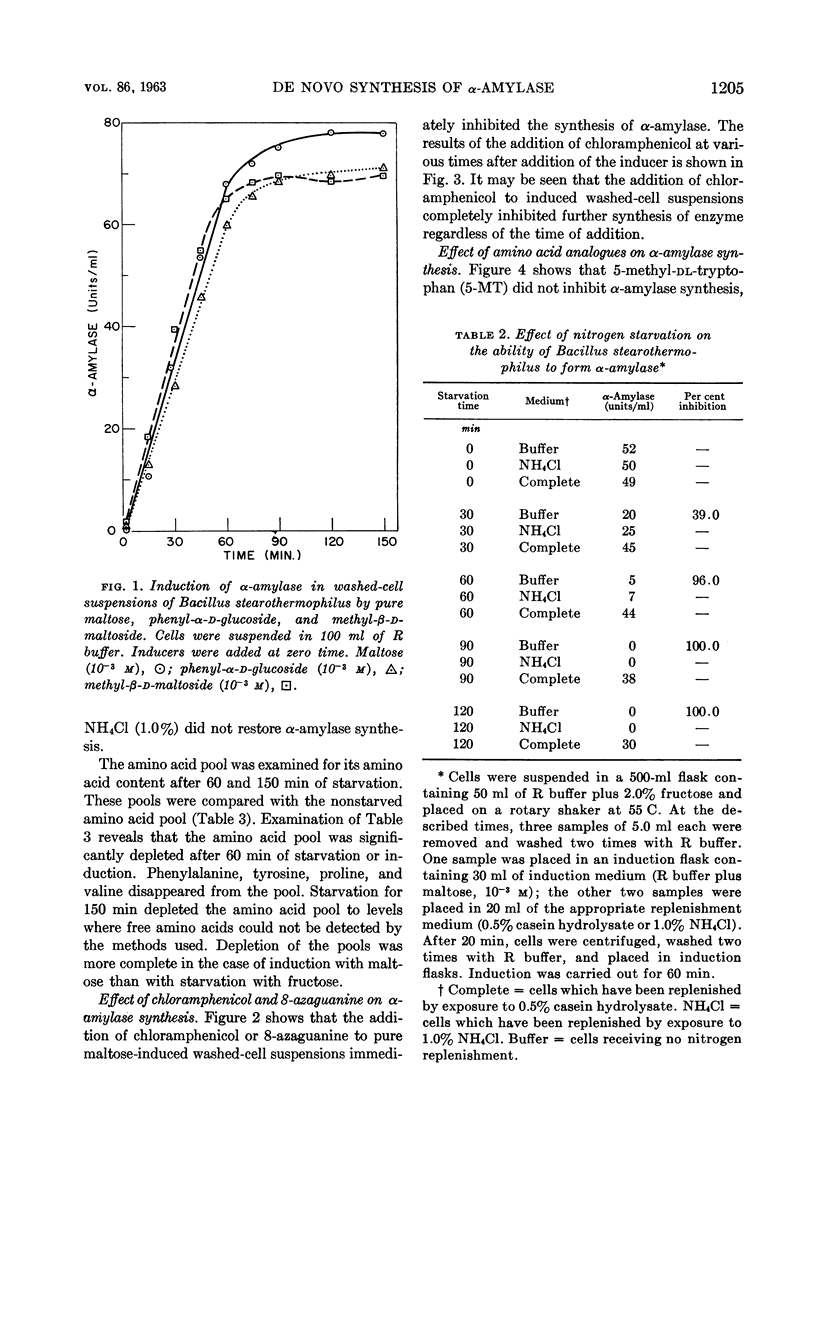
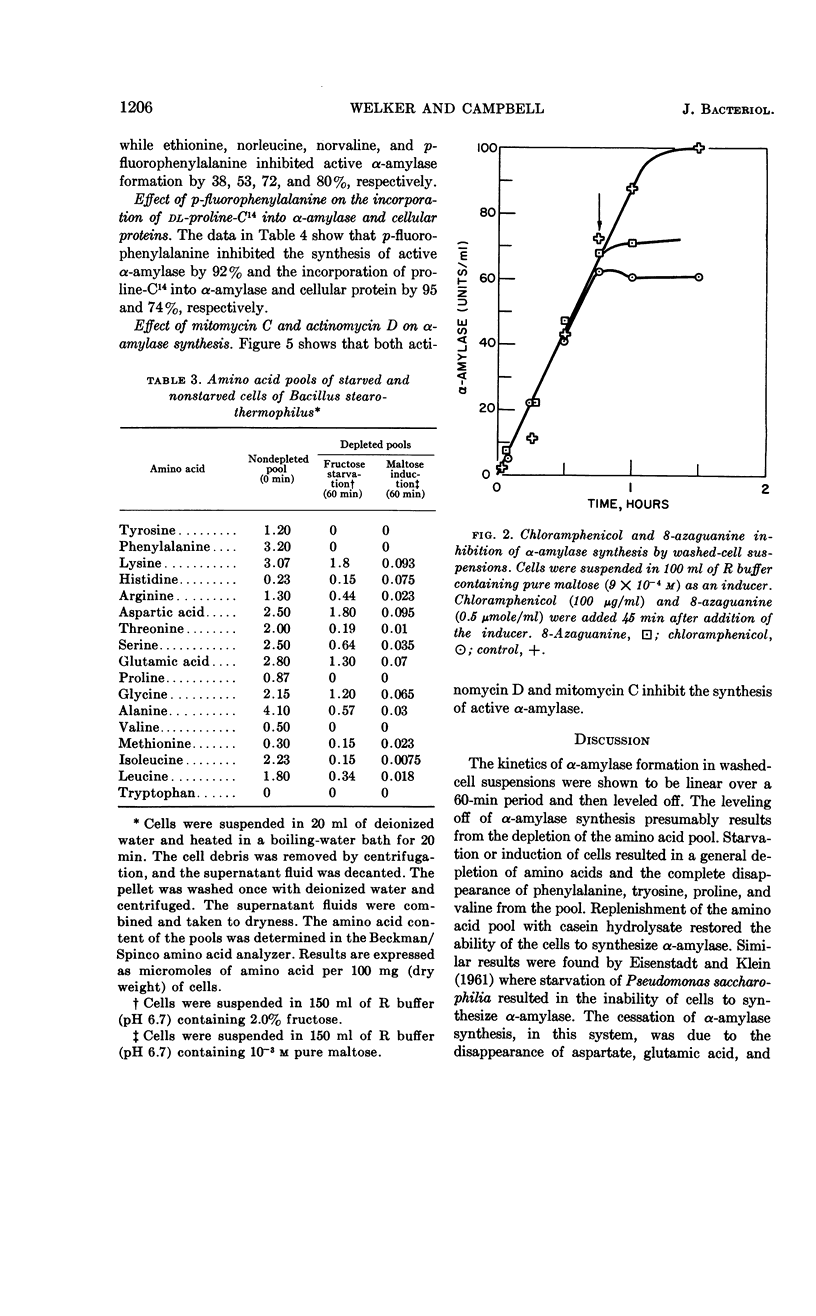
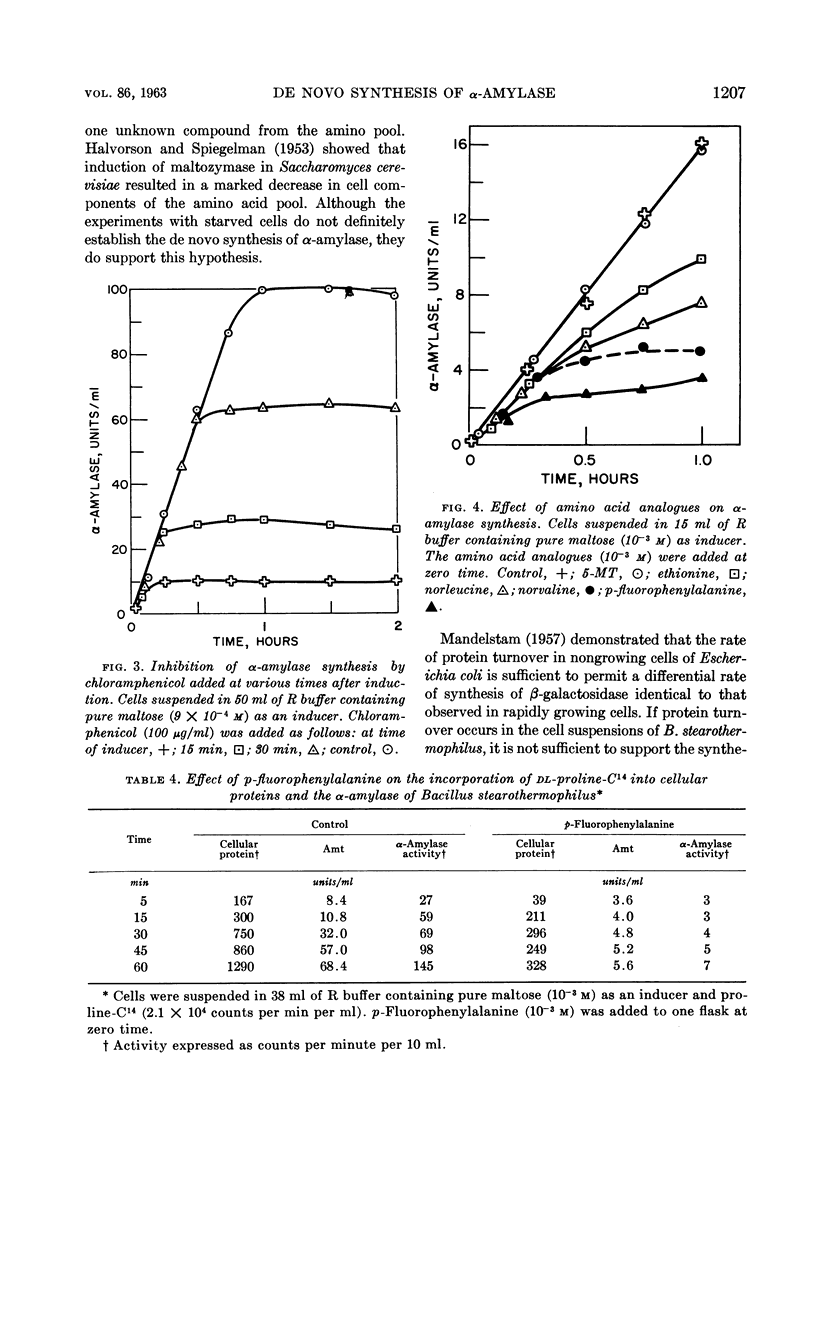
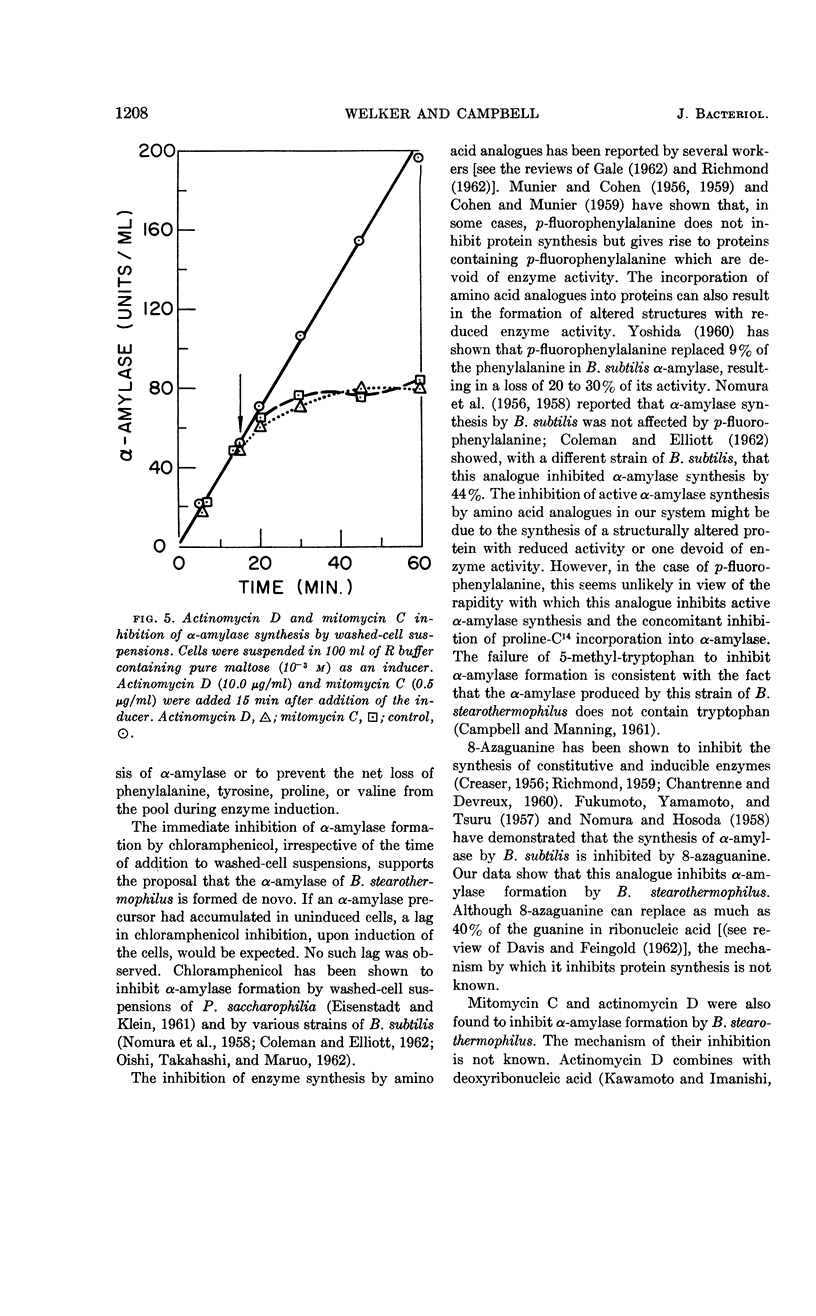
Abstract
Welker, N. E. (Western Reserve University, Cleveland, Ohio and University of Illinois, Urbana), and L. Leon Campbell. De novo synthesis of α-amylase by Bacillus stearothermophilus. J. Bacteriol. 86:1202–1210. 1963.—The pH optimum for the synthesis of α-amylase by washed-cell suspensions was 6.7. α-Amylase synthesis began soon after the addition of the inducer (maltose, methyl-β-d-maltoside, or phenyl-α-d-glucoside, at 10−3m), proceeded at a linear rate for 60 min, and then leveled off. Cell suspensions without inducer produced small amounts of α-amylase. The addition of glucose (2 × 10−3m), sucrose (10−3m), or glycerol (4 × 10−3m) to washed-cell suspensions failed to stimulate the production of α-amylase. Nitrogen starvation of washed cells for 60 min with fructose as a carbon source or by induction with pure maltose showed that the ability to produce α-amylase was lost. Examination of the amino acid pool at this time showed a general depletion of amino acids and the complete disappearance of tyrosine, phenyl-alanine, proline, and valine. Replenishment of the amino acid pool with casein hydrolysate (0.5%) restored the ability of the cells to produce α-amylase. Chloramphenicol and 8-azaguanine were shown to inhibit α-amylase synthesis. Inhibition was observed immediately upon the addition of chloramphenicol to cell suspensions preinduced for varying periods of time. Actinomycin D and mitomycin C also inhibited α-amylase synthesis when added to induced washed-cell suspensions. The amino acid analogues, norvaline, norleucine, and ethionine, inhibited α-amylase formation by 72, 53, and 38%, respectively. p-Fluorophenylalanine inhibited the synthesis of active α-amylase by 92% and the incorporation of proline-C14 into α-amylase and cellular proteins by 95 and 74%, respectively.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CAMPBELL L. L., MANNING G. B. Thermostable alpha-amylase of Bacillus stearothermophilus. III. Amino acid composition. J Biol Chem. 1961 Nov;236:2962–2965. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHANTRENNE H., DEVREUX S. [Restoration of the synthesis of enzymes after inhibition by azaquanine]. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1960 Jul 1;41:239–245. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(60)90006-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHEN G. N., MUNIER R. Effets des analogues structuraux d'aminoacides sur la croissance, la synthèse de protéines et la synthèse d'enzymes chez Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1959 Feb;31(2):347–356. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(59)90007-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHEN G. N., MUNIER R. Incorporation d'analogues structuraux d'aminoacides dans les protéines bactériennes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1956 Sep;21(3):592–593. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(56)90207-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COLEMAN G., ELLIOTT W. H. Studies on alpha-amylase formation by Bacillus subtilis. Biochem J. 1962 May;83:256–263. doi: 10.1042/bj0830256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CREASER E. H. The assimilation of amino acids by bacteria. 22. The effect of 8-azaguanine upon enzyme formation in Staphylococcus aureus. Biochem J. 1956 Nov;64(3):539–545. doi: 10.1042/bj0640539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EISENSTADT J. M., KLEIN H. P. Evidence for the de novo synthesis of the alpha-amylase of Pseudomonas saccharophila. J Bacteriol. 1961 Dec;82:798–807. doi: 10.1128/jb.82.6.798-807.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FUKUMOTO J., YAMAMOTO T., TSURU D. Effects of carbon sources and base analogues of nucleic acid on the formation of bacterial amylase. Nature. 1957 Aug 31;180(4583):438–439. doi: 10.1038/180438b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALVORSON H. O., SPIEGELMAN S. Net utilization of free amino acids during the induced synthesis of maltozymase in yeast. J Bacteriol. 1953 May;65(5):601–608. doi: 10.1128/jb.65.5.601-608.1953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KERSTEN H. [On the method of action of mitomycin C. I. Effect of mitomycin C on desoxyribonucleic acid degradation in resting bacteria]. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1962 Sep 6;329:31–39. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1962.329.1.31. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MANDELSTAM J. Turnover of protein in starved bacteria and its relationship to the induced synthesis of enzyme. Nature. 1957 Jun 8;179(4571):1179–1181. doi: 10.1038/1791179a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MUNIER R., COHEN G. N. Incorporation d'analogues structuraux d'aminoacides dans les protéines bactériennes au cours de leur synthèse in vivo. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1959 Feb;31(2):378–391. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(59)90011-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEIDHARDT F. C., MAGASANIK B. Studies on the role of ribonucleic acid in the growth of bacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1960 Jul 29;42:99–116. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(60)90757-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OISHI M., TAKAHASHI H., MARUO B. The synthesis of alpha-amylase by a cell-free system from Bacillus subtilis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1962 Aug 7;8:342–347. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(62)90004-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RICHMOND M. H. The effect of amino acid analogues on growth and protein synthesis in microorganisms. Bacteriol Rev. 1962 Dec;26:398–420. doi: 10.1128/br.26.4.398-420.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THAYER P. S. The amylases of pseudomonas saccharophila. J Bacteriol. 1953 Dec;66(6):656–663. doi: 10.1128/jb.66.6.656-663.1953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WELKER N. E., CAMPBELL L. L. EFFECT OF CARBON SOURCES ON FORMATION OF ALPHA-AMYLASE BY BACILLUS STEAROTHERMOPHILUS. J Bacteriol. 1963 Oct;86:681–686. doi: 10.1128/jb.86.4.681-686.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WELKER N. E., CAMPBELL L. L. INDUCED BIOSYNTHESIS OF ALPHA-AMYLASE BY GROWING CULTURES OF BACILLUS STEAROTHERMOPHILUS. J Bacteriol. 1963 Dec;86:1196–1201. doi: 10.1128/jb.86.6.1196-1201.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WELKER N. E., CAMPBELL L. L. INDUCTION OF ALPHA-AMYLASE OF BACILLUS STEAROTHERMOPHILUS BY MALTODEXTRINS. J Bacteriol. 1963 Oct;86:687–691. doi: 10.1128/jb.86.4.687-691.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YOSHIDA A. Studies on the mechanism of protein synthesis; incorporation of p-fluorophenylalanine into alpha-amylase of Bacillus subtilis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1960 Jun 17;41:98–103. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(60)90373-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


