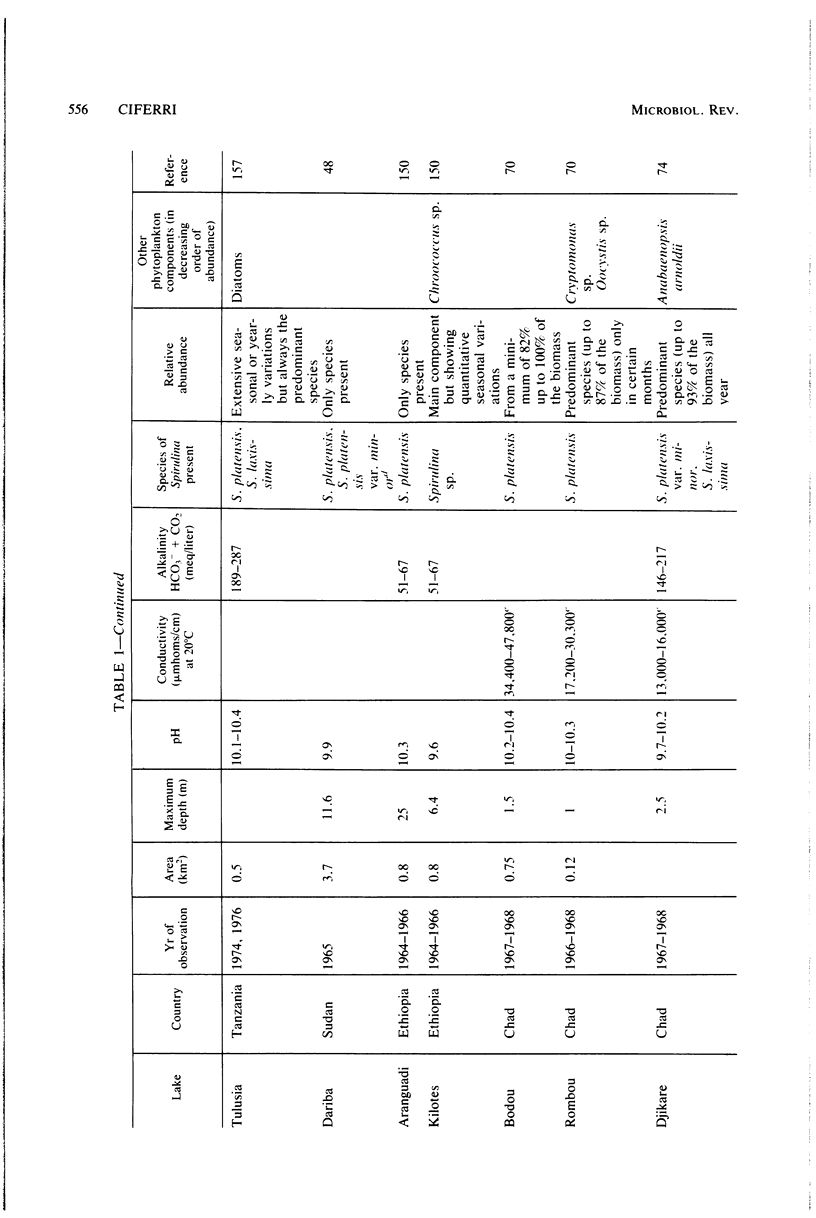
Full text
PDF
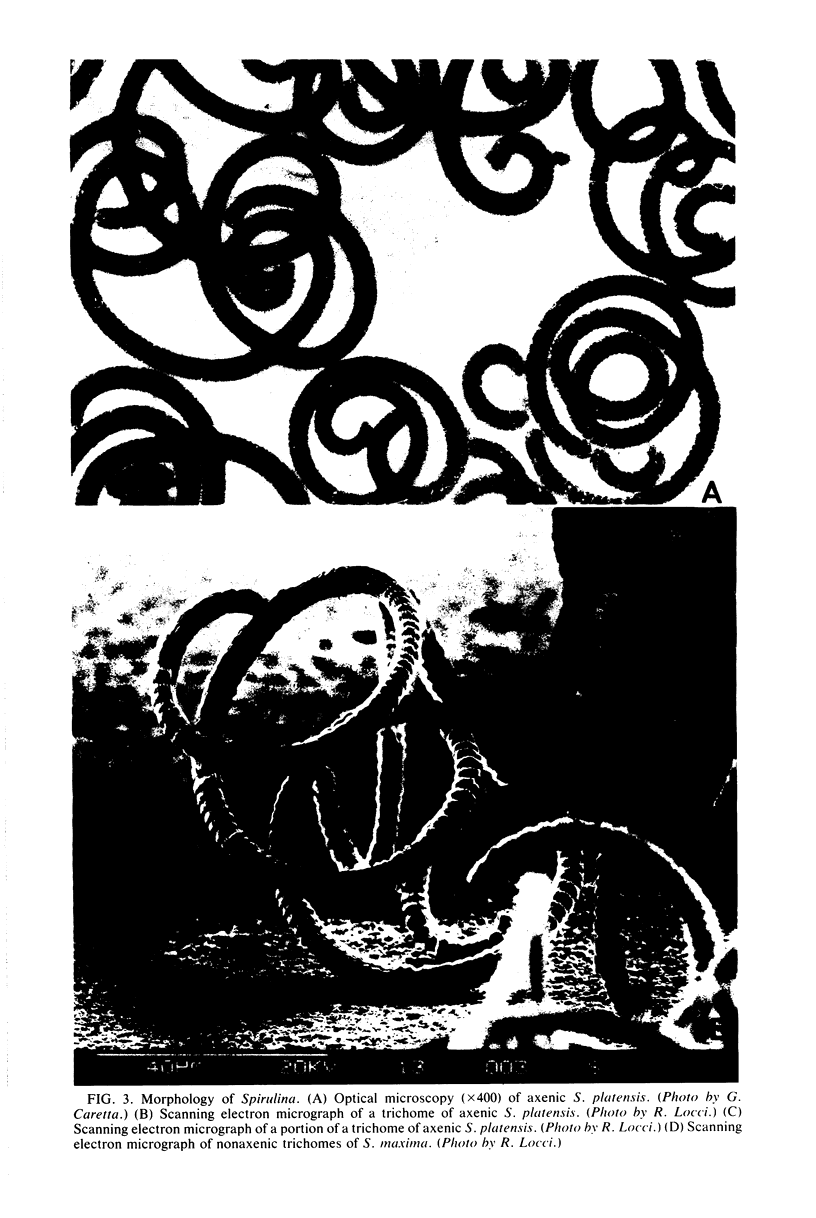






















Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen M. M. Mesosomes in blue-green algae. Arch Mikrobiol. 1972;84(3):199–206. doi: 10.1007/BF00425198. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ambler R. P., Bartsch R. G. Amino acid sequence similarity between cytochrome f from a blue-green bacterium and algal chloroplasts. Nature. 1975 Jan 24;253(5489):285–288. doi: 10.1038/253285a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blum J. C., Calet C. Valeur alimentaire des algues spirulines pour la croissance du poulet de chair. Ann Nutr Aliment. 1975;29(6):651–674. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cammack R., Rao K. K., Bargeron C. P., Hutson K. G., Andrew P. W., Rogers L. J. Midpoint redox potentials of plant and algal ferredoxins. Biochem J. 1977 Nov 15;168(2):205–209. doi: 10.1042/bj1680205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell J., 3rd, Stevens S. E., Jr, Balkwill D. L. Accumulation of poly-beta-hydroxybutyrate in Spirulina platensis. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jan;149(1):361–363. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.1.361-363.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clément G., Giddey C., Menzi R. Amino acid composition and nutritive valve of the alga Spirulina maxima. J Sci Food Agric. 1967 Nov;18(11):497–501. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.2740181101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cozzone A., Busson F. Electrophorèse en gel de polyacrylamide des protéines de Spirulina platensis (Gom.) Geitler et de Spirulina geitler J. de Toni. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1970 Jun 8;270(23):2878–2881. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delk A. S., Dekker C. A. Characterization of rhapidosomes of Saprospira grandis. J Mol Biol. 1972 Feb 28;64(1):287–295. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90336-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delpeuch F., Joseph A., Cavelier C. Consommation alimentaire et apport nutritionnel des algues bleues (Oscillatoria platensis) chez quelques populations du Kanem (Tchad). Ann Nutr Aliment. 1975;29(6):497–516. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devi M. A., Subbulakshmi G., Devi K. M., Venkataraman L. V. Studies on the proteins of mass-cultivated, blue-green alga (Spirulina platensis). J Agric Food Chem. 1981 May-Jun;29(3):522–525. doi: 10.1021/jf00105a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ershoff B. H., Wildman S. G., Kwanyuen P. Biological evaluation of crystalline fraction I protein from tobacco. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1978 Apr;157(4):626–630. doi: 10.3181/00379727-157-40110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faucher O., Coupal B., Leduy A. Utilization of seawater-urea as a culture medium for Spirulina maxima. Can J Microbiol. 1979 Jun;25(6):752–759. doi: 10.1139/m79-109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
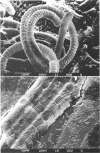
- Feroci L. T., Margheri M. C., Pelosi E. Die ultrastruktur von spirulina im vergleich zu oscillatoria. Zentralbl Bakteriol Parasitenkd Infektionskr Hyg. 1976;131(7):592–601. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fevrier C., Seve B. Essais d'incorporation de spiruline (Spirulina maxima) dans les aliments des porcins. Ann Nutr Aliment. 1975;29(6):625–650. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall D. O., Rao K. K., Cammack R. A stable and easily extractable plant-type ferredoxin from the blue-green alga Spirulina maxima. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 May 26;47(4):798–802. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90562-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall G., Flick M. B., Jensen R. A. Approach to recognition of regulatory mutants of cyanobacteria. J Bacteriol. 1980 Aug;143(2):981–988. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.2.981-988.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall T. R., Urueña G., Figueroa H. R. In vivo and in vitro effects of temperature on monoamine oxidase activity in brain and other tissues of the goldfish. Carassius auratus L. Comp Biochem Physiol C. 1982;73(1):177–180. doi: 10.1016/0306-4492(82)90187-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho K. K., Krogmann D. W. Cytochrome f from spinach and cyanobacteria. Purification and characterization. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 10;255(9):3855–3861. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho K. K., Ulrich E. L., Krogmann D. W., Gomez-Lojero C. Isolation of photosynthetic catalysts from cyanobacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Feb 8;545(2):236–248. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(79)90203-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudson B. J., Karis I. G. The lipids of the alga Spirulina. J Sci Food Agric. 1974 Jul;25(7):759–763. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.2740250703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hulse J. H. Food science and nutrition: the gulf between rich and poor. Science. 1982 Jun 18;216(4552):1291–1294. doi: 10.1126/science.7079760. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacquet J. [Microflora of spiruline preparations]. Ann Nutr Aliment. 1975;29(6):589–601. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenyon C. N., Rippka R., Stanier R. Y. Fatty acid composition and physiological properties of some filamentous blue-green algae. Arch Mikrobiol. 1972;83(3):216–236. doi: 10.1007/BF00645123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenyon C. N., Stanier R. Y. Possible evolutionary significance of polyunsaturated fatty acids in blue-green algae. Nature. 1970 Sep 12;227(5263):1164–1166. doi: 10.1038/2271164a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhlemeier C. J., Borrias W. E., van den Hondel C. A., van Arkel G. A. Vectors for cloning in cyanobacteria: construction and characterization of two recombinant plasmids capable of transformation of Escherichia coli K12 and Anacystis nidulans R2. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;184(2):249–254. doi: 10.1007/BF00272912. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lumsden J., Hall D. O. Soluble & membrane-bound superoxide dismutases in a blue-green algae (Spirulina)and spinach. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 May 7;58(1):35–41. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90887-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lumsden J., Hall D. O. Superoxide dismutase in photosynthetic organisms provides an evolutionary hypothesis. Nature. 1975 Oct 23;257(5528):670–672. doi: 10.1038/257670a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichols B. W., Wood B. J. The occurrence and biosynthesis of gamma-linolenic acid in a blue-green alga,Spirulina platensis. Lipids. 1968 Jan;3(1):46–50. doi: 10.1007/BF02530968. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Omstedt P. T., von der Decken A., Hedenskog G., Mogren H. Nutritive value of processed Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Scenedesmus obliquus and Spirulina platensis as measured by protein synthesis in vitro in rat skeletal muscle. J Sci Food Agric. 1973 Sep;24(9):1103–1113. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.2740240913. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owers-Narhi L., Robinson S. J., DeRoo C. S., Yocum C. F. Reconstitution of cyanobacterial photophosphorylation by a latent Ca2+-ATPase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Oct 12;90(3):1025–1031. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91929-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padan E., Shilo M. Cyanophages-viruses attacking blue-green algae. Bacteriol Rev. 1973 Sep;37(3):343–370. doi: 10.1128/br.37.3.343-370.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palla J. C., Busson F. Etude des caroténoïdes de Spirulina platensis (Gom.) Geitler (Cyanophycées) C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1969 Oct 29;269(17):1704–1707. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelloquin A., Laï R., Busson F. Etude comparée des lipides de Spirulina platensis (Gom.) Geitler et de Spirulina geitleri J. de Toni. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1970 Sep 14;271(11):932–935. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quillet M. Recherches sur les substances glucidiques elaborees par les spirulines. Ann Nutr Aliment. 1975;29(6):553–561. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riccardi G., Sanangelantoni A. M., Sarasini A., Ciferri O. Altered methionyl-tRNA synthetase in a Spirulina platensis mutant resistant to ethionine. J Bacteriol. 1982 Aug;151(2):1053–1055. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.2.1053-1055.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riccardi G., Sora S., Ciferri O. Production of amino acids by analog-resistant mutants of the cyanobacterium Spirulina platensis. J Bacteriol. 1981 Sep;147(3):1002–1007. doi: 10.1128/jb.147.3.1002-1007.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson S. J., Deroo C. S., Yocum C. F. Photosynthetic Electron Transfer in Preparations of the Cyanobacterium Spirulina platensis. Plant Physiol. 1982 Jul;70(1):154–161. doi: 10.1104/pp.70.1.154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz R. M., Dayhoff M. O. Chloroplast origins: inferences from protein and nucleic acid sequences. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1981;361:260–272. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1981.tb46523.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart W. D. Some aspects of structure and function in N2-fixing cyanobacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1980;34:497–536. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.34.100180.002433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka M., Haniu M., Zeitlin S., Yasunobu K. T., Evans M. C., Rao K. K., Hall D. O. Amino acid sequence of the Spirulina maxima ferredoxin, a ferredoxin from a procaryote. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 May 5;64(1):399–407. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90267-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tel-Or E., Cammack R., Rao K. K., Rogers L. J., Stewart W. D., Hall D. O. Comparative immunochemistry of bacterial, algal and plant ferredoxins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Jan 25;490(1):120–131. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(77)90112-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tulliez J., Bories G., Boudene C., Fevrier C. Les hydrocarbures des algues spirulines: nature, etude du devenir de l'heptadecane chez le rat et le porc. Ann Nutr Aliment. 1975;29(6):563–572. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vermorel M., Toullec G., Dumond D., Pion R. Valeur proteique et energetique des algues bleues spirulines supplementees en acides amines: utizisation digestive et metabolique par le rat en croissance. Ann Nutr Aliment. 1975;29(6):535–552. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wada K., Hase T., Tokunaga H., Matsubara H. Amino acid sequence of Spirulina platensis ferredoxin: a far divergency of blue-green algal ferredoxins. FEBS Lett. 1975 Jul 15;55(1):102–104. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80969-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Eykelenburg C. A glucan from the cell wall of the cyanobacterium Spirulina platensis. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1978;44(3-4):321–327. doi: 10.1007/BF00394309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
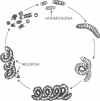
- van Eykelenburg C. Ecophysiological studies on Spirulina platensis. Effect of temperature, light intensity and nitrate concentration on growth and ultrastructure. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1980;46(2):113–127. doi: 10.1007/BF00444067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Eykelenburg C., Fuchs A., Schmidt G. H. Some theoretical considerations on the in vitro shape of the cross-walls in Spirulina spp. J Theor Biol. 1980 Jan 21;82(2):271–282. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(80)90103-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Eykelenburg C. On the morphology and ultrastructure of the cell wall of Spirulina platensis. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1977;43(2):89–99. doi: 10.1007/BF00395664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Eykelenburg C. The ultrastructure of Spirulina platensis in relation to temperature and light intensity. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1979;45(3):369–390. doi: 10.1007/BF00443277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]