Abstract
Highly purified molybdoferredoxin, with a specific activity of 2.6 μmoles of acetylene reduced per min per mg of protein, was obtained from Clostridium pasteurianum. The protein at concentrations above 5 mg/ml exists in solution as a tetrameric complex with two subunits each of about 60,000 and 50,000 daltons. Two atoms of molybdenum are present per protein molecule of 220,000 daltons. The S020, w was found to be 10.5. The tetramer dissociates into a dimer as demonstrated by a decreasing sedimentation coefficient with decreasing protein concentration. At low pH and ionic strength, further dissociation into the monomers is achieved. A method for the isolation of the protein subunits is described.
Full text
PDF

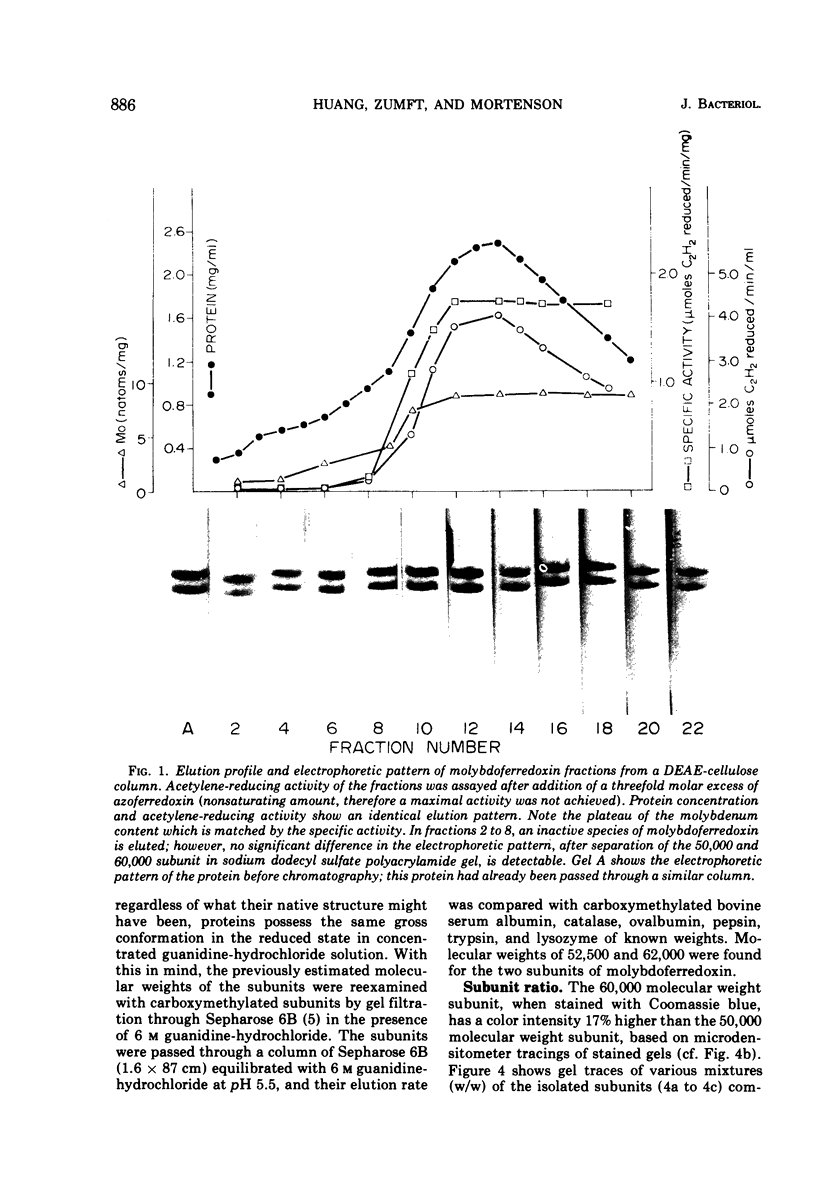
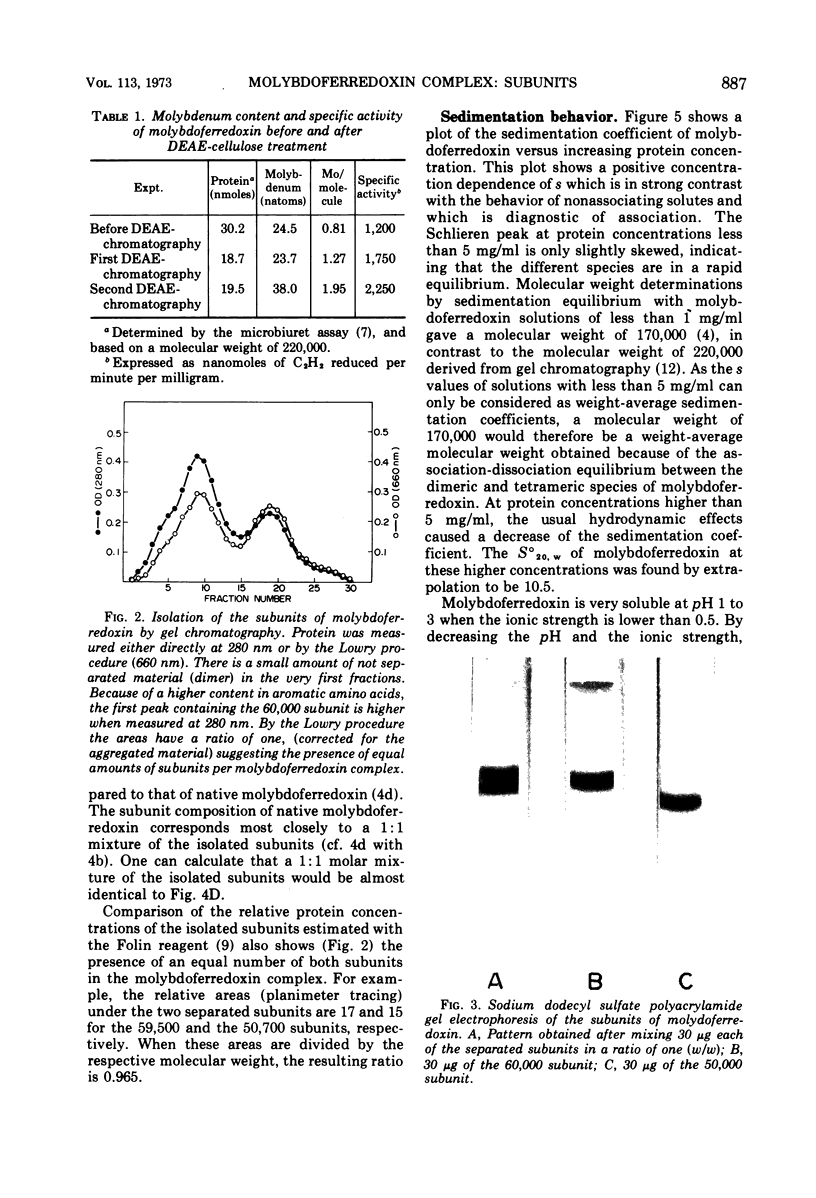


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews P. The gel-filtration behaviour of proteins related to their molecular weights over a wide range. Biochem J. 1965 Sep;96(3):595–606. doi: 10.1042/bj0960595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRUMBY P. E., MILLER R. W., MASSEY V. THE CONTENT AND POSSIBLE CATALYTIC SIGNIFICANCE OF LABILE SULFIDE IN SOME METALLOFLAVOPROTEINS. J Biol Chem. 1965 May;240:2222–2228. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalton H., Morris J. A., Ward M. A., Mortenson L. E. Purification and some properties of molybdoferredoxin, a component of nitrogenase from Clostridium pasteurianum. Biochemistry. 1971 May 25;10(11):2066–2072. doi: 10.1021/bi00787a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fish W. W., Mann K. G., Tanford C. The estimation of polypeptide chain molecular weights by gel filtration in 6 M guanidine hydrochloride. J Biol Chem. 1969 Sep 25;244(18):4989–4994. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOA J. A micro biuret method for protein determination; determination of total protein in cerebrospinal fluid. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1953;5(3):218–222. doi: 10.3109/00365515309094189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOVENBERG W., BUCHANAN B. B., RABINOWITZ J. C. STUDIES ON THE CHEMICAL NATURE OF CLOSTRIDIAL FERREDOXIN. J Biol Chem. 1963 Dec;238:3899–3913. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moustafa E., Mortenson L. E. Properties of azoferredoxin purified from nitrogen-fixing extracts of Clostridium pasteurianum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Jan 14;172(1):106–115. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(69)90095-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakos G., Mortenson L. Molecular weight and subunit structure of molybdoferredoxin from Clostridium pasteurianum W5. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Feb 16;229(2):431–436. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(71)90202-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petering D., Fee J. A., Palmer G. The oxygen sensitivity of spinach ferredoxin and other iron-sulfur proteins. The formation of protein-bound sulfur-zero. J Biol Chem. 1971 Feb 10;246(3):643–653. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandecasteele J. P., Burris R. H. Purification and properties of the constituents of the nitrogenase complex from Clostridium pasteurianum. J Bacteriol. 1970 Mar;101(3):794–801. doi: 10.1128/jb.101.3.794-801.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zumft W. G., Cretney W. C., Huang T. C., Mortenson L. E., Palmer G. On the structure and function of nitrogenase from Clostridium pasteurianum W5. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Sep 26;48(6):1525–1532. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90887-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]