Abstract
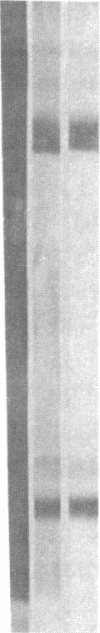
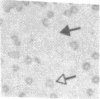
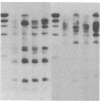
The cDNA sequence and the deduced amino acid sequence of the Mr 34,000 C-terminal fragment of Xenopus laevis complement component C3 are presented. The sequence of Xenopus C3 has 57% nucleotide identity to the corresponding sequence of human C3 and approximately 49% amino acid identity to C3 from human, mouse, and rabbit. The Xenopus C3 sequence shows clusters of high and of low similarity to the mammalian C3 sequences. One of these regions of high similarity represents the domain of mammalian C3b involved in the binding of properdin, a regulator of the alternative pathway of complement activation. It is not clear whether the other highly conserved regions are involved in binding to other C3 ligands. The Xenopus C3 sequence completely lacks the Arg-Gly-Asp sequence, which has been suggested to be the recognition site of the human complement receptor type 3 on the iC3b fragment of human C3. The Xenopus C3 gene is shown not to be linked to the Xenopus major histocompatibility complex, as is also the case in mammals. Since the gene of the related molecule C4 is MHC-linked in both mammals and Xenopus, the C3 and C4 genes may have separated before Xenopus and mammals speciated.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alper C. A., Johnson A. M., Birtch A. G., Moore F. D. Human C'3: evidence for the liver as the primary site of synthesis. Science. 1969 Jan 17;163(3864):286–288. doi: 10.1126/science.163.3864.286. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belt K. T., Carroll M. C., Porter R. R. The structural basis of the multiple forms of human complement component C4. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):907–914. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90040-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen E. Y., Seeburg P. H. Supercoil sequencing: a fast and simple method for sequencing plasmid DNA. DNA. 1985 Apr;4(2):165–170. doi: 10.1089/dna.1985.4.165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daoudaki M. E., Becherer J. D., Lambris J. D. A 34-amino acid peptide of the third component of complement mediates properdin binding. J Immunol. 1988 Mar 1;140(5):1577–1580. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eggertsen G., Lundwall A., Hellman U., Sjöquist J. Antigenic relationships between human and cobra complement factors C3 and cobra venom factor (CVF) from the Indian cobra (Naja naja). J Immunol. 1983 Oct;131(4):1920–1923. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira A., Nussenzweig V. Genetic linkage between serum levels of the third component of complement and the H-2 complex. J Exp Med. 1975 Feb 1;141(2):513–517. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.2.513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujii T., Sekizawa A., Katagiri C. Characterization of the fourth component of complement in the serum of the clawed frog Xenopus laevis. Immunology. 1985 Dec;56(4):743–750. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jurd R. D. A natural heterohaemagglutinin in Xenopus laevis serum. Immunology. 1978 Mar;34(3):389–396. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kai C., Yoshikawa Y., Yamanouchi K., Okada H. Isolation and identification of the third component of complement of Japanese quails. J Immunol. 1983 Jun;130(6):2814–2820. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaidoh T., Gigli I. Phylogeny of C4b-C3b cleaving activity: similar fragmentation patterns of human C4b and C3b produced by lower animals. J Immunol. 1987 Jul 1;139(1):194–201. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kan C. C., Solomon E., Belt K. T., Chain A. C., Hiorns L. R., Fey G. Nucleotide sequence of cDNA encoding human alpha 2-macroglobulin and assignment of the chromosomal locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(8):2282–2286. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.8.2282. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein J., Figueroa F. Evolution of the major histocompatibility complex. Crit Rev Immunol. 1986;6(4):295–386. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kusano M., Choi N. H., Tomita M., Yamamoto K., Migita S., Sekiya T., Nishimura S. Nucleotide sequence of cDNA and derived amino acid sequence of rabbit complement component C3 alpha-chain. Immunol Invest. 1986 Jun;15(4):365–378. doi: 10.3109/08820138609052955. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambris J. D., Müller-Eberhard H. J. The multifunctional role of C3: structural analysis of its interactions with physiological ligands. Mol Immunol. 1986 Nov;23(11):1237–1242. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(86)90157-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambris J. D. The multifunctional role of C3, the third component of complement. Immunol Today. 1988 Dec;9(12):387–393. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(88)91240-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura T., Sekizawa A., Fujii T., Katagiri C. Cosegregation of the polymorphic C4 with the MHC in the frog, Xenopus laevis. Immunogenetics. 1986;23(3):181–186. doi: 10.1007/BF00373819. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Needleman S. B., Wunsch C. D. A general method applicable to the search for similarities in the amino acid sequence of two proteins. J Mol Biol. 1970 Mar;48(3):443–453. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90057-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nonaka M., Fujii T., Kaidoh T., Natsuume-Sakai S., Nonaka M., Yamaguchi N., Takahashi M. Purification of a lamprey complement protein homologous to the third component of the mammalian complement system. J Immunol. 1984 Dec;133(6):3242–3249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nonaka M., Fujii T., Kaidoh T., Natsuume-Sakai S., Nonaka M., Yamaguchi N., Takahashi M. Purification of a lamprey complement protein homologous to the third component of the mammalian complement system. J Immunol. 1984 Dec;133(6):3242–3249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nonaka M., Iwaki M., Nakai C., Nozaki M., Kaidoh T., Nonaka M., Natsuume-Sakai S., Takahashi M. Purification of a major serum protein of rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri) homologous to the third component of mammalian complement. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 25;259(10):6327–6333. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pangburn M. K., Müller-Eberhard H. J. The alternative pathway of complement. Springer Semin Immunopathol. 1984;7(2-3):163–192. doi: 10.1007/BF01893019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruoslahti E., Pierschbacher M. D. Arg-Gly-Asp: a versatile cell recognition signal. Cell. 1986 Feb 28;44(4):517–518. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90259-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwager J., Grossberger D., Du Pasquier L. Organization and rearrangement of immunoglobulin M genes in the amphibian Xenopus. EMBO J. 1988 Aug;7(8):2409–2415. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03086.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekizawa A., Fujii T., Katagiri C. Isolation and characterization of the third component of complement in the serum of the clawed frog, Xenopus laevis. J Immunol. 1984 Sep;133(3):1436–1443. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekizawa A., Fujii T., Tochinai S. Membrane receptors on Xenopus macrophages for two classes of immunoglobulins (IgM and IgY) and the third complement component (C3). J Immunol. 1984 Sep;133(3):1431–1435. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmons D., Makgoba M. W., Seed B. ICAM, an adhesion ligand of LFA-1, is homologous to the neural cell adhesion molecule NCAM. Nature. 1988 Feb 18;331(6157):624–627. doi: 10.1038/331624a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sottrup-Jensen L., Stepanik T. M., Kristensen T., Lønblad P. B., Jones C. M., Wierzbicki D. M., Magnusson S., Domdey H., Wetsel R. A., Lundwall A. Common evolutionary origin of alpha 2-macroglobulin and complement components C3 and C4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(1):9–13. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.1.9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tack B. F. The beta-Cys-gamma-Glu thiolester bond in human C3, C4, and alpha 2-macroglobulin. Springer Semin Immunopathol. 1983;6(4):259–282. doi: 10.1007/BF02116276. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Shine J., Chirgwin J., Pictet R., Tischer E., Rutter W. J., Goodman H. M. Rat insulin genes: construction of plasmids containing the coding sequences. Science. 1977 Jun 17;196(4296):1313–1319. doi: 10.1126/science.325648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogelstein B., Gillespie D. Preparative and analytical purification of DNA from agarose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):615–619. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wetsel R. A., Lundwall A., Davidson F., Gibson T., Tack B. F., Fey G. H. Structure of murine complement component C3. II. Nucleotide sequence of cloned complementary DNA coding for the alpha chain. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 25;259(22):13857–13862. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wetsel R. A., Ogata R. T., Tack B. F. Primary structure of the fifth component of murine complement. Biochemistry. 1987 Feb 10;26(3):737–743. doi: 10.1021/bi00377a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitehead A. S., Solomon E., Chambers S., Bodmer W. F., Povey S., Fey G. Assignment of the structural gene for the third component of human complement to chromosome 19. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(16):5021–5025. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.16.5021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright S. D., Reddy P. A., Jong M. T., Erickson B. W. C3bi receptor (complement receptor type 3) recognizes a region of complement protein C3 containing the sequence Arg-Gly-Asp. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(7):1965–1968. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.7.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Davis R. W. Efficient isolation of genes by using antibody probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(5):1194–1198. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.5.1194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Davis R. W. Yeast RNA polymerase II genes: isolation with antibody probes. Science. 1983 Nov 18;222(4625):778–782. doi: 10.1126/science.6356359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Bruijn M. H., Fey G. H. Human complement component C3: cDNA coding sequence and derived primary structure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(3):708–712. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.3.708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]