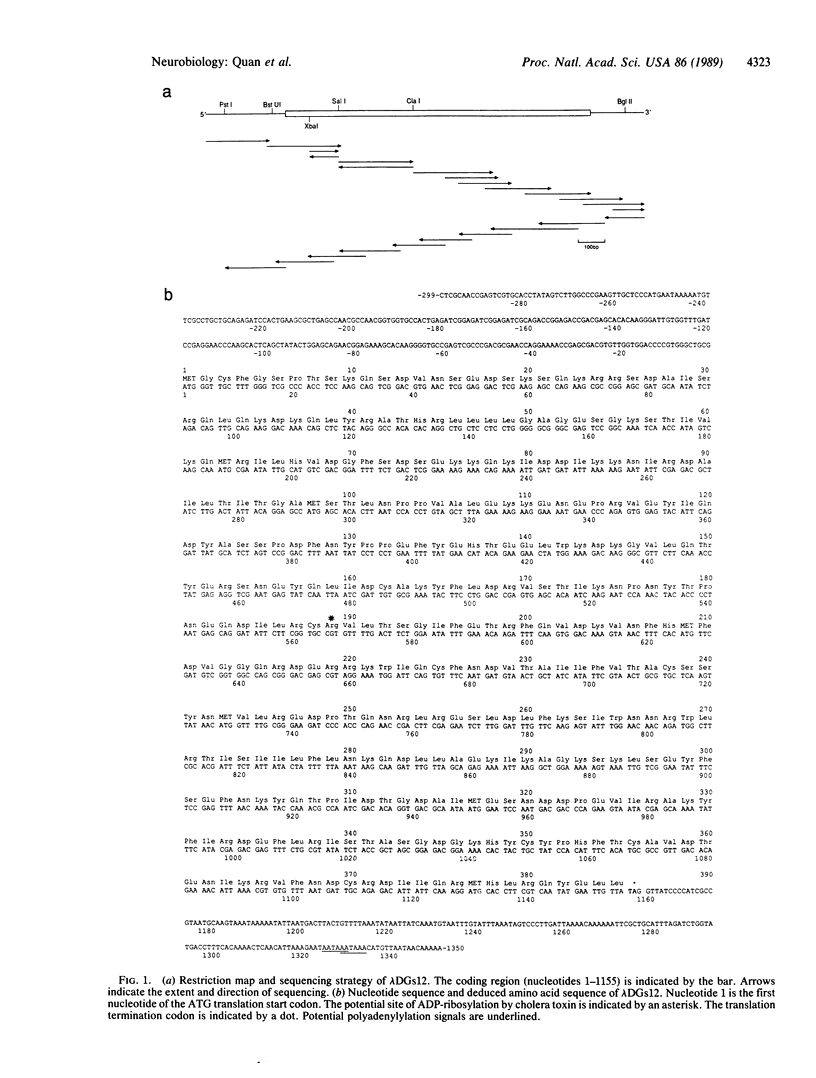
Abstract
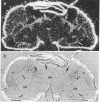
In mammals, the alpha subunit of the stimulatory guanine nucleotide-binding protein (Gs alpha) functions to couple a variety of extracellular membrane receptors to adenylate cyclase. Activation of Gs alpha results in the stimulation of adenylate cyclase and an increase in the second messenger cAMP. A 1.7-kilobase cDNA has been identified and characterized from Drosophila that codes for a protein 71% identical to bovine Gs alpha. The similarity is most striking in the regions thought to be responsible for the interactions with receptors and effectors, suggesting that the basic components of this signal-transduction pathway have been conserved through evolution. RNA blot hybridization and DNA sequence analysis suggest that a single transcript, expressed predominantly in the head, is present in Drosophila. In situ hybridization studies indicate that the Drosophila Gs alpha transcript is localized primarily in the cells of the central nervous system and in the eyes.
Full text
PDF


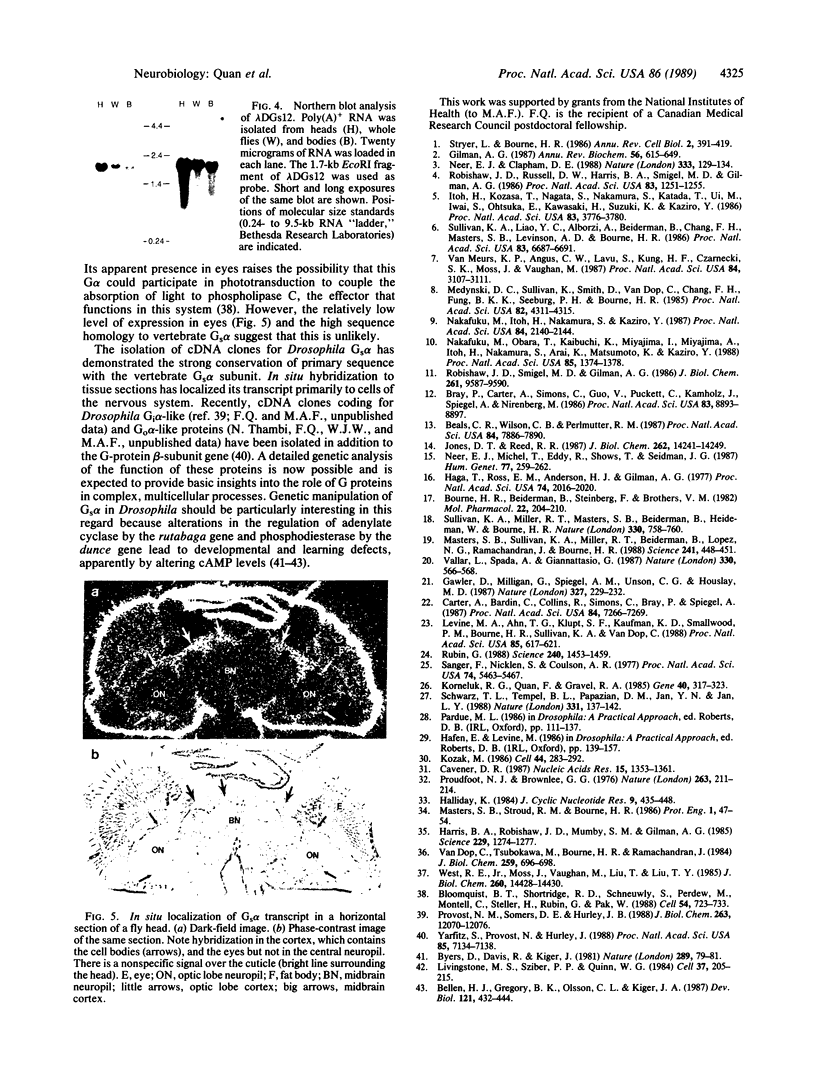
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beals C. R., Wilson C. B., Perlmutter R. M. A small multigene family encodes Gi signal-transduction proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(22):7886–7890. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.22.7886. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellen H. J., Gregory B. K., Olsson C. L., Kiger J. A., Jr Two Drosophila learning mutants, dunce and rutabaga, provide evidence of a maternal role for cAMP on embryogenesis. Dev Biol. 1987 Jun;121(2):432–444. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(87)90180-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloomquist B. T., Shortridge R. D., Schneuwly S., Perdew M., Montell C., Steller H., Rubin G., Pak W. L. Isolation of a putative phospholipase C gene of Drosophila, norpA, and its role in phototransduction. Cell. 1988 Aug 26;54(5):723–733. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80017-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourne H. R., Beiderman B., Steinberg F., Brothers V. M. Three adenylate cyclase phenotypes in S49 lymphoma cells produced by mutations of one gene. Mol Pharmacol. 1982 Jul;22(1):204–210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bray P., Carter A., Simons C., Guo V., Puckett C., Kamholz J., Spiegel A., Nirenberg M. Human cDNA clones for four species of G alpha s signal transduction protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):8893–8897. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.8893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byers D., Davis R. L., Kiger J. A., Jr Defect in cyclic AMP phosphodiesterase due to the dunce mutation of learning in Drosophila melanogaster. Nature. 1981 Jan 1;289(5793):79–81. doi: 10.1038/289079a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter A., Bardin C., Collins R., Simons C., Bray P., Spiegel A. Reduced expression of multiple forms of the alpha subunit of the stimulatory GTP-binding protein in pseudohypoparathyroidism type Ia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):7266–7269. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.7266. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavener D. R. Comparison of the consensus sequence flanking translational start sites in Drosophila and vertebrates. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Feb 25;15(4):1353–1361. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.4.1353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gawler D., Milligan G., Spiegel A. M., Unson C. G., Houslay M. D. Abolition of the expression of inhibitory guanine nucleotide regulatory protein Gi activity in diabetes. Nature. 1987 May 21;327(6119):229–232. doi: 10.1038/327229a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. G proteins: transducers of receptor-generated signals. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:615–649. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haga T., Ross E. M., Anderson H. J., Gilman A. G. Adenylate cyclase permanently uncoupled from hormone receptors in a novel variant of S49 mouse lymphoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 May;74(5):2016–2020. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.5.2016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halliday K. R. Regional homology in GTP-binding proto-oncogene products and elongation factors. J Cyclic Nucleotide Protein Phosphor Res. 1983;9(6):435–448. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris B. A., Robishaw J. D., Mumby S. M., Gilman A. G. Molecular cloning of complementary DNA for the alpha subunit of the G protein that stimulates adenylate cyclase. Science. 1985 Sep 20;229(4719):1274–1277. doi: 10.1126/science.3839937. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoh H., Kozasa T., Nagata S., Nakamura S., Katada T., Ui M., Iwai S., Ohtsuka E., Kawasaki H., Suzuki K. Molecular cloning and sequence determination of cDNAs for alpha subunits of the guanine nucleotide-binding proteins Gs, Gi, and Go from rat brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):3776–3780. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.3776. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones D. T., Reed R. R. Molecular cloning of five GTP-binding protein cDNA species from rat olfactory neuroepithelium. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 15;262(29):14241–14249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korneluk R. G., Quan F., Gravel R. A. Rapid and reliable dideoxy sequencing of double-stranded DNA. Gene. 1985;40(2-3):317–323. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90055-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Point mutations define a sequence flanking the AUG initiator codon that modulates translation by eukaryotic ribosomes. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):283–292. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90762-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. A., Ahn T. G., Klupt S. F., Kaufman K. D., Smallwood P. M., Bourne H. R., Sullivan K. A., Van Dop C. Genetic deficiency of the alpha subunit of the guanine nucleotide-binding protein Gs as the molecular basis for Albright hereditary osteodystrophy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(2):617–621. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.2.617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livingstone M. S., Sziber P. P., Quinn W. G. Loss of calcium/calmodulin responsiveness in adenylate cyclase of rutabaga, a Drosophila learning mutant. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):205–215. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90316-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masters S. B., Stroud R. M., Bourne H. R. Family of G protein alpha chains: amphipathic analysis and predicted structure of functional domains. Protein Eng. 1986 Oct-Nov;1(1):47–54. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masters S. B., Sullivan K. A., Miller R. T., Beiderman B., Lopez N. G., Ramachandran J., Bourne H. R. Carboxyl terminal domain of Gs alpha specifies coupling of receptors to stimulation of adenylyl cyclase. Science. 1988 Jul 22;241(4864):448–451. doi: 10.1126/science.2899356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medynski D. C., Sullivan K., Smith D., Van Dop C., Chang F. H., Fung B. K., Seeburg P. H., Bourne H. R. Amino acid sequence of the alpha subunit of transducin deduced from the cDNA sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(13):4311–4315. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.13.4311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakafuku M., Itoh H., Nakamura S., Kaziro Y. Occurrence in Saccharomyces cerevisiae of a gene homologous to the cDNA coding for the alpha subunit of mammalian G proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2140–2144. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakafuku M., Obara T., Kaibuchi K., Miyajima I., Miyajima A., Itoh H., Nakamura S., Arai K., Matsumoto K., Kaziro Y. Isolation of a second yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae gene (GPA2) coding for guanine nucleotide-binding regulatory protein: studies on its structure and possible functions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(5):1374–1378. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.5.1374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neer E. J., Clapham D. E. Roles of G protein subunits in transmembrane signalling. Nature. 1988 May 12;333(6169):129–134. doi: 10.1038/333129a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neer E. J., Michel T., Eddy R., Shows T., Seidman J. G. Genes for two homologous G-protein alpha subunits map to different human chromosomes. Hum Genet. 1987 Nov;77(3):259–262. doi: 10.1007/BF00284481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proudfoot N. J., Brownlee G. G. 3' non-coding region sequences in eukaryotic messenger RNA. Nature. 1976 Sep 16;263(5574):211–214. doi: 10.1038/263211a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Provost N. M., Somers D. E., Hurley J. B. A Drosophila melanogaster G protein alpha subunit gene is expressed primarily in embryos and pupae. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 25;263(24):12070–12076. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robishaw J. D., Russell D. W., Harris B. A., Smigel M. D., Gilman A. G. Deduced primary structure of the alpha subunit of the GTP-binding stimulatory protein of adenylate cyclase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(5):1251–1255. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.5.1251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robishaw J. D., Smigel M. D., Gilman A. G. Molecular basis for two forms of the G protein that stimulates adenylate cyclase. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 25;261(21):9587–9590. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin G. M. Drosophila melanogaster as an experimental organism. Science. 1988 Jun 10;240(4858):1453–1459. doi: 10.1126/science.3131880. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz T. L., Tempel B. L., Papazian D. M., Jan Y. N., Jan L. Y. Multiple potassium-channel components are produced by alternative splicing at the Shaker locus in Drosophila. Nature. 1988 Jan 14;331(6152):137–142. doi: 10.1038/331137a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stryer L., Bourne H. R. G proteins: a family of signal transducers. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1986;2:391–419. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.02.110186.002135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan K. A., Liao Y. C., Alborzi A., Beiderman B., Chang F. H., Masters S. B., Levinson A. D., Bourne H. R. Inhibitory and stimulatory G proteins of adenylate cyclase: cDNA and amino acid sequences of the alpha chains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):6687–6691. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.6687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallar L., Spada A., Giannattasio G. Altered Gs and adenylate cyclase activity in human GH-secreting pituitary adenomas. Nature. 1987 Dec 10;330(6148):566–568. doi: 10.1038/330566a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Dop C., Tsubokawa M., Bourne H. R., Ramachandran J. Amino acid sequence of retinal transducin at the site ADP-ribosylated by cholera toxin. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jan 25;259(2):696–698. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Meurs K. P., Angus C. W., Lavu S., Kung H. F., Czarnecki S. K., Moss J., Vaughan M. Deduced amino acid sequence of bovine retinal Go alpha: similarities to other guanine nucleotide-binding proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(10):3107–3111. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West R. E., Jr, Moss J., Vaughan M., Liu T., Liu T. Y. Pertussis toxin-catalyzed ADP-ribosylation of transducin. Cysteine 347 is the ADP-ribose acceptor site. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 25;260(27):14428–14430. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarfitz S., Provost N. M., Hurley J. B. Cloning of a Drosophila melanogaster guanine nucleotide regulatory protein beta-subunit gene and characterization of its expression during development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(19):7134–7138. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.19.7134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]