Abstract
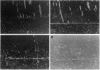
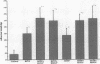
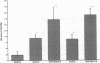
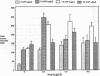
The trefoil peptides, a recently recognized family of protease-resistant peptides, expressed in a regional specific pattern throughout the normal gastrointestinal tract. Although these peptides have been hypothesized to act as growth factors, their functional properties are largely unknown. Addition of recombinant trefoil peptides human spasmolytic polypeptide (HSP), rat and human intestinal trefoil factor (RITF and HITF) to subconfluent nontransformed rat intestinal epithelial cell lines (IEC-6 and IEC-17), human colon cancer-derived cell lines (HT-29 and CaCO2) or nontransformed fibroblasts (NRK and BHK) had no significant effect on proliferation. However addition of the trefoil peptides to wounded monolayers of confluent IEC-6 cells in an in vitro model of epithelial restitution resulted in a 3-6-fold increase in the rate of epithelial migration into the wound. Stimulation of restitution by the trefoil peptide HSP was enhanced in a cooperative fashion by the addition of mucin glycoproteins purified from the colon or small intestine of either rat or man, achieving up to a 15-fold enhancement in restitution. No synergistic effect was observed by the addition of nonmucin glycoproteins. In contrast to cytokine stimulation of intestinal epithelial cell restitution which is mediated through enhanced TGF beta bioactivity, trefoil peptide, and trefoil peptide-mucin glycoprotein stimulation of restitution was not associated with alteration in concentrations of bioactive TGF-beta and was not affected by the presence of immunoneutralizing anti-TGF beta antiserum. Collectively, these findings suggest that the trefoil peptides which are secreted onto the lumenal surface of the gastrointestinal tract may act in conjunction with the mucin glycoprotein products of goblet cells to promote reestablishment of mucosal integrity after injury through mechanisms distinct from those which may act at the basolateral pole of the epithelium.
Full text
PDF


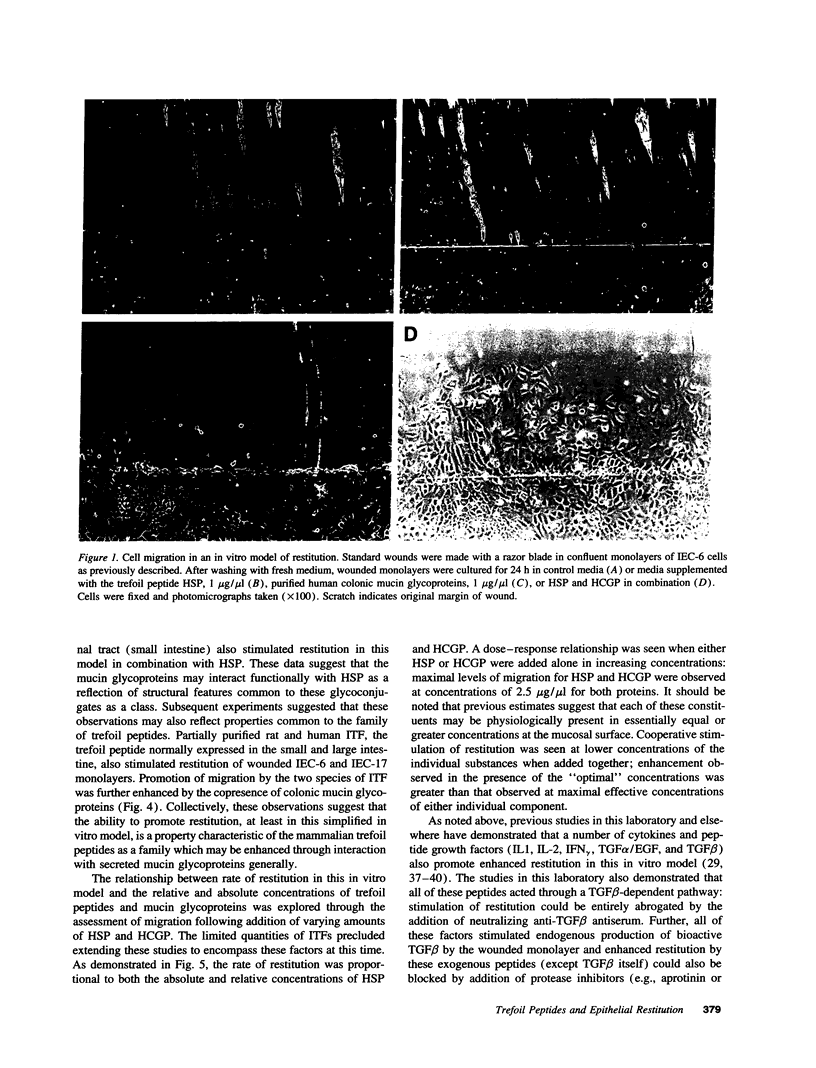
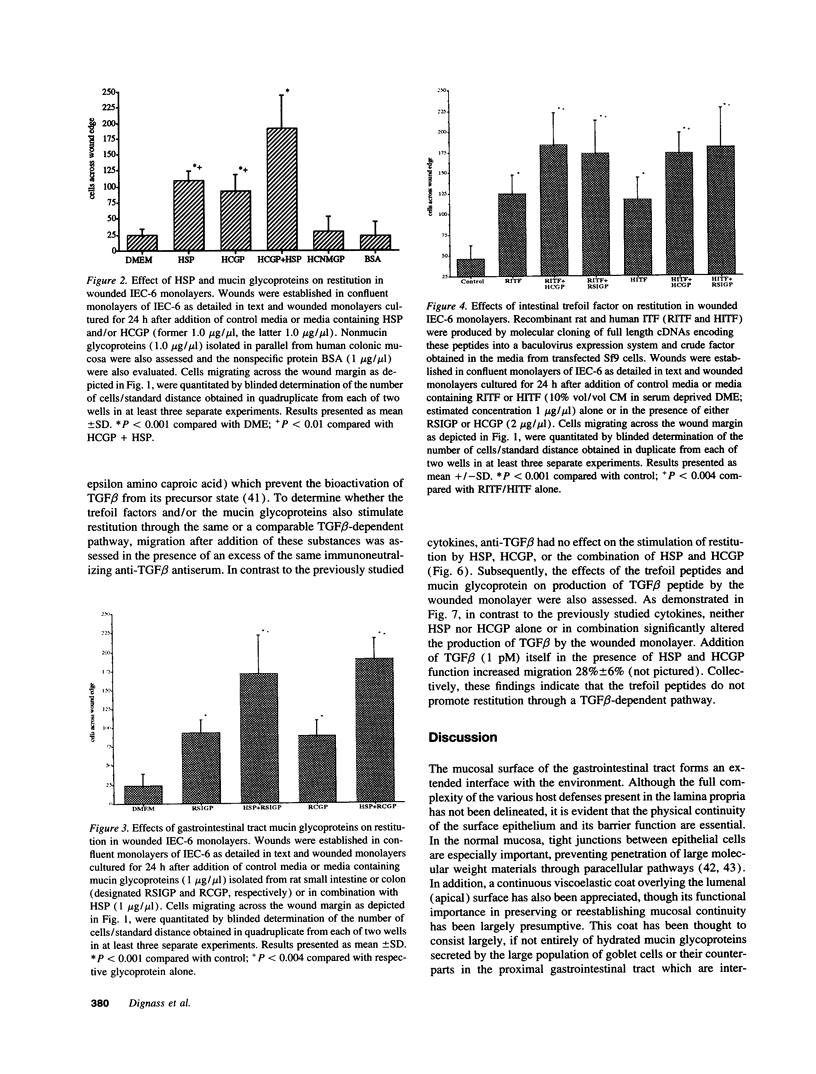
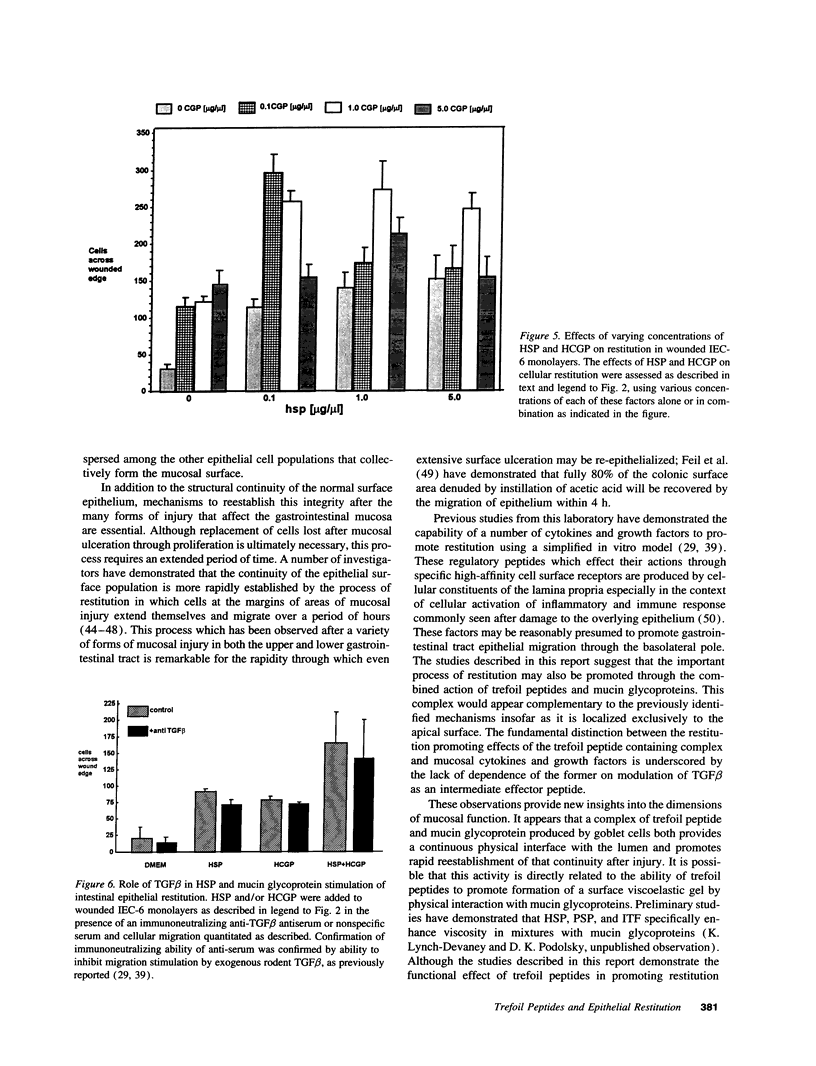


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Basson M. D., Modlin I. M., Flynn S. D., Jena B. P., Madri J. A. Independent modulation of enterocyte migration and proliferation by growth factors, matrix proteins, and pharmacologic agents in an in vitro model of mucosal healing. Surgery. 1992 Aug;112(2):299–308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basson M. D., Modlin I. M., Madri J. A. Human enterocyte (Caco-2) migration is modulated in vitro by extracellular matrix composition and epidermal growth factor. J Clin Invest. 1992 Jul;90(1):15–23. doi: 10.1172/JCI115828. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blay J., Brown K. D. Epidermal growth factor promotes the chemotactic migration of cultured rat intestinal epithelial cells. J Cell Physiol. 1985 Jul;124(1):107–112. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041240117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A. M., Jeltsch J. M., Roberts M., Chambon P. Activation of pS2 gene transcription is a primary response to estrogen in the human breast cancer cell line MCF-7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(20):6344–6348. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.20.6344. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carr M. D. 1H NMR-based determination of the secondary structure of porcine pancreatic spasmolytic polypeptide: one of a new family of "trefoil" motif containing cell growth factors. Biochemistry. 1992 Feb 25;31(7):1998–2004. doi: 10.1021/bi00122a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chinery R., Poulsom R., Elia G., Hanby A. M., Wright N. A. Expression and purification of a trefoil peptide motif in a beta-galactosidase fusion protein and its use to search for trefoil-binding sites. Eur J Biochem. 1993 Mar 1;212(2):557–563. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1993.tb17693.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciacci C., Lind S. E., Podolsky D. K. Transforming growth factor beta regulation of migration in wounded rat intestinal epithelial monolayers. Gastroenterology. 1993 Jul;105(1):93–101. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(93)90014-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danielpour D., Dart L. L., Flanders K. C., Roberts A. B., Sporn M. B. Immunodetection and quantitation of the two forms of transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta 1 and TGF-beta 2) secreted by cells in culture. J Cell Physiol. 1989 Jan;138(1):79–86. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041380112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignass A. U., Podolsky D. K. Cytokine modulation of intestinal epithelial cell restitution: central role of transforming growth factor beta. Gastroenterology. 1993 Nov;105(5):1323–1332. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(93)90136-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feil W., Wenzl E., Vattay P., Starlinger M., Sogukoglu T., Schiessel R. Repair of rabbit duodenal mucosa after acid injury in vivo and in vitro. Gastroenterology. 1987 Jun;92(6):1973–1986. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(87)90632-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frandsen E. K., Jørgensen K. H., Thim L. Receptor binding of pancreatic spasmolytic polypeptide (PSP) in rat intestinal mucosal cell membranes inhibits the adenylate cyclase activity. Regul Pept. 1986 Dec 30;16(3-4):291–297. doi: 10.1016/0167-0115(86)90028-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauser F., Gertzen E. M., Hoffmann W. Expression of spasmolysin (FIM-A.1): an integumentary mucin from Xenopus laevis. Exp Cell Res. 1990 Aug;189(2):157–162. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(90)90230-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauser F., Hoffmann W. P-domains as shuffled cysteine-rich modules in integumentary mucin C.1 (FIM-C.1) from Xenopus laevis. Polydispersity and genetic polymorphism. J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 5;267(34):24620–24624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauser F., Hoffmann W. xP1 and xP4. P-domain peptides expressed in Xenopus laevis stomach mucosa. J Biol Chem. 1991 Nov 5;266(31):21306–21309. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauser F., Roeben C., Hoffmann W. xP2, a new member of the P-domain peptide family of potential growth factors, is synthesized in Xenopus laevis skin. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 15;267(20):14451–14455. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann W. A new repetitive protein from Xenopus laevis skin highly homologous to pancreatic spasmolytic polypeptide. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 5;263(16):7686–7690. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann W., Hauser F. The P-domain or trefoil motif: a role in renewal and pathology of mucous epithelia? Trends Biochem Sci. 1993 Jul;18(7):239–243. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(93)90170-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoosein N. M., Thim L., Jørgensen K. H., Brattain M. G. Growth stimulatory effect of pancreatic spasmolytic polypeptide on cultured colon and breast tumor cells. FEBS Lett. 1989 Apr 24;247(2):303–306. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81357-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jørgensen K. D., Diamant B., Jørgensen K. H., Thim L. Pancreatic spasmolytic polypeptide (PSP): III. Pharmacology of a new porcine pancreatic polypeptide with spasmolytic and gastric acid secretion inhibitory effects. Regul Pept. 1982 Mar;3(3-4):231–243. doi: 10.1016/0167-0115(82)90128-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jørgensen K. H., Thim L., Jacobsen H. E. Pancreatic spasmolytic polypeptide (PSP): I. Preparation and initial chemical characterization of a new polypeptide from porcine pancreas. Regul Pept. 1982 Mar;3(3-4):207–219. doi: 10.1016/0167-0115(82)90126-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurokowa M., Lynch K., Podolsky D. K. Effects of growth factors on an intestinal epithelial cell line: transforming growth factor beta inhibits proliferation and stimulates differentiation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Feb 13;142(3):775–782. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)91481-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaMont J. T., Ventola A. S. Purification and composition of colonic epithelial mucin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Nov 20;626(1):234–243. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(80)90214-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madara J. L., Stafford J. Interferon-gamma directly affects barrier function of cultured intestinal epithelial monolayers. J Clin Invest. 1989 Feb;83(2):724–727. doi: 10.1172/JCI113938. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massagué J. The transforming growth factor-beta family. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1990;6:597–641. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.06.110190.003121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore R., Carlson S., Madara J. L. Rapid barrier restitution in an in vitro model of intestinal epithelial injury. Lab Invest. 1989 Feb;60(2):237–244. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C., Sporn M. Cytokines in context. J Cell Biol. 1991 Jun;113(5):981–986. doi: 10.1083/jcb.113.5.981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nusrat A., Delp C., Madara J. L. Intestinal epithelial restitution. Characterization of a cell culture model and mapping of cytoskeletal elements in migrating cells. J Clin Invest. 1992 May;89(5):1501–1511. doi: 10.1172/JCI115741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pircher R., Jullien P., Lawrence D. A. Beta-transforming growth factor is stored in human blood platelets as a latent high molecular weight complex. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Apr 14;136(1):30–37. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90872-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podolsky D. K., Isselbacher K. J. Composition of human colonic mucin. Selective alteration in inflammatory bowel disease. J Clin Invest. 1983 Jul;72(1):142–153. doi: 10.1172/JCI110952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podolsky D. K., Lynch-Devaney K., Stow J. L., Oates P., Murgue B., DeBeaumont M., Sands B. E., Mahida Y. R. Identification of human intestinal trefoil factor. Goblet cell-specific expression of a peptide targeted for apical secretion. J Biol Chem. 1993 Mar 25;268(9):6694–6702. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podolsky D. K. Oligosaccharide structures of human colonic mucin. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jul 15;260(14):8262–8271. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quaroni A., Wands J., Trelstad R. L., Isselbacher K. J. Epithelioid cell cultures from rat small intestine. Characterization by morphologic and immunologic criteria. J Cell Biol. 1979 Feb;80(2):248–265. doi: 10.1083/jcb.80.2.248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rio M. C., Bellocq J. P., Daniel J. Y., Tomasetto C., Lathe R., Chenard M. P., Batzenschlager A., Chambon P. Breast cancer-associated pS2 protein: synthesis and secretion by normal stomach mucosa. Science. 1988 Aug 5;241(4866):705–708. doi: 10.1126/science.3041593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rio M. C., Chenard M. P., Wolf C., Marcellin L., Tomasetto C., Lathe R., Bellocq J. P., Chambon P. Induction of pS2 and hSP genes as markers of mucosal ulceration of the digestive tract. Gastroenterology. 1991 Feb;100(2):375–379. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(91)90205-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato Y., Rifkin D. B. Inhibition of endothelial cell movement by pericytes and smooth muscle cells: activation of a latent transforming growth factor-beta 1-like molecule by plasmin during co-culture. J Cell Biol. 1989 Jul;109(1):309–315. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.1.309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suemori S., Lynch-Devaney K., Podolsky D. K. Identification and characterization of rat intestinal trefoil factor: tissue- and cell-specific member of the trefoil protein family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 15;88(24):11017–11021. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.24.11017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thim L. A new family of growth factor-like peptides. 'Trefoil' disulphide loop structures as a common feature in breast cancer associated peptide (pS2), pancreatic spasmolytic polypeptide (PSP), and frog skin peptides (spasmolysins). FEBS Lett. 1989 Jun 19;250(1):85–90. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80690-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thim L. A surprising sequence homology. Biochem J. 1988 Jul 1;253(1):309–309. doi: 10.1042/bj2530309a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thim L., Jørgensen K. H., Jørgensen K. D. Pancreatic spasmolytic polypeptide (PSP): II. Radioimmunological determination of PSP in porcine tissues, plasma and pancreatic juice. Regul Pept. 1982 Mar;3(3-4):221–230. doi: 10.1016/0167-0115(82)90127-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thim L., Norris K., Norris F., Nielsen P. F., Bjørn S. E., Christensen M., Petersen J. Purification and characterization of the trefoil peptide human spasmolytic polypeptide (hSP) produced in yeast. FEBS Lett. 1993 Mar 8;318(3):345–352. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)80543-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomasetto C., Rio M. C., Gautier C., Wolf C., Hareuveni M., Chambon P., Lathe R. hSP, the domain-duplicated homolog of pS2 protein, is co-expressed with pS2 in stomach but not in breast carcinoma. EMBO J. 1990 Feb;9(2):407–414. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08125.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waller D. A., Thomas N. W., Self T. J. Epithelial restitution in the large intestine of the rat following insult with bile salts. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histopathol. 1988;414(1):77–81. doi: 10.1007/BF00749741. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright N. A., Pike C., Elia G. Induction of a novel epidermal growth factor-secreting cell lineage by mucosal ulceration in human gastrointestinal stem cells. Nature. 1990 Jan 4;343(6253):82–85. doi: 10.1038/343082a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright N. A., Poulsom R., Stamp G., Van Noorden S., Sarraf C., Elia G., Ahnen D., Jeffery R., Longcroft J., Pike C. Trefoil peptide gene expression in gastrointestinal epithelial cells in inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology. 1993 Jan;104(1):12–20. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(93)90830-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]