Abstract
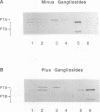
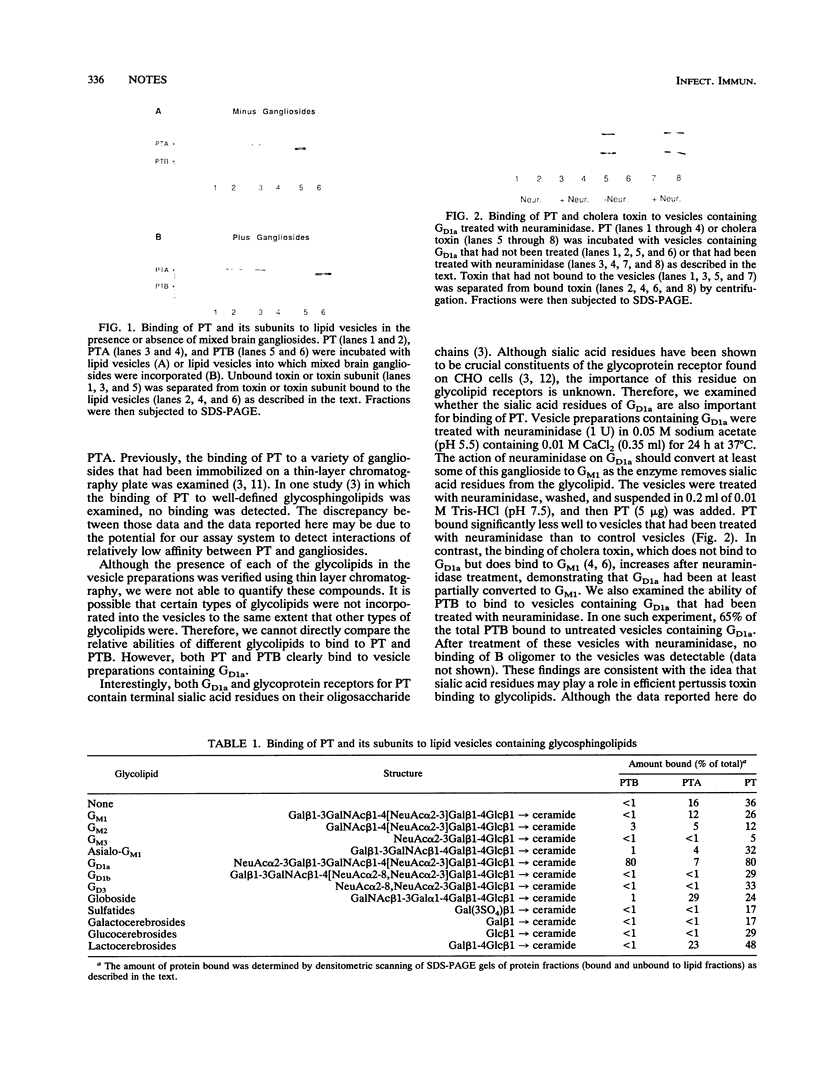
The binding of pertussis toxin and its B oligomer to lipid vesicles containing glycosphingolipids was studied. Both pertussis toxin and the B oligomer bound to lipid vesicles containing ganglioside GD1a. Binding of pertussis toxin to these vesicles decreased upon treatment of the vesicles with neuraminidase, suggesting that sialic acid residues are important for efficient binding of the toxin to GD1a.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arciniega J. L., Burns D. L., Garcia-Ortigoza E., Manclark C. R. Immune response to the B oligomer of pertussis toxin. Infect Immun. 1987 May;55(5):1132–1136. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.5.1132-1136.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong G. D., Howard L. A., Peppler M. S. Use of glycosyltransferases to restore pertussis toxin receptor activity to asialoagalactofetuin. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 25;263(18):8677–8684. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brennan M. J., David J. L., Kenimer J. G., Manclark C. R. Lectin-like binding of pertussis toxin to a 165-kilodalton Chinese hamster ovary cell glycoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 5;263(10):4895–4899. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P. Gangliosides and membrane receptors for cholera toxin. Biochemistry. 1973 Aug 28;12(18):3558–3566. doi: 10.1021/bi00742a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hausman S. Z., Burns D. L. Interaction of pertussis toxin with cells and model membranes. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 5;267(19):13735–13739. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmgren J., Lönnroth I., Svennerholm L. Tissue receptor for cholera exotoxin: postulated structure from studies with GM1 ganglioside and related glycolipids. Infect Immun. 1973 Aug;8(2):208–214. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.2.208-214.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinsky S. C., Haxby J. A., Zopf D. A., Alving C. R., Kinsky C. B. Complement-dependent damage to liposomes prepared from pure lipids and Forssman hapten. Biochemistry. 1969 Oct;8(10):4149–4158. doi: 10.1021/bi00838a036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saukkonen K., Burnette W. N., Mar V. L., Masure H. R., Tuomanen E. I. Pertussis toxin has eukaryotic-like carbohydrate recognition domains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jan 1;89(1):118–122. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.1.118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura M., Nogimori K., Murai S., Yajima M., Ito K., Katada T., Ui M., Ishii S. Subunit structure of islet-activating protein, pertussis toxin, in conformity with the A-B model. Biochemistry. 1982 Oct 26;21(22):5516–5522. doi: 10.1021/bi00265a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuomanen E., Towbin H., Rosenfelder G., Braun D., Larson G., Hansson G. C., Hill R. Receptor analogs and monoclonal antibodies that inhibit adherence of Bordetella pertussis to human ciliated respiratory epithelial cells. J Exp Med. 1988 Jul 1;168(1):267–277. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.1.267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witvliet M. H., Burns D. L., Brennan M. J., Poolman J. T., Manclark C. R. Binding of pertussis toxin to eucaryotic cells and glycoproteins. Infect Immun. 1989 Nov;57(11):3324–3330. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.11.3324-3330.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]