Abstract
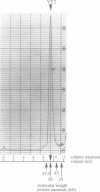
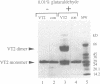
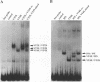
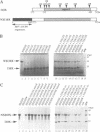
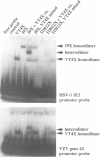
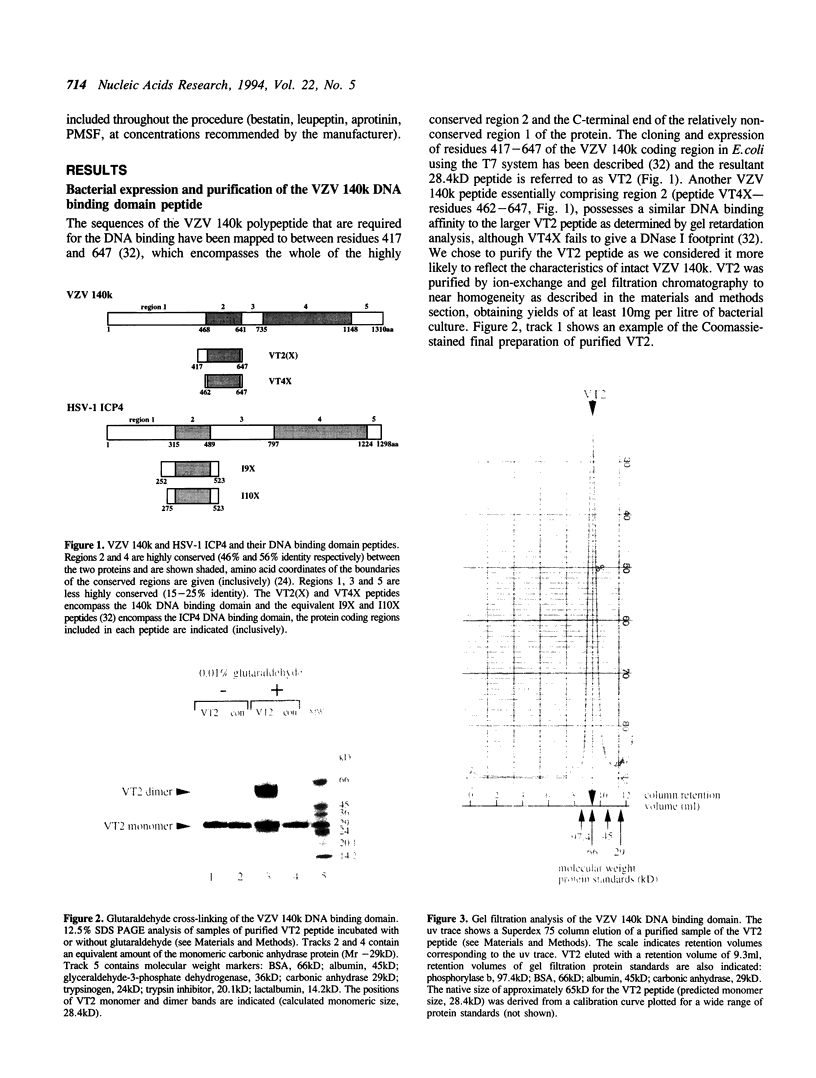
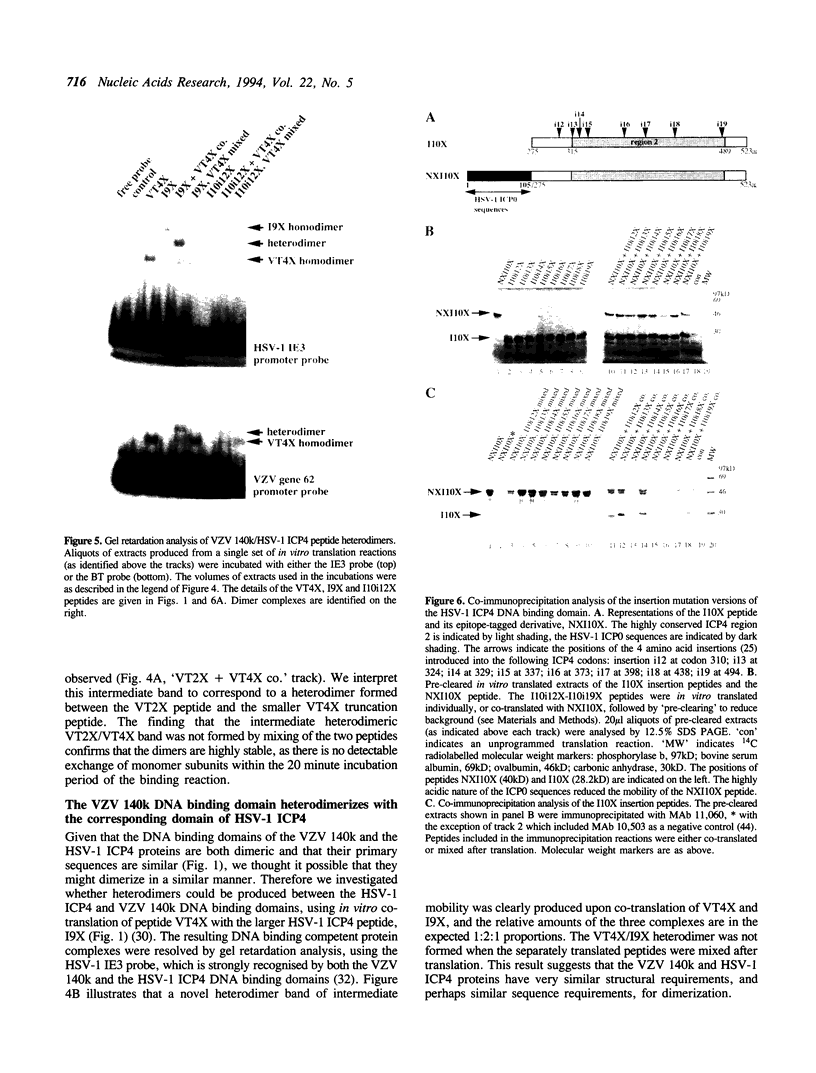
The product of varicella-zoster virus gene 62 (VZV 140k) is the functional counterpart of the major transcriptional regulatory protein of herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1), ICP4. We have found that the purified bacterially expressed DNA binding domain of VZV 140k (residues 417-647) is a stable dimer in solution. As demonstrated by the appearance of a novel protein--DNA complex of intermediate mobility in gel retardation assays, following in vitro co-translation of a pair of differently sized VZV 140k DNA binding domain peptides, the 140k DNA binding domain peptide binds to DNA as a dimer. In addition, the DNA binding domain peptide of HSV-1 ICP4 readily heterodimerizes with the VZV 140k peptide on co-translation, indicating that HSV-1 ICP4 and VZV 140k possess very similar dimerization interfaces. It appears that only one fully wild type subunit of the dimer is sufficient to mediate sequence specific DNA recognition in certain circumstances. Co-immunoprecipitation analysis of mutant DNA binding domain peptides, co-translated with an epitope-tagged ICP4 DNA binding domain, shows that the sequence requirements for dimerization are lower than those necessary for DNA binding.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson A. S., Francesconi A., Morgan R. W. Complete nucleotide sequence of the Marek's disease virus ICP4 gene. Virology. 1992 Aug;189(2):657–667. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90589-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brennan R. G., Roderick S. L., Takeda Y., Matthews B. W. Protein-DNA conformational changes in the crystal structure of a lambda Cro-operator complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(20):8165–8169. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.20.8165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabirac G. F., Mahalingam R., Wellish M., Gilden D. H. Trans-activation of viral tk promoters by proteins encoded by varicella zoster virus open reading frames 61 and 62. Virus Res. 1990 Jan;15(1):57–68. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(90)90013-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung A. K. DNA nucleotide sequence analysis of the immediate-early gene of pseudorabies virus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jun 26;17(12):4637–4646. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.12.4637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison A. J., Scott J. E. The complete DNA sequence of varicella-zoster virus. J Gen Virol. 1986 Sep;67(Pt 9):1759–1816. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-9-1759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLuca N. A., McCarthy A. M., Schaffer P. A. Isolation and characterization of deletion mutants of herpes simplex virus type 1 in the gene encoding immediate-early regulatory protein ICP4. J Virol. 1985 Nov;56(2):558–570. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.2.558-570.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLuca N. A., Schaffer P. A. Activation of immediate-early, early, and late promoters by temperature-sensitive and wild-type forms of herpes simplex virus type 1 protein ICP4. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;5(8):1997–2008. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.8.1997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiDonato J. A., Muller M. T. DNA binding and gene regulation by the herpes simplex virus type 1 protein ICP4 and involvement of the TATA element. J Virol. 1989 Sep;63(9):3737–3747. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.9.3737-3747.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Disney G. H., Everett R. D. A herpes simplex virus type 1 recombinant with both copies of the Vmw175 coding sequences replaced by the homologous varicella-zoster virus open reading frame. J Gen Virol. 1990 Nov;71(Pt 11):2681–2689. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-71-11-2681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Disney G. H., McKee T. A., Preston C. M., Everett R. D. The product of varicella-zoster virus gene 62 autoregulates its own promoter. J Gen Virol. 1990 Dec;71(Pt 12):2999–3003. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-71-12-2999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon R. A., Schaffer P. A. Fine-structure mapping and functional analysis of temperature-sensitive mutants in the gene encoding the herpes simplex virus type 1 immediate early protein VP175. J Virol. 1980 Oct;36(1):189–203. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.1.189-203.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellenberger T. E., Brandl C. J., Struhl K., Harrison S. C. The GCN4 basic region leucine zipper binds DNA as a dimer of uninterrupted alpha helices: crystal structure of the protein-DNA complex. Cell. 1992 Dec 24;71(7):1223–1237. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(05)80070-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everett R. D., Cross A., Orr A. A truncated form of herpes simplex virus type 1 immediate-early protein Vmw110 is expressed in a cell type dependent manner. Virology. 1993 Dec;197(2):751–756. doi: 10.1006/viro.1993.1651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everett R. D., Elliott M., Hope G., Orr A. Purification of the DNA binding domain of herpes simplex virus type 1 immediate-early protein Vmw175 as a homodimer and extensive mutagenesis of its DNA recognition site. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Sep 25;19(18):4901–4908. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.18.4901. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everett R. D., Orr A., Elliott M. High level expression and purification of herpes simplex virus type 1 immediate early polypeptide Vmw110. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Nov 25;19(22):6155–6161. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.22.6155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everett R. D., Paterson T., Elliott M. The major transcriptional regulatory protein of herpes simplex virus type 1 includes a protease resistant DNA binding domain. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Aug 11;18(15):4579–4585. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.15.4579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everett R. D. The regulation of transcription of viral and cellular genes by herpesvirus immediate-early gene products (review). Anticancer Res. 1987 Jul-Aug;7(4A):589–604. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everett R. D. Trans activation of transcription by herpes virus products: requirement for two HSV-1 immediate-early polypeptides for maximum activity. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 20;3(13):3135–3141. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02270.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everett R., Cross A., Tyler J., Orr A. An epitope within the DNA-binding domain of the herpes simplex virus immediate early protein Vmw175 is conserved in the varicella-zoster virus gene 62 protein. J Gen Virol. 1993 Sep;74(Pt 9):1955–1958. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-74-9-1955. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faber S. W., Wilcox K. W. Association of the herpes simplex virus regulatory protein ICP4 with specific nucleotide sequences in DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Aug 11;14(15):6067–6083. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.15.6067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felser J. M., Kinchington P. R., Inchauspe G., Straus S. E., Ostrove J. M. Cell lines containing varicella-zoster virus open reading frame 62 and expressing the "IE" 175 protein complement ICP4 mutants of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Virol. 1988 Jun;62(6):2076–2082. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.6.2076-2082.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felser J. M., Straus S. E., Ostrove J. M. Varicella-zoster virus complements herpes simplex virus type 1 temperature-sensitive mutants. J Virol. 1987 Jan;61(1):225–228. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.1.225-228.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godowski P. J., Knipe D. M. Transcriptional control of herpesvirus gene expression: gene functions required for positive and negative regulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jan;83(2):256–260. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.2.256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grundy F. J., Baumann R. P., O'Callaghan D. J. DNA sequence and comparative analyses of the equine herpesvirus type 1 immediate early gene. Virology. 1989 Sep;172(1):223–236. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90124-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison S. C. A structural taxonomy of DNA-binding domains. Nature. 1991 Oct 24;353(6346):715–719. doi: 10.1038/353715a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hope I. A., Struhl K. GCN4, a eukaryotic transcriptional activator protein, binds as a dimer to target DNA. EMBO J. 1987 Sep;6(9):2781–2784. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02573.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inchauspe G., Nagpal S., Ostrove J. M. Mapping of two varicella-zoster virus-encoded genes that activate the expression of viral early and late genes. Virology. 1989 Dec;173(2):700–709. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90583-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inchauspe G., Ostrove J. M. Differential regulation by varicella-zoster virus (VZV) and herpes simplex virus type-1 trans-activating genes. Virology. 1989 Dec;173(2):710–714. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90584-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kattar-Cooley P., Wilcox K. W. Characterization of the DNA-binding properties of herpes simplex virus regulatory protein ICP4. J Virol. 1989 Feb;63(2):696–704. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.2.696-704.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landschulz W. H., Johnson P. F., McKnight S. L. The leucine zipper: a hypothetical structure common to a new class of DNA binding proteins. Science. 1988 Jun 24;240(4860):1759–1764. doi: 10.1126/science.3289117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGeoch D. J., Dalrymple M. A., Davison A. J., Dolan A., Frame M. C., McNab D., Perry L. J., Scott J. E., Taylor P. The complete DNA sequence of the long unique region in the genome of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Gen Virol. 1988 Jul;69(Pt 7):1531–1574. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-7-1531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGeoch D. J., Dolan A., Donald S., Brauer D. H. Complete DNA sequence of the short repeat region in the genome of herpes simplex virus type 1. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Feb 25;14(4):1727–1745. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.4.1727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metzler D. W., Wilcox K. W. Isolation of herpes simplex virus regulatory protein ICP4 as a homodimeric complex. J Virol. 1985 Aug;55(2):329–337. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.2.329-337.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michael N., Roizman B. Binding of the herpes simplex virus major regulatory protein to viral DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(24):9808–9812. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.24.9808. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller M. T. Binding of the herpes simplex virus immediate-early gene product ICP4 to its own transcription start site. J Virol. 1987 Mar;61(3):858–865. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.3.858-865.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murre C., McCaw P. S., Baltimore D. A new DNA binding and dimerization motif in immunoglobulin enhancer binding, daughterless, MyoD, and myc proteins. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):777–783. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90682-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Hare P., Hayward G. S. Three trans-acting regulatory proteins of herpes simplex virus modulate immediate-early gene expression in a pathway involving positive and negative feedback regulation. J Virol. 1985 Dec;56(3):723–733. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.3.723-733.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliphant A. R., Brandl C. J., Struhl K. Defining the sequence specificity of DNA-binding proteins by selecting binding sites from random-sequence oligonucleotides: analysis of yeast GCN4 protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jul;9(7):2944–2949. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.7.2944. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson T., Everett R. D. Mutational dissection of the HSV-1 immediate-early protein Vmw175 involved in transcriptional transactivation and repression. Virology. 1988 Sep;166(1):186–196. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90160-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson T., Everett R. D. The regions of the herpes simplex virus type 1 immediate early protein Vmw175 required for site specific DNA binding closely correspond to those involved in transcriptional regulation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Dec 9;16(23):11005–11025. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.23.11005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perera L. P., Mosca J. D., Ruyechan W. T., Hay J. Regulation of varicella-zoster virus gene expression in human T lymphocytes. J Virol. 1992 Sep;66(9):5298–5304. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.9.5298-5304.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perera L. P., Mosca J. D., Sadeghi-Zadeh M., Ruyechan W. T., Hay J. The varicella-zoster virus immediate early protein, IE62, can positively regulate its cognate promoter. Virology. 1992 Nov;191(1):346–354. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90197-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perisic O., Xiao H., Lis J. T. Stable binding of Drosophila heat shock factor to head-to-head and tail-to-tail repeats of a conserved 5 bp recognition unit. Cell. 1989 Dec 1;59(5):797–806. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90603-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters K., Richards F. M. Chemical cross-linking: reagents and problems in studies of membrane structure. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:523–551. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.002515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pizer L. I., Everett R. D., Tedder D. G., Elliott M., Litman B. Nucleotides within both proximal and distal parts of the consensus sequence are important for specific DNA recognition by the herpes simplex virus regulatory protein ICP4. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Feb 11;19(3):477–483. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.3.477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston C. M. Control of herpes simplex virus type 1 mRNA synthesis in cells infected with wild-type virus or the temperature-sensitive mutant tsK. J Virol. 1979 Jan;29(1):275–284. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.1.275-284.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepard A. A., DeLuca N. A. Activities of heterodimers composed of DNA-binding- and transactivation-deficient subunits of the herpes simplex virus regulatory protein ICP4. J Virol. 1991 Jan;65(1):299–307. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.1.299-307.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepard A. A., DeLuca N. A. Intragenic complementation among partial peptides of herpes simplex virus regulatory protein ICP4. J Virol. 1989 Mar;63(3):1203–1211. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.3.1203-1211.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepard A. A., Imbalzano A. N., DeLuca N. A. Separation of primary structural components conferring autoregulation, transactivation, and DNA-binding properties to the herpes simplex virus transcriptional regulatory protein ICP4. J Virol. 1989 Sep;63(9):3714–3728. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.9.3714-3728.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepard A. A., Tolentino P., DeLuca N. A. trans-dominant inhibition of herpes simplex virus transcriptional regulatory protein ICP4 by heterodimer formation. J Virol. 1990 Aug;64(8):3916–3926. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.8.3916-3926.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiraki K., Hyman R. W. The immediate early proteins of varicella-zoster virus. Virology. 1987 Feb;156(2):423–426. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90423-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Rosenberg A. H., Dunn J. J., Dubendorff J. W. Use of T7 RNA polymerase to direct expression of cloned genes. Methods Enzymol. 1990;185:60–89. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)85008-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyler J. K., Everett R. D. The DNA binding domain of the varicella-zoster virus gene 62 protein interacts with multiple sequences which are similar to the binding site of the related protein of herpes simplex virus type 1. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Feb 11;21(3):513–522. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.3.513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson R. J., Clements J. B. A herpes simplex virus type 1 function continuously required for early and late virus RNA synthesis. Nature. 1980 May 29;285(5763):329–330. doi: 10.1038/285329a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C. L., Wilcox K. W. Codons 262 to 490 from the herpes simplex virus ICP4 gene are sufficient to encode a sequence-specific DNA binding protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Feb 11;18(3):531–538. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.3.531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C. L., Wilcox K. W. The conserved DNA-binding domains encoded by the herpes simplex virus type 1 ICP4, pseudorabies virus IE180, and varicella-zoster virus ORF62 genes recognize similar sites in the corresponding promoters. J Virol. 1991 Mar;65(3):1149–1159. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.3.1149-1159.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]