Abstract
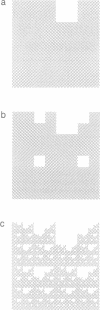
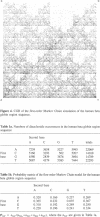
The chaos game representation (CGR) is a scatter plot derived from a DNA sequence, with each point of the plot corresponding to one base of the sequence. If the DNA sequence were a random collection of bases, the CGR would be a uniformly filled square; conversely, any patterns visible in the CGR represent some pattern (information) in the DNA sequence. In this paper, patterns previously observed in a variety of DNA sequences are explained solely in terms of nucleotide, dinucleotide and trinucleotide frequencies.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Almagor H. A Markov analysis of DNA sequences. J Theor Biol. 1983 Oct 21;104(4):633–645. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(83)90251-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avery P. J. The analysis of intron data and their use in the detection of short signals. J Mol Evol. 1987;26(4):335–340. doi: 10.1007/BF02101152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird A. P. DNA methylation and the frequency of CpG in animal DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Apr 11;8(7):1499–1504. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.7.1499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaisdell B. E. Markov chain analysis finds a significant influence of neighboring bases on the occurrence of a base in eucaryotic nuclear DNA sequences both protein-coding and noncoding. J Mol Evol. 1984;21(3):278–288. doi: 10.1007/BF02102360. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bulmer M. A statistical analysis of nucleotide sequences of introns and exons in human genes. Mol Biol Evol. 1987 Jul;4(4):395–405. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutta C., Das J. Mathematical characterization of Chaos Game Representation. New algorithms for nucleotide sequence analysis. J Mol Biol. 1992 Dec 5;228(3):715–719. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90857-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grantham R., Gautier C., Gouy M., Mercier R., Pavé A. Codon catalog usage and the genome hypothesis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jan 11;8(1):r49–r62. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.1.197-c. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill K. A., Schisler N. J., Singh S. M. Chaos game representation of coding regions of human globin genes and alcohol dehydrogenase genes of phylogenetically divergent species. J Mol Evol. 1992 Sep;35(3):261–269. doi: 10.1007/BF00178602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOSSE J., KAISER A. D., KORNBERG A. Enzymatic synthesis of deoxyribonucleic acid. VIII. Frequencies of nearest neighbor base sequences in deoxyribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1961 Mar;236:864–875. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffrey H. J. Chaos game representation of gene structure. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Apr 25;18(8):2163–2170. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.8.2163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]