Abstract
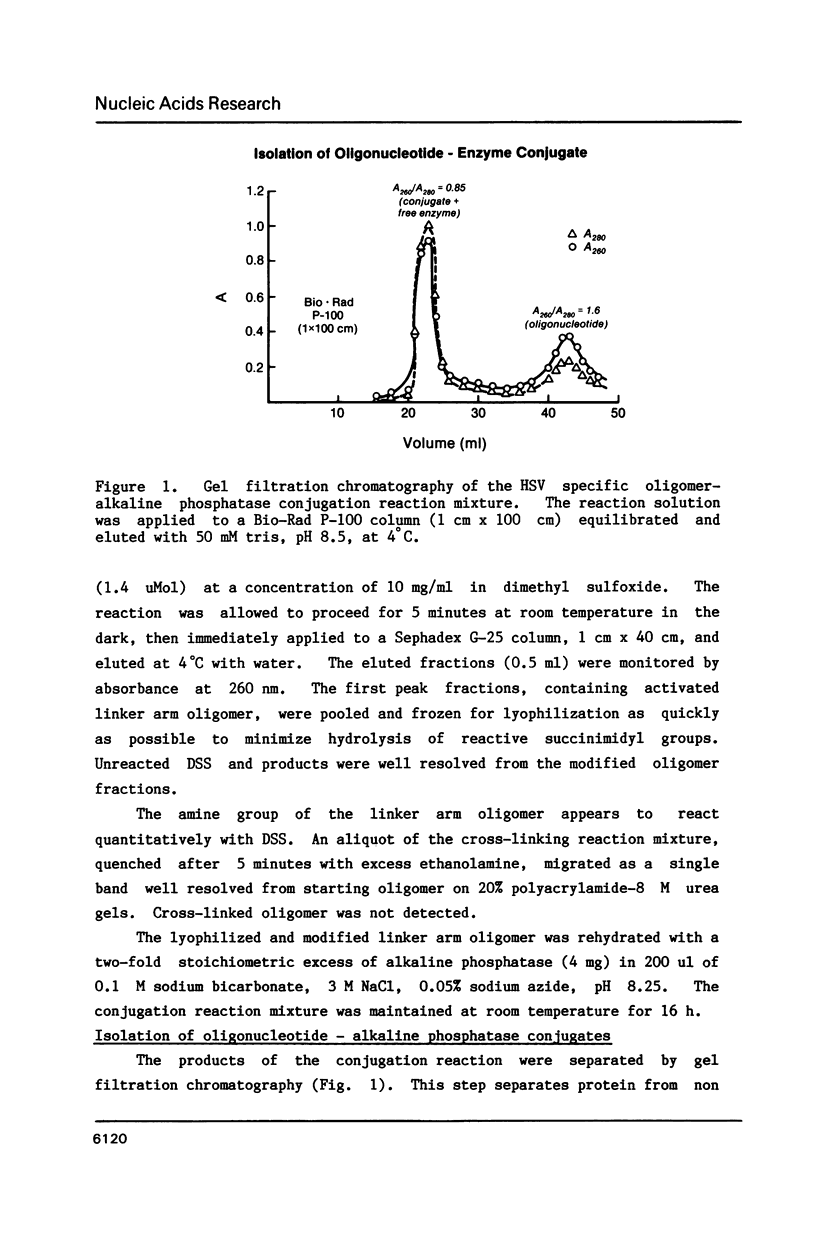
Short synthetic oligonucleotides have been covalently cross-linked to alkaline phosphatase using the homobifunctional reagent disuccinimidyl suberate. The oligomers, twenty-one to twenty-six bases in length, are complementary to unique sequences found in herpes simplex virus, hepatitis B virus, Campylobacter jejuni and enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Each oligomer contains a single modified base with a 12-atom "linker arm" terminating in a reactive primary amine. Cross-linking through this amine results in oligomer-enzyme conjugates composed of one oligomer per enzyme molecule that have full alkaline phosphatase activity and can hybridize to target DNA fixed to nitrocellulose within 15 minutes. The hybrids are detected directly with a dye precipitation assay at a sensitivity of 10(6) molecules (2 X 10(-18) mol) of target DNA in 4 hours development time. The enzyme has no apparent effect on selectivity or kinetics of oligonucleotide hybridization and the conjugates can be hybridized and melted off in a conventional manner.
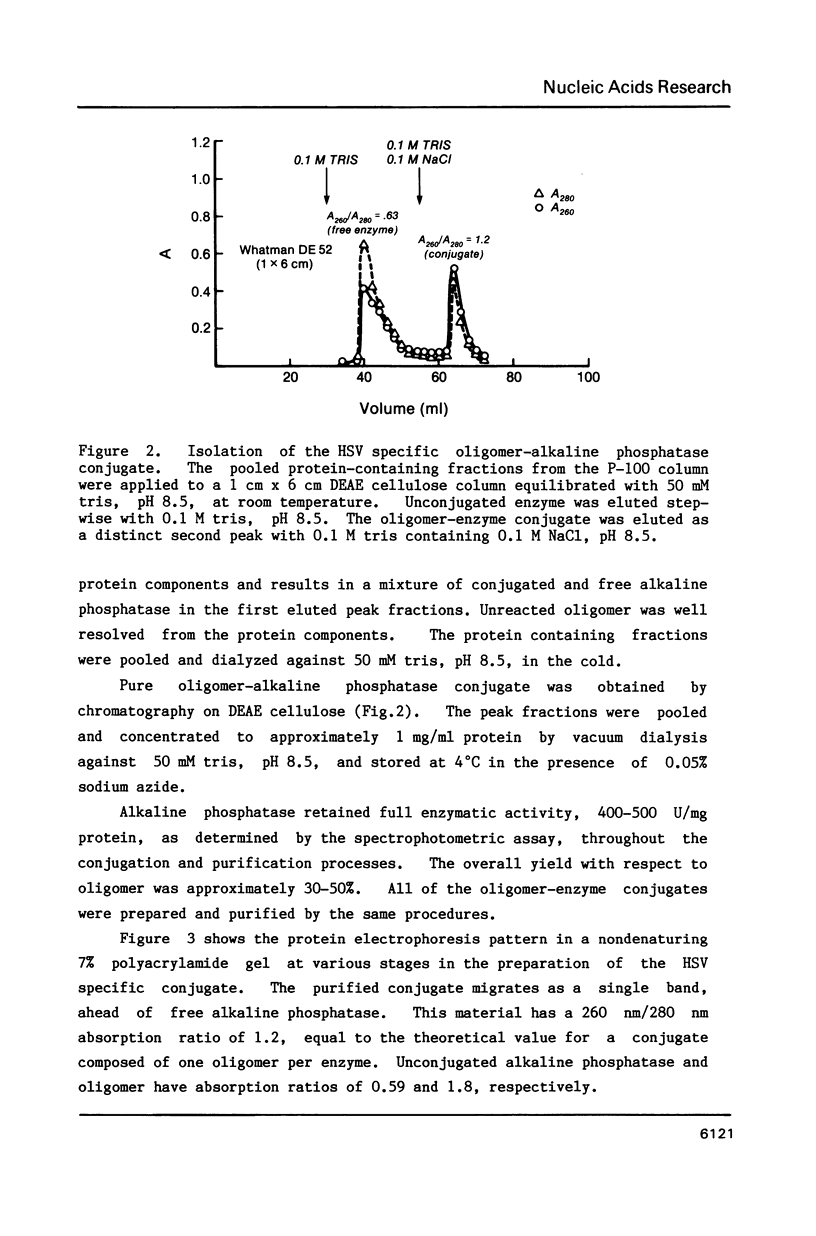
Full text
PDF










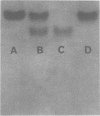
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bauman J. G., Wiegant J., van Duijn P. Cytochemical hybridization with fluorochrome-labeled RNA. I. Development of a method using nucleic acids bound to agarose beads as a model. J Histochem Cytochem. 1981 Feb;29(2):227–237. doi: 10.1177/29.2.6166653. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chollet A., Kawashima E. H. Biotin-labeled synthetic oligodeoxyribonucleotides: chemical synthesis and uses as hybridization probes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Mar 11;13(5):1529–1541. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.5.1529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu B. C., Orgel L. E. Detection of specific DNA sequences with short biotin-labeled probes. DNA. 1985 Aug;4(4):327–331. doi: 10.1089/dna.1985.4.327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu B. C., Wahl G. M., Orgel L. E. Derivatization of unprotected polynucleotides. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Sep 24;11(18):6513–6529. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.18.6513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connolly B. A., Rider P. Chemical synthesis of oligonucleotides containing a free sulphydryl group and subsequent attachment of thiol specific probes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jun 25;13(12):4485–4502. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.12.4485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cosstick R., McLaughlin L. W., Eckstein F. Fluorescent labelling of tRNA and oligodeoxynucleotides using T4 RNA ligase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Feb 24;12(4):1791–1810. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.4.1791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draper D. E. Attachment of reporter groups to specific, selected cytidine residues in RNA using a bisulfite-catalyzed transamination reaction. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 25;12(2):989–1002. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.2.989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Echeverria P., Taylor D. N., Seriwatana J., Chatkaeomorakot A., Khungvalert V., Sakuldaipeara T., Smith R. D. A comparative study of enterotoxin gene probes and tests for toxin production to detect enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. J Infect Dis. 1986 Feb;153(2):255–260. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.2.255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forster A. C., McInnes J. L., Skingle D. C., Symons R. H. Non-radioactive hybridization probes prepared by the chemical labelling of DNA and RNA with a novel reagent, photobiotin. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Feb 11;13(3):745–761. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.3.745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fosset M., Chappelet-Tordo D., Lazdunski M. Intestinal alkaline phosphatase. Physical properties and quaternary structure. Biochemistry. 1974 Apr 23;13(9):1783–1788. doi: 10.1021/bi00706a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill M., Bechet J. J., d'Albis A. Disuccinimidyl esters as bifunctional crosslinking reagents for proteins: assays with myosin. FEBS Lett. 1979 Jun 15;102(2):282–286. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80019-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue H., Imura A., Ohtsuka E. Synthesis and hybridization of dodecadeoxyribonucleotides containing a fluorescent pyridopyrimidine deoxynucleoside. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Oct 11;13(19):7119–7128. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.19.7119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kafatos F. C., Jones C. W., Efstratiadis A. Determination of nucleic acid sequence homologies and relative concentrations by a dot hybridization procedure. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1541–1552. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langer-Safer P. R., Levine M., Ward D. C. Immunological method for mapping genes on Drosophila polytene chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(14):4381–4385. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.14.4381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langer P. R., Waldrop A. A., Ward D. C. Enzymatic synthesis of biotin-labeled polynucleotides: novel nucleic acid affinity probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):6633–6637. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.6633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazdunski C., Lazdunski M. Etude cinétique deu mecanisme d'action catalytique de la phosphatase alcaline d'Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Mar 7;113(3):551–566. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leary J. J., Brigati D. J., Ward D. C. Rapid and sensitive colorimetric method for visualizing biotin-labeled DNA probes hybridized to DNA or RNA immobilized on nitrocellulose: Bio-blots. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):4045–4049. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.4045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manning J. E., Hershey N. D., Broker T. R., Pellegrini M., Mitchell H. K., Davidson N. A new method of in situ hybridization. Chromosoma. 1975 Nov 24;53(2):107–117. doi: 10.1007/BF00333039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moriarty A. M., Hoyer B. H., Shih J. W., Gerin J. L., Hamer D. H. Expression of the hepatitis B virus surface antigen gene in cell culture by using a simian virus 40 vector. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2606–2610. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2606. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murasugi A., Wallace R. B. Biotin-labeled oligonucleotides: enzymatic synthesis and use as hybridization probes. DNA. 1984 Jun;3(3):269–277. doi: 10.1089/dna.1.1984.3.269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ORNSTEIN L. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. I. BACKGROUND AND THEORY. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:321–349. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14207.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson E. M., Aarnaes S. L., Bryan R. N., Ruth J. L., de la Maza L. M. Typing of herpes simplex virus with synthetic DNA probes. J Infect Dis. 1986 Apr;153(4):757–762. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.4.757. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed K. C., Mann D. A. Rapid transfer of DNA from agarose gels to nylon membranes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Oct 25;13(20):7207–7221. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.20.7207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renz M., Kurz C. A colorimetric method for DNA hybridization. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Apr 25;12(8):3435–3444. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.8.3435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith L. M., Fung S., Hunkapiller M. W., Hunkapiller T. J., Hood L. E. The synthesis of oligonucleotides containing an aliphatic amino group at the 5' terminus: synthesis of fluorescent DNA primers for use in DNA sequence analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Apr 11;13(7):2399–2412. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.7.2399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Syvänen A. C., Alanen M., Söderlund H. A complex of single-strand binding protein and M13 DNA as hybridization probe. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Apr 25;13(8):2789–2802. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.8.2789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Syvänen A. C., Tchen P., Ranki M., Söderlund H. Time-resolved fluorometry: a sensitive method to quantify DNA-hybrids. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jan 24;14(2):1017–1028. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.2.1017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tchen P., Fuchs R. P., Sage E., Leng M. Chemically modified nucleic acids as immunodetectable probes in hybridization experiments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(11):3466–3470. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.11.3466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent C., Tchen P., Cohen-Solal M., Kourilsky P. Synthesis of 8-(2-4 dinitrophenyl 2-6 aminohexyl) amino-adenosine 5' triphosphate: biological properties and potential uses. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Nov 11;10(21):6787–6796. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.21.6787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viscidi R. P., Connelly C. J., Yolken R. H. Novel chemical method for the preparation of nucleic acids for nonisotopic hybridization. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Feb;23(2):311–317. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.2.311-317.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]