Abstract
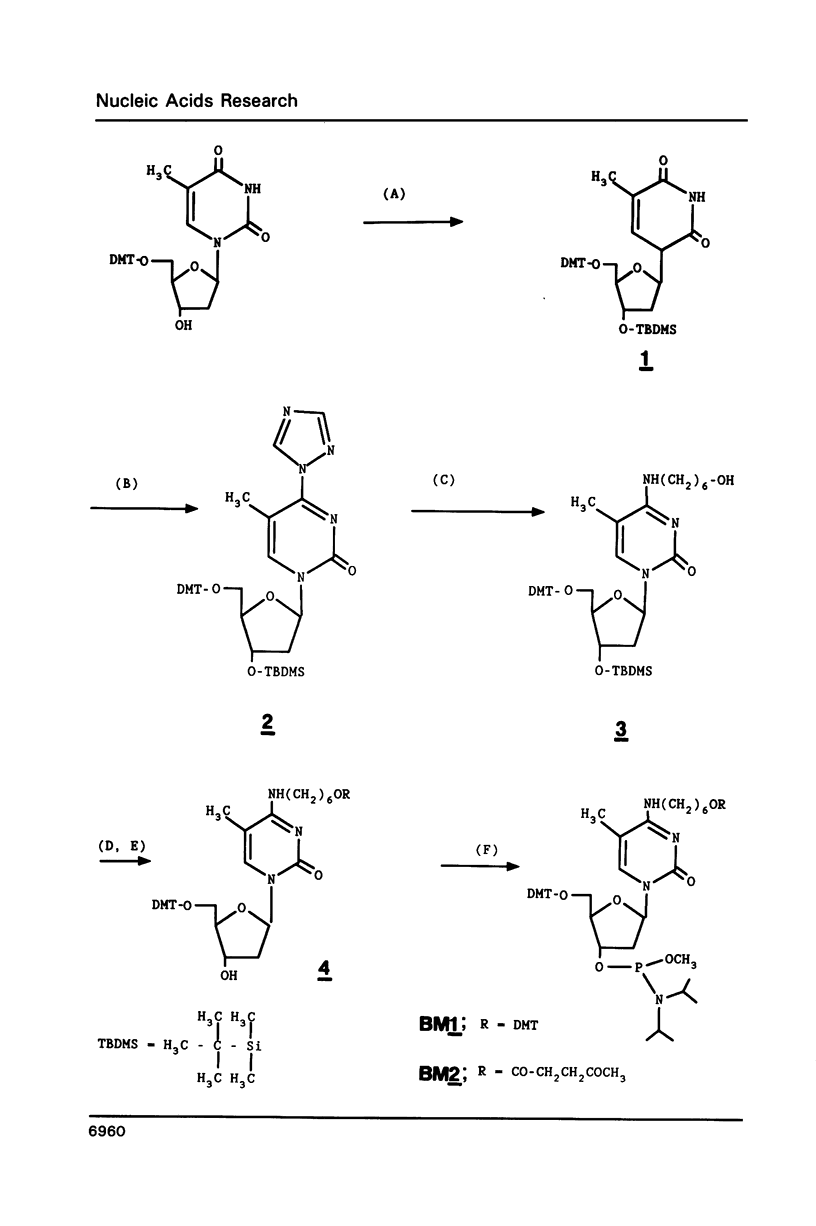
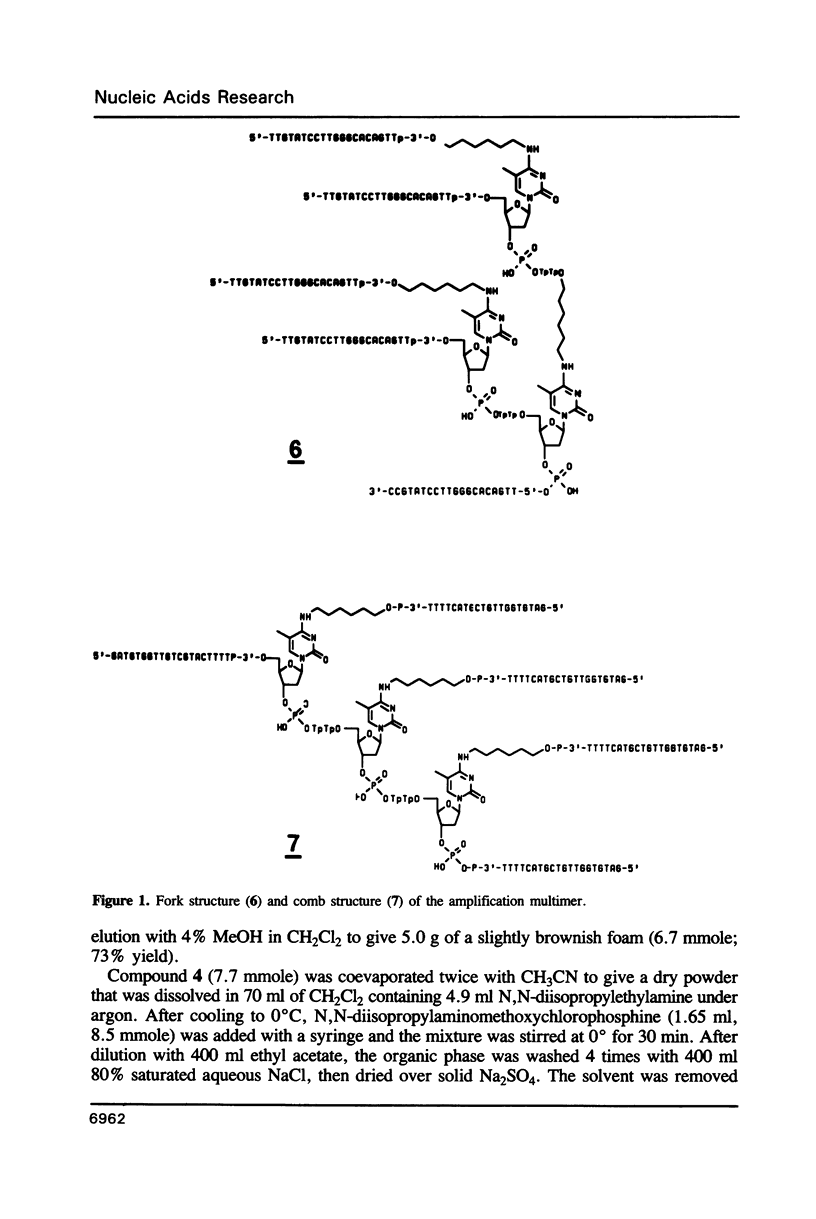
Nucleoside phosphoramidite derivatives containing two protected primary hydroxyl functions have been incorporated into synthetic oligonucleotides as 'branching monomers'. With selective deprotection, multiple identical copies of an additional oligonucleotide can be incorporated to form fork- or comb-like structures for use as signal amplification materials in nucleic acid hybridization assays.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Hassner A., Strand G., Rubenstein M., Patchornik A. Letter: Levulinic esters. An alcohol protecting group applicable to some nucleosides. J Am Chem Soc. 1975 Mar 19;97(6):1614–1615. doi: 10.1021/ja00839a077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwai S., Ohtsuka E. 5'-Levulinyl and 2'-tetrahydrofuranyl protection for the synthesis of oligoribonucleotides by the phosphoramidite approach. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Oct 25;16(20):9443–9456. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.20.9443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padgett R. A., Konarska M. M., Grabowski P. J., Hardy S. F., Sharp P. A. Lariat RNA's as intermediates and products in the splicing of messenger RNA precursors. Science. 1984 Aug 31;225(4665):898–903. doi: 10.1126/science.6206566. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruskin B., Krainer A. R., Maniatis T., Green M. R. Excision of an intact intron as a novel lariat structure during pre-mRNA splicing in vitro. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):317–331. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90553-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urdea M. S. Design, chemical synthesis, and molecular cloning of a gene for human epidermal growth factor. Methods Enzymol. 1987;146:22–41. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(87)46006-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urdea M. S., Running J. A., Horn T., Clyne J., Ku L. L., Warner B. D. A novel method for the rapid detection of specific nucleotide sequences in crude biological samples without blotting or radioactivity; application to the analysis of hepatitis B virus in human serum. Gene. 1987;61(3):253–264. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90189-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urdea M. S., Warner B. D., Running J. A., Stempien M., Clyne J., Horn T. A comparison of non-radioisotopic hybridization assay methods using fluorescent, chemiluminescent and enzyme labeled synthetic oligodeoxyribonucleotide probes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jun 10;16(11):4937–4956. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.11.4937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace J. C., Edmonds M. Polyadenylylated nuclear RNA contains branches. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(4):950–954. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.4.950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner B. D., Warner M. E., Karns G. A., Ku L., Brown-Shimer S., Urdea M. S. Construction and evaluation of an instrument for the automated synthesis of oligodeoxyribonucleotides. DNA. 1984 Oct;3(5):401–411. doi: 10.1089/dna.1984.3.401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]