Abstract
Thirty thousand colonies of a bovine liver cDNA library were screened with a mixture of synthetic oligodeoxyribonucleotides coding for bovine factor X. Five positive colonies were identified, and plasmid DNA was isolated. Cleavage with restriction endonucleases showed that these plasmids (designated pBX1 -5) contained inserts of 1530bp , 770bp , 700bp , 1100bp and 930bp . DNA sequence analysis of the plasmid with the largest insert ( pBX1 ) confirmed that bovine factor X cDNAs had been cloned. The cDNA sequence predicts that factor X is synthesized as a single chain precursor in which the light and heavy chains of plasma factor X are linked by the dipeptide Arg-Arg. The cDNA sequence also predicts that factor X is synthesized with a prepro leader peptide. We propose that at least five specific proteolytic events occur during the conversion of prepro -factor X to plasma factor Xa.
Full text
PDF


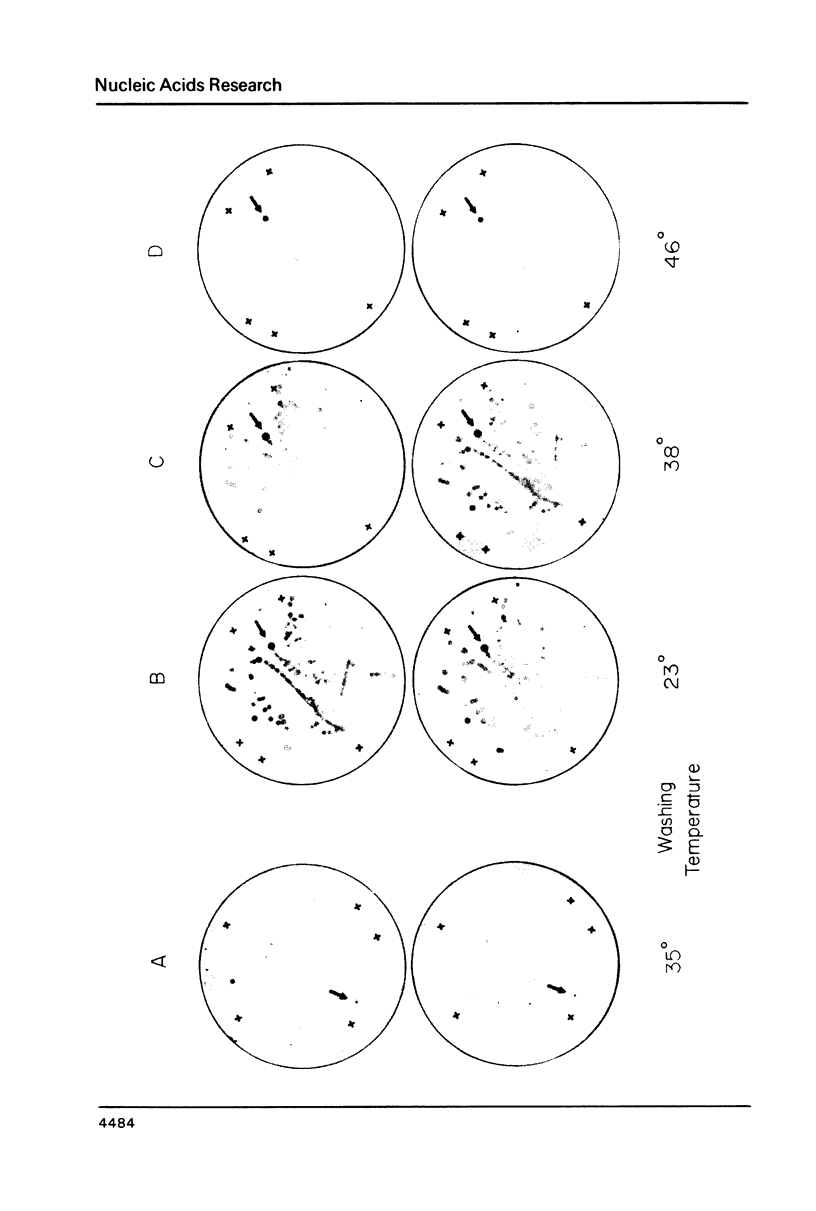

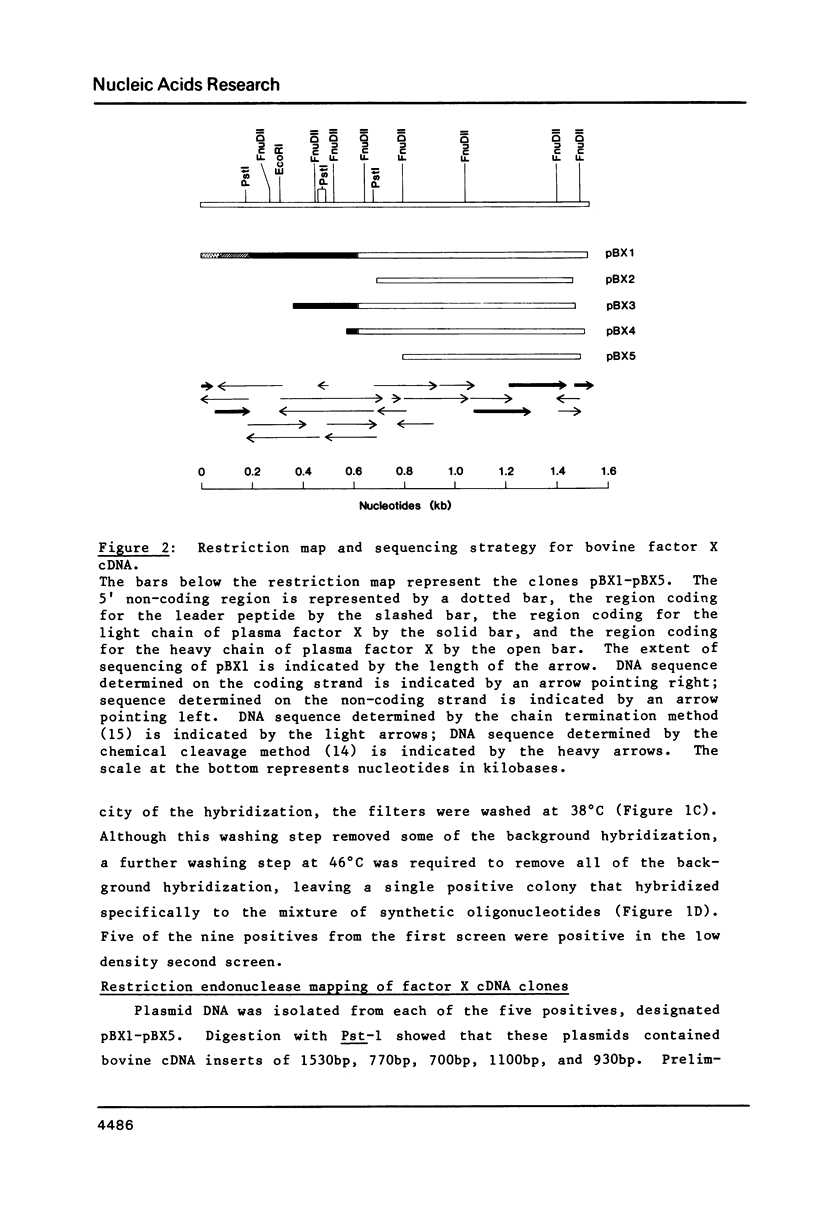






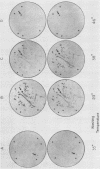
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barnes W. M., Bevan M., Son P. H. Kilo-sequencing: creation of an ordered nest of asymmetric deletions across a large target sequence carried on phage M13. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:98–122. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01008-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaconas G., van de Sande J. H. 5'-32P labeling of RNA and DNA restriction fragments. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):75–85. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65012-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Degen S. J., MacGillivray R. T., Davie E. W. Characterization of the complementary deoxyribonucleic acid and gene coding for human prothrombin. Biochemistry. 1983 Apr 26;22(9):2087–2097. doi: 10.1021/bi00278a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enfield D. L., Ericsson L. H., Fujikawa K., Walsh K. A., Neurath H., Titani K. Amino acid sequence of the light chain of bovine factor X1 (Stuart factor). Biochemistry. 1980 Feb 19;19(4):659–667. doi: 10.1021/bi00545a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujikawa K., Coan M. H., Legaz M. E., Davie E. W. The mechanism of activation of bovine factor X (Stuart factor) by intrinsic and extrinsic pathways. Biochemistry. 1974 Dec 17;13(26):5290–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00723a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J. I., Budelier K. A., Sims H. F., Edelstein C., Scanu A. M., Strauss A. W. Biosynthesis of human preproapolipoprotein A-II. J Biol Chem. 1983 Nov 25;258(22):14054–14059. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graves C. B., Munns T. W., Willingham A. K., Strauss A. W. Rat factor X is synthesized as a single chain precursor inducible by prothrombin fragments. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 10;257(21):13108–13113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunstein M., Hogness D. S. Colony hybridization: a method for the isolation of cloned DNAs that contain a specific gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):3961–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.3961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D., Meselson M. Plasmid screening at high colony density. Gene. 1980 Jun;10(1):63–67. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90144-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson C. M., Nemerson Y. Blood coagulation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:765–811. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.004001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaye M., de la Salle H., Schamber F., Balland A., Kohli V., Findeli A., Tolstoshev P., Lecocq J. P. Isolation of a human anti-haemophilic factor IX cDNA clone using a unique 52-base synthetic oligonucleotide probe deduced from the amino acid sequence of bovine factor IX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Apr 25;11(8):2325–2335. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.8.2325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurachi K., Davie E. W. Isolation and characterization of a cDNA coding for human factor IX. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6461–6464. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattock P., Esnouf M. P. A form of bovine factor X with a single polypeptide chain. Nat New Biol. 1973 Mar 21;242(116):90–92. doi: 10.1038/newbio242090a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg J. S., Beeler D. L., Rosenberg R. D. Activation of human prothrombin by highly purified human factors V and X-a in presence of human antithrombin. J Biol Chem. 1975 Mar 10;250(5):1607–1617. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R. The use of thin acrylamide gels for DNA sequencing. FEBS Lett. 1978 Mar 1;87(1):107–110. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80145-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder W. A., Shelton J. B., Shelton J. R. An examination of conditions for the cleavage of polypeptide chains with cyanogen bromide: application to catalase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1969 Mar;130(1):551–556. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(69)90069-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner D. F., Quinn P. S., Chan S. J., Marsh J., Tager H. S. Processing mechanisms in the biosynthesis of proteins. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1980;343:1–16. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1980.tb47238.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauss A. W., Bennett C. A., Donohue A. M., Rodkey J. A., Boime I., Alberts A. W. Conversion of rat pre-proalbumin to proalbumin in vitro by ascites membranes. Demonstration by NH2-TERMINAL SEQUENCE ANALYSIS. J Biol Chem. 1978 Sep 10;253(17):6270–6274. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thibodeau S. N., Palmiter R. D., Walsh K. A. Precursor of egg white ovomucoid. Amino acid sequence of an NH2-terminal extension. J Biol Chem. 1978 Dec 25;253(24):9018–9023. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Titani K., Fujikawa K., Enfield D. L., Ericsson L. H., Walsh K. A., Neurath H. Bovine factor X1 (Stuart factor): amino-acid sequence of heavey chain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Aug;72(8):3082–3086. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.8.3082. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]