Abstract
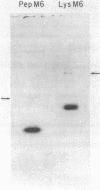
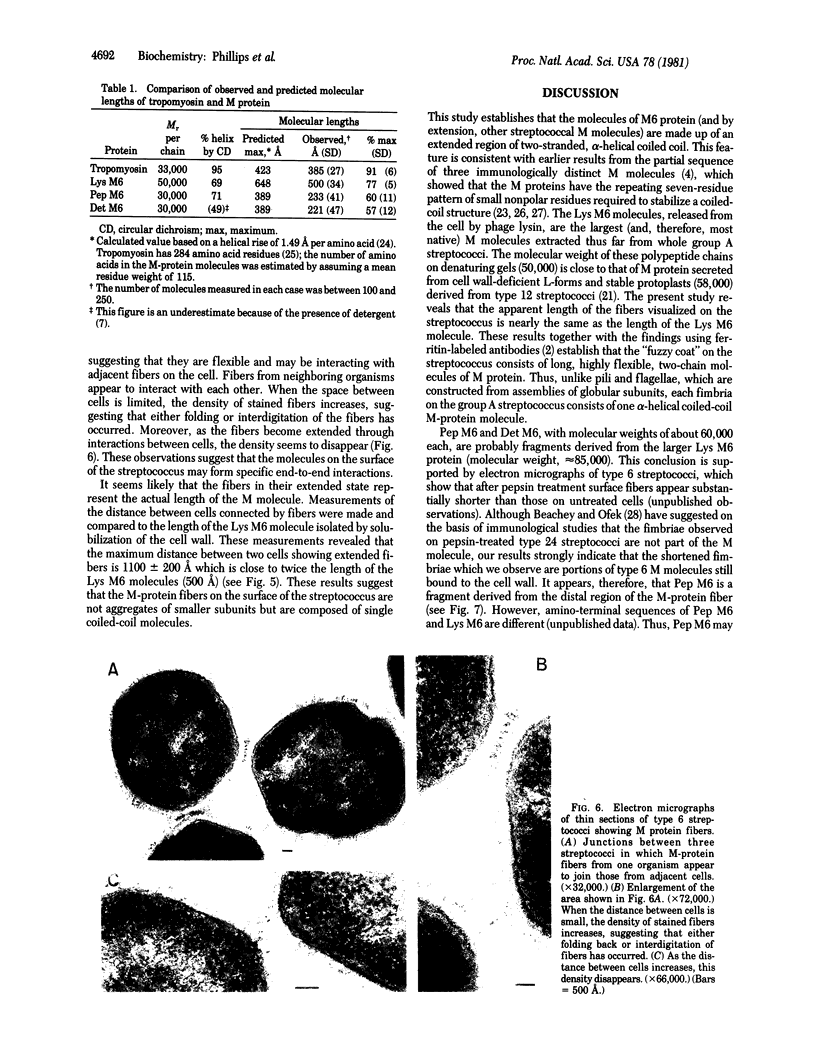
The conformation and molecular dimensions of purified type 6 streptococcal M proteins establish the close structural relationship of these molecules to tropomyosin. Ultracentrifuge studies reveal that the M molecules exist as stable dimers; circular dichroism spectra indicate that the molecules contain about 70% alpha helix; and fiber x-ray diffraction diagrams show the characteristic reflections of the alpha-helical pattern. Electron microscopic images of M protein shadowed with platinum reveal rod-shaped molecules having the same width as tropomyosin. However, the lengths of the M molecules are about 30% shorter than lengths predicted by assuming a completely alpha-helical molecule. These findings indicate that the structure of the M6 protein is primarily alpha-helical coiled coil. Comparison of the lengths of the fibers on the surface of the streptococcus and the isolated M proteins suggests that each fiber on the cell wall consists of a single M-protein molecule approximately 500 A long. The structure determined for these fimbriae is the first alpha-helical coiled-coil conformation to be demonstrated for bacterial surface projections.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beachey E. H., Ofek I. Epithelial cell binding of group A streptococci by lipoteichoic acid on fimbriae denuded of M protein. J Exp Med. 1976 Apr 1;143(4):759–771. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.4.759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHEN C., HOLMES K. C. X-ray diffraction evidence for alpha-helical coiled-coils in native muscle. J Mol Biol. 1963 May;6:423–432. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(63)80053-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen C., Longley W. Tropomyosin paracrystals formed by divalent cations. Science. 1966 May 6;152(3723):794–796. doi: 10.1126/science.152.3723.794. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham M. W., Beachey E. H. Peptic digestion of streptococcal M protein. I. Effect of digestion at suboptimal pH upon the biological and immunochemical properties of purified M protein extracts. Infect Immun. 1974 Feb;9(2):244–248. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.2.244-248.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeRosier D. J., Munk P., Cox D. J. Automatic measurement of interference photographs from the ultracentrifuge. Anal Biochem. 1972 Nov;50(1):139–153. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(72)90493-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellen R. P., Gibbons R. J. M protein-associated adherence of Streptococcus pyogenes to epithelial surfaces: prerequisite for virulence. Infect Immun. 1972 May;5(5):826–830. doi: 10.1128/iai.5.5.826-830.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischetti V. A., Gotschlich E. C., Bernheimer A. W. Purification and physical properties of group C streptococcal phage-associated lysin. J Exp Med. 1971 May 1;133(5):1105–1117. doi: 10.1084/jem.133.5.1105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischetti V. A., Gotschlich E. C., Siviglia G., Zabriskie J. B. Streptococcal M protein extracted by nonionic detergent. I. Properties of the antiphagocytic and type-specific molecules. J Exp Med. 1976 Jul 1;144(1):32–53. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.1.32. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox E. N., Wittner M. K. The multiple molecular structure of the M proteins of group A streptococci. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Oct;54(4):1118–1125. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.4.1118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUXLEY H. E., PERUTZ M. F. Polypeptide chains in frog sartorius muscle. Nature. 1951 Jun 30;167(4261):1054–1054. doi: 10.1038/1671054a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hosein B., McCarty M., Fischetti V. A. Amino acid sequence and physicochemical similarities between streptococcal M protein and mammalian tropomyosin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3765–3768. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANCEFIELD R. C. Persistence of type-specific antibodies in man following infection with group A streptococci. J Exp Med. 1959 Aug 1;110(2):271–292. doi: 10.1084/jem.110.2.271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manjula B. N., Fischetti V. A. Studies on group A streptococcal M-proteins: purification of type 5 M-protein and comparison of its amino terminal sequence with two immunologically unrelated M-protein molecules. J Immunol. 1980 Jan;124(1):261–267. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manjula B. N., Fischetti V. A. Tropomyosin-like seven residue periodicity in three immunologically distinct streptococal M proteins and its implications for the antiphagocytic property of the molecule. J Exp Med. 1980 Mar 1;151(3):695–708. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.3.695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLachlan A. D., Stewart M., Smillie L. B. Sequence repeats in alpha-tropomyosin. J Mol Biol. 1975 Oct 25;98(2):281–291. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80118-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLachlan A. D. The double helix coiled coil structure of murein lipoprotein from Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1978 Jun 5;121(4):493–506. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90396-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips G. N., Jr, Lattman E. E., Cummins P., Lee K. Y., Cohen C. Crystal structure and molecular interactions of tropomyosin. Nature. 1979 Mar 29;278(5703):413–417. doi: 10.1038/278413a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roark D. E., Yphantis D. A. Studies of self-associating systems by equilibrium ultracentrifugation. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1969 Nov 7;164(1):245–278. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1969.tb14043.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotta J., Krause R. M., Lancefield R. C., Everly W., Lackland H. New approaches for the laboratory recognition of M types of group A streptococci. J Exp Med. 1971 Nov 1;134(5):1298–1315. doi: 10.1084/jem.134.5.1298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shotton D. M., Burke B. E., Branton D. The molecular structure of human erythrocyte spectrin. Biophysical and electron microscopic studies. J Mol Biol. 1979 Jun 25;131(2):303–329. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90078-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staprans I., Watanabe S. Optical properties of troponin, tropomyosin, and relaxing protein of rabbit skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem. 1970 Nov 25;245(22):5962–5966. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone D., Smillie L. B. The amino acid sequence of rabbit skeletal alpha-tropomyosin. The NH2-terminal half and complete sequence. J Biol Chem. 1978 Feb 25;253(4):1137–1148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson J., Hsu K. C., Gotschlich E. C. Electron microscopic studies on streptococci. I. M antigen. J Exp Med. 1969 Nov 1;130(5):1063–1091. doi: 10.1084/jem.130.5.1063. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TOMASZ A., JAMIESON J. D., OTTOLENGHI E. THE FINE STRUCTURE OF DIPLOCOCCUS PNEUMONIAE. J Cell Biol. 1964 Aug;22:453–467. doi: 10.1083/jcb.22.2.453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson I. A., Skehel J. J., Wiley D. C. Structure of the haemagglutinin membrane glycoprotein of influenza virus at 3 A resolution. Nature. 1981 Jan 29;289(5796):366–373. doi: 10.1038/289366a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YPHANTIS D. A. EQUILIBRIUM ULTRACENTRIFUGATION OF DILUTE SOLUTIONS. Biochemistry. 1964 Mar;3:297–317. doi: 10.1021/bi00891a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Rijn I., Fischetti V. A. Immunochemical analysis of intact M protein secreted from cell wall-less streptococci. Infect Immun. 1981 Apr;32(1):86–91. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.1.86-91.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]