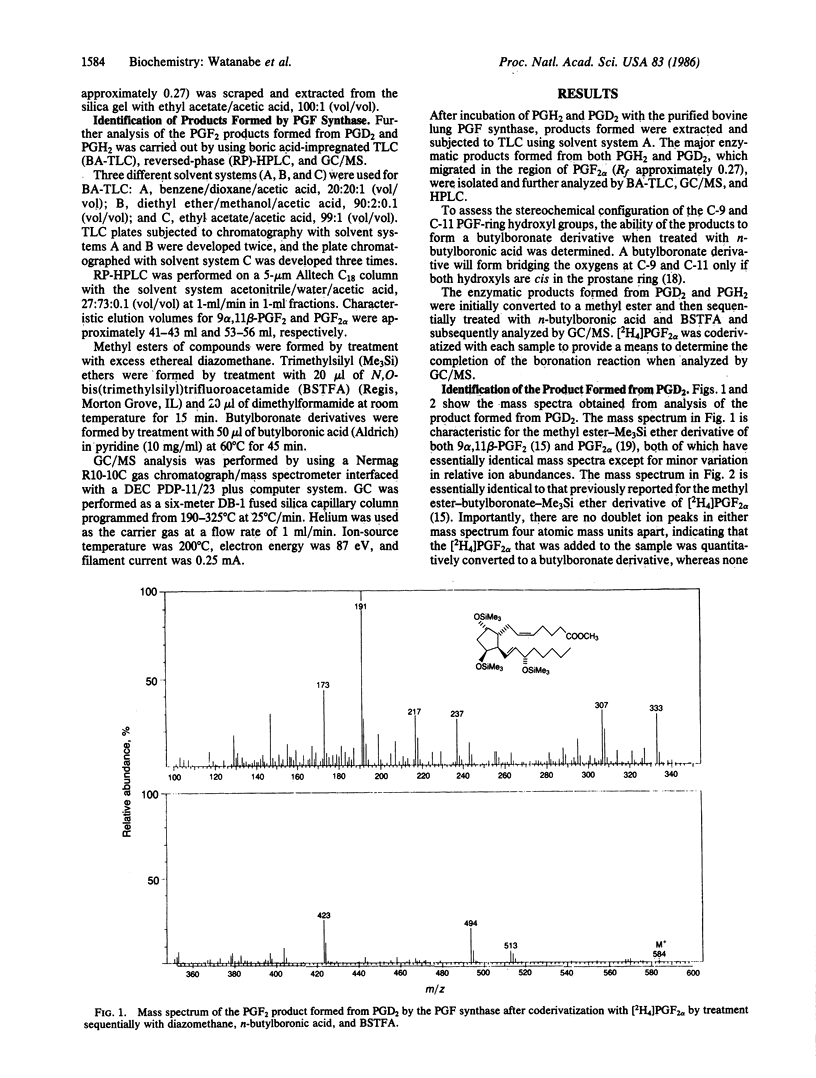
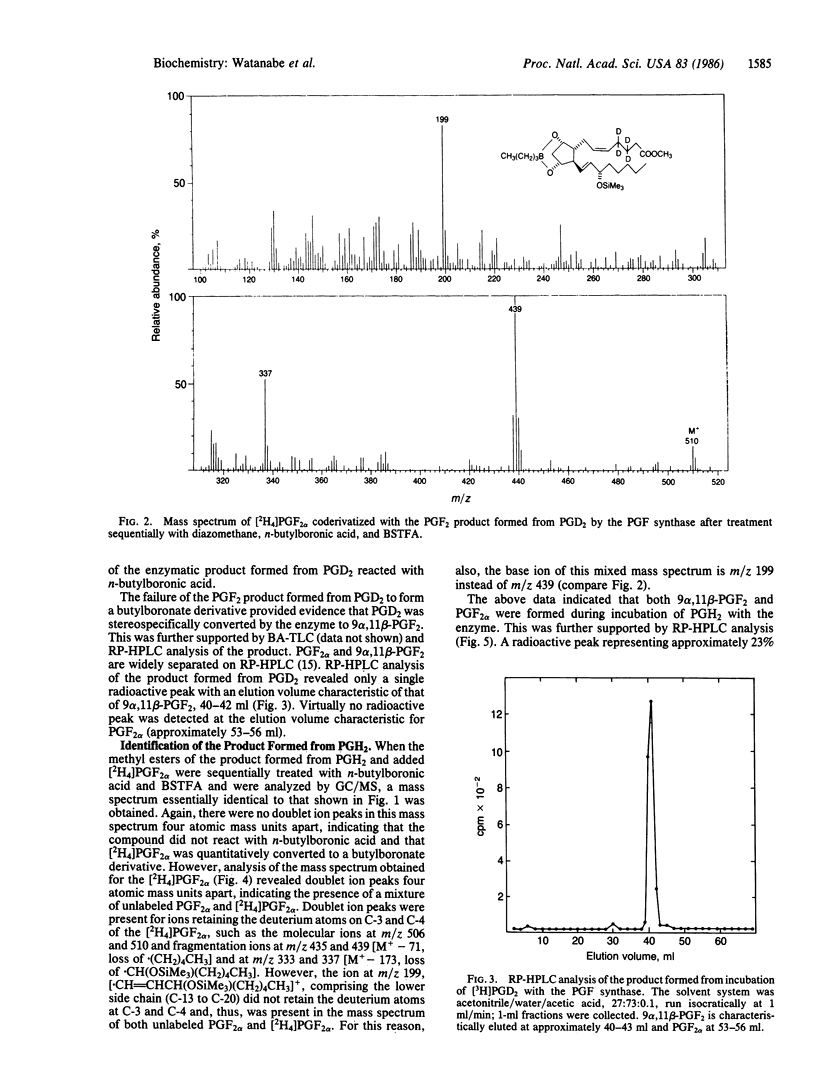
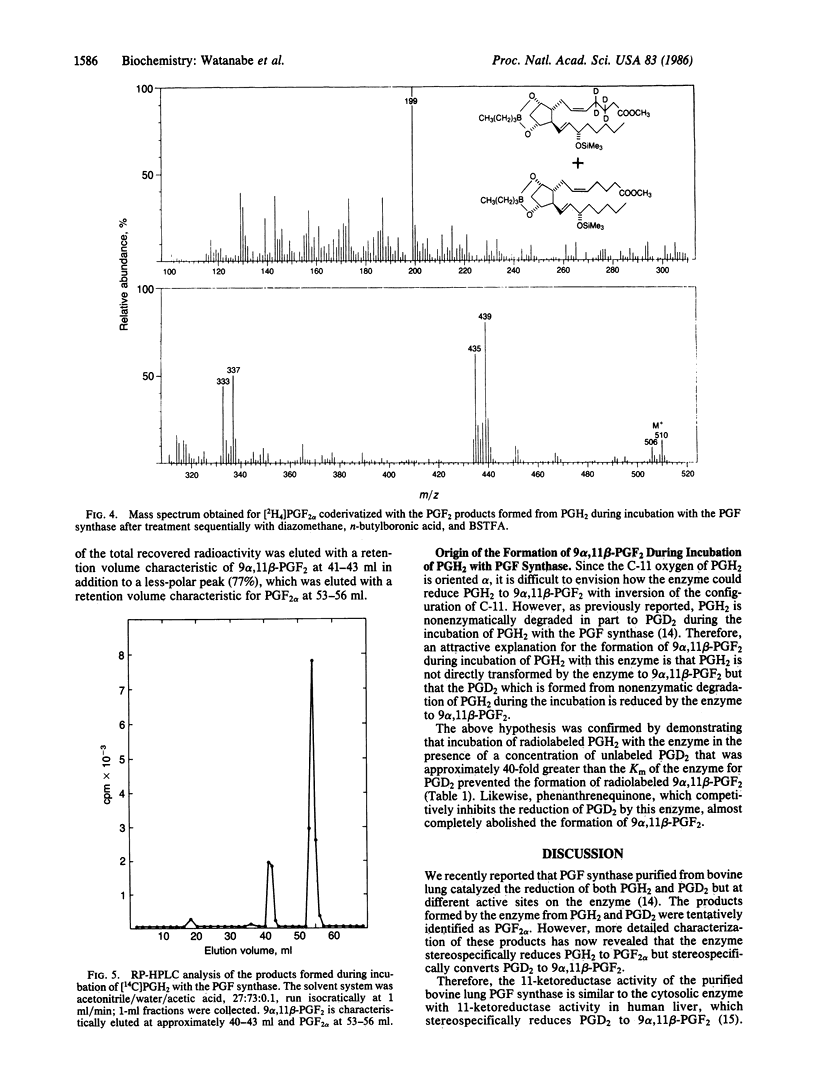
Abstract
A prostaglandin F (PGF) synthase was recently purified from bovine lung that catalyzed the reduction of both PGH2 and PGD2 but at different active sites on the enzyme. In view of the recent finding that PGD2 is stereospecifically reduced to a unique biologically active compound, (5Z, 13E)-(15S)-9 alpha, 11 beta, 15-trihydroxyprosta-5,13-dien-1-oic acid (9 alpha,11 beta-PGF2 or 11-epi-PGF2 alpha), by a human liver cytosolic enzyme, detailed characterization of the products formed from PGH2 and PGD2 by the bovine lung PGF synthase was carried out. Chromatographic characteristics of the products formed and stereochemical analysis procedures using mass spectrometry indicated that the enzyme stereospecifically reduces PGH2 to PGF2 alpha, whereas PGD2 is stereospecifically converted to 9 alpha,11 beta-PGF2. The finding that this enzyme catalyzes the formation of both C-11 hydroxy epimers of PGF2, albeit from different substrates, is of interest in that these two compounds may exert different biological actions.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Embrey M. P., Morrison D. L. The effect of prostaglandins on human pregnant myometrium in vitro. J Obstet Gynaecol Br Commonw. 1968 Aug;75(8):829–832. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.1968.tb01600.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamberg M., Samuelsson B. On the mechanism of the biosynthesis of prostaglandins E-1 and F-1-alpha. J Biol Chem. 1967 Nov 25;242(22):5336–5343. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hensby C. N. The enzymatic conversion of prostaglandin D2 to prostaglandin F2 alpha. Prostaglandins. 1974 Dec 10;8(5):369–375. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(74)90111-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyman A. L. The active responses of pulmonary veins in intact dogs to prostaglandins F2 alpha and E1. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1969 Feb;165(2):267–273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karim S. M., Sandler M., Williams E. D. Distribution of prostaglandins in human tissues. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1967;31:340–344. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1967.tb02003.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karim S. M., Trussell R. R., Patel R. C., Hillier K. Response of pregnant human uterus to prostaglandin-F2-alpha-induction of labour. Br Med J. 1968 Dec 7;4(5631):621–623. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5631.621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leslie C. A., Levine L. Evidence for the presence of a prostaglandin E 2 -9-keto reductase in rat organs. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Jun 8;52(3):717–724. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90996-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin Y. M., Jarabak J. Isolation of two proteins with 9-ketoprostaglandin reductase and NADP-linked 15-hydroxyprostaglandin dehydrogenase activities and studies on their inhibition. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Apr 28;81(4):1227–1234. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91267-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lincoln F. H., Schneider W. P., Pike J. E. Prostanoic acid chemistry. II. Hydrogenation studies and preparation of 11-deoxyprostaglandins. J Org Chem. 1973 Mar 9;38(5):951–956. doi: 10.1021/jo00945a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liston T. E., Roberts L. J., 2nd Transformation of prostaglandin D2 to 9 alpha, 11 beta-(15S)-trihydroxyprosta-(5Z,13E)-dien-1-oic acid (9 alpha, 11 beta-prostaglandin F2): a unique biologically active prostaglandin produced enzymatically in vivo in humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(18):6030–6034. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.18.6030. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pace-Asciak C., Wolfe L. S. Biosynthesis of prostaglandins E2 and F2-alpha from tritium-labelled arachidonic acid by rat stomach homogenates. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Dec 15;218(3):539–542. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(70)90017-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pace-Asciak C., Wolfe L. S. N-butylboronate derivatives of the F prostaglandins. Resolution of prostaglandins of the E and F series by gas-liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr. 1971 Mar 24;56(1):129–133. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(00)97786-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qureshi Z., Cagen L. M. Prostaglandins F2 alpha produced by rabbit renal slices is not a metabolite of prostaglandins E2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Feb 26;104(4):1255–1263. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91385-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reingold D. F., Kawasaki A., Needleman P. A novel prostaglandin 11-keto reductase found in rabbit liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 May 14;659(1):179–188. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(81)90282-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe K., Yoshida R., Shimizu T., Hayaishi O. Enzymatic formation of prostaglandin F2 alpha from prostaglandin H2 and D2. Purification and properties of prostaglandin F synthetase from bovine lung. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 10;260(11):7035–7041. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wlodawer P., Kindahl H., Hamberg M. Biosynthesis of prostaglandin F2alpha from arachidonic acid and prostaglandin endoperoxides in the uterus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Jun 22;431(3):603–614. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(76)90224-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong P. Y. Purification and partial characterization of prostaglandin D2 11-keto reductase in rabbit liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 May 14;659(1):169–178. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(81)90281-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


